
Apoptosis and DiseasesPathophysiology Department, ShiHeZiMedical College,HUST
Apoptosis and Diseases Pathophysiology Department, ShiHeZiMedical College, HUST

Contents1. Concept2.Majorpathways3. Key molecules4. Apoptosis-related diseasesInsufficient apoptosis in diseasesExcessive apoptosis in diseasesCoexistence of insufficient and excessiveapoptosis in diseases5.Principles of treatment
1. Concept 2. Major pathways 3. Key molecules 4. Apoptosis-related diseases • Insufficient apoptosis in diseases • Excessive apoptosis in diseases • Coexistence of insufficient and excessive apoptosis in diseases 5. Principles of treatment Contents
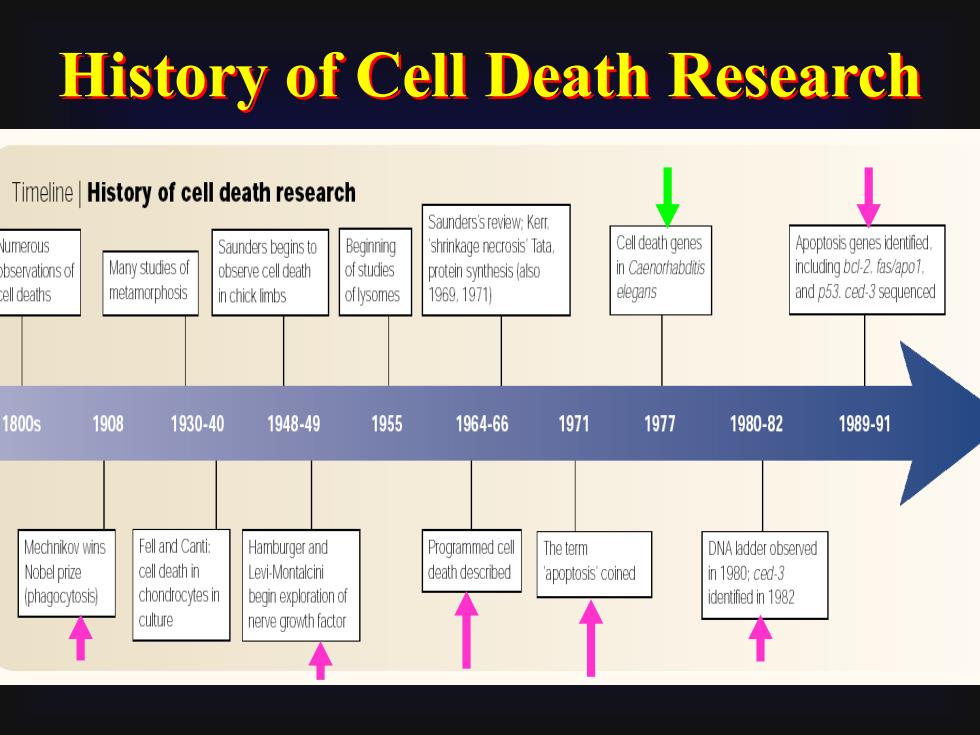
History of Cell Death ResearchTimeline History of cell death researchSaunders's review: KertCell death genesApoptosis genes identiiedNumerousBegqinringSaunders begins toshrinkage necrosis TataMany studies ofincludingbcl-2.fas/apo1inCaenorhabditisof studiesobservationsofobserve cell deathprotein synthesis (alsoelegansandp53.ced-3sequencedmetamorphosis1969, 1971)cell deathsoflysomesin chick limbs1800s19081930-401948-491955197119771980-821989-911964-66Fell and Canti:Mechnikov winsHamburger andProgrammed cellThe termDNA ladder observedNobel prizecell death inLevi-Montalcinideath describedin 1980; ced-3'apoptosis'coinedchondrocytes inbegin exploration of(phagocytosis)identified in 1982↑1culurenerve growth factor全个个
History of Cell Death Research

TheNobel Prize inPhvsiology orMedicine 2002"fortheir discoveries concerning'genetic regulation.of organdevelopmentandprogrammedcell deathSydney BrennerH.RobertHorvitz John E.Sulston1/3of theprizeO1/3oftheprize①1/3 of the prizeUnitedKingdomUSAUnited KingdomThe MolecularMassachusettsThe WellcomeTrustInstitute ofSciencesInstituteSanger InstituteTechnology (MIT)BerkeleyCA,USACambridge,UnitedCambridge, MA,KingdomUSA
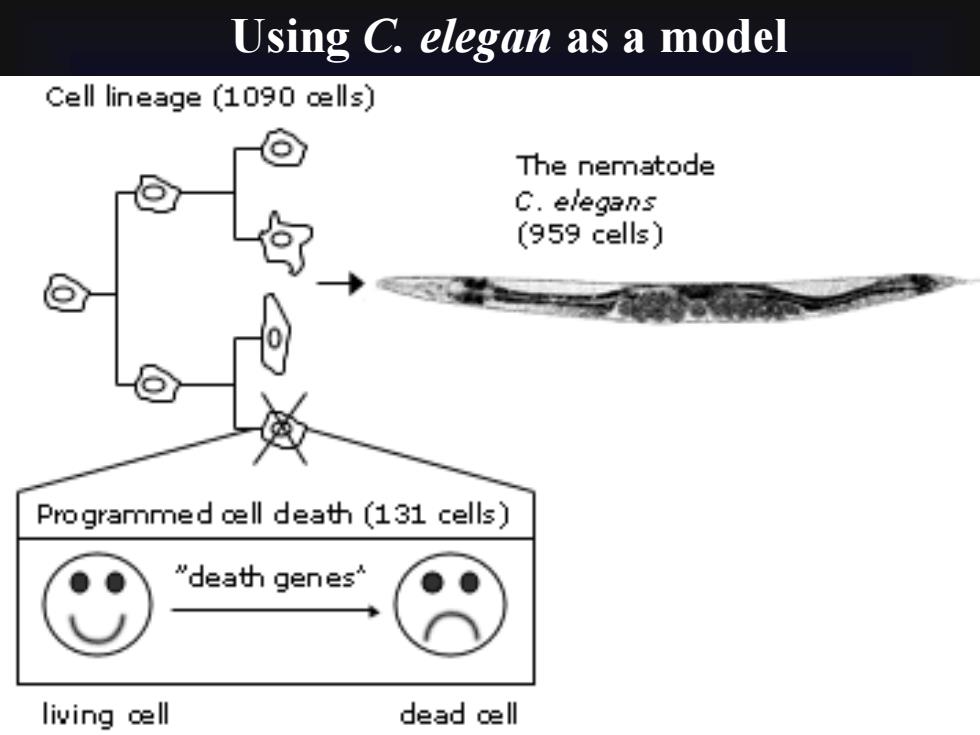
Using C. elegan as a modelCell lineage (1090 cells)The nematodeC.elegans(959 cells)Programmed cell death(131 cells)"death genes"living ce lldead cell
Using C. elegan as a model