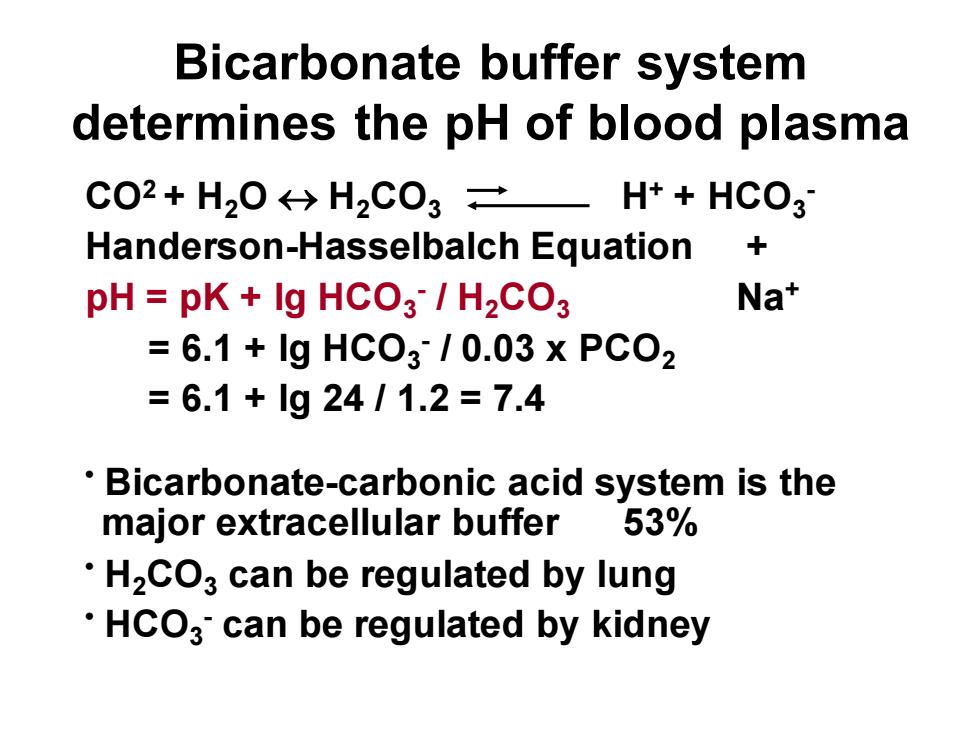
Bicarbonate buffer systemdetermines the pH of blood plasmaCO2+ H,O H2CO3 =H+ + HCO3+Handerson-Hasselbalch EquationNa*pH= pK + Ig HCO3 / H2CO3= 6.1 + Ig HCO3 / 0.03 x PCO2= 6.1 + Ig 24 / 1.2 = 7.4: Bicarbonate-carbonic acid system is the53%major extracellular buffer: HzcO3 can be regulated by lung: HcO3' can be regulated by kidney
Bicarbonate buffer system determines the pH of blood plasma CO2 + H2O H2CO3 H+ + HCO3 - Handerson-Hasselbalch Equation + pH = pK + lg HCO3 - / H2CO3 Na+ = 6.1 + lg HCO3 - / 0.03 x PCO2 = 6.1 + lg 24 / 1.2 = 7.4 • Bicarbonate-carbonic acid system is the major extracellular buffer 53% • H2CO3 can be regulated by lung • HCO3 - can be regulated by kidney
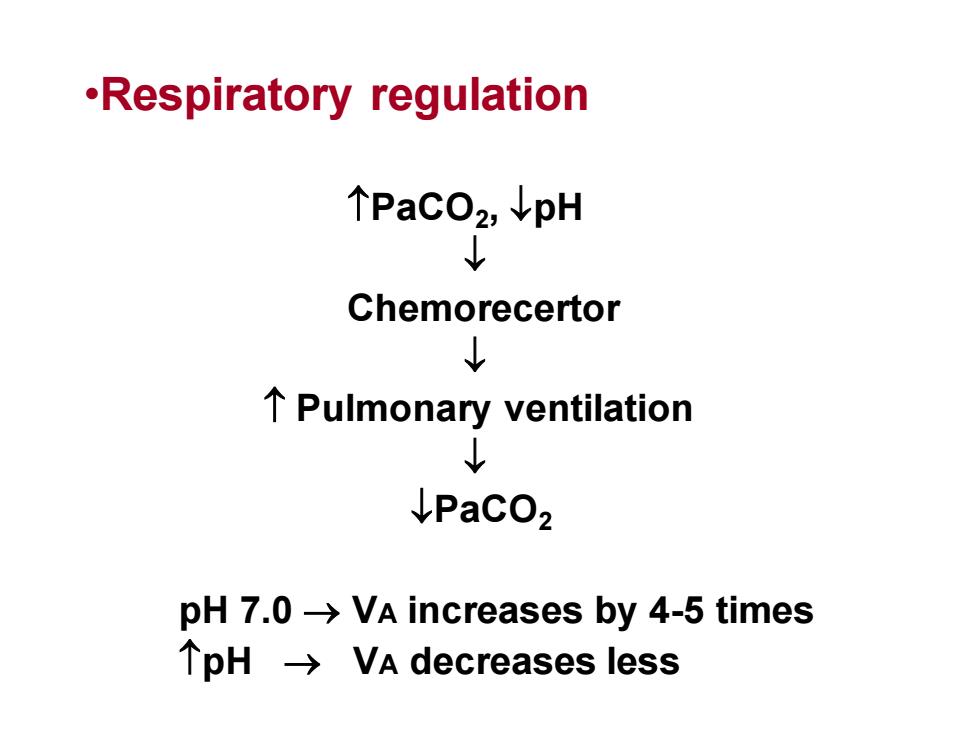
·Respiratoryregulation个PaCO2, ↓pH?ChemorecertorL个 Pulmonary ventilation?IPaCO2pH 7.0 → VA increases by 4-5 times个pH → VA decreases less
•Respiratory regulation PaCO2 , pH Chemorecertor Pulmonary ventilation PaCO2 pH 7.0 → VA increases by 4-5 times pH → VA decreases less
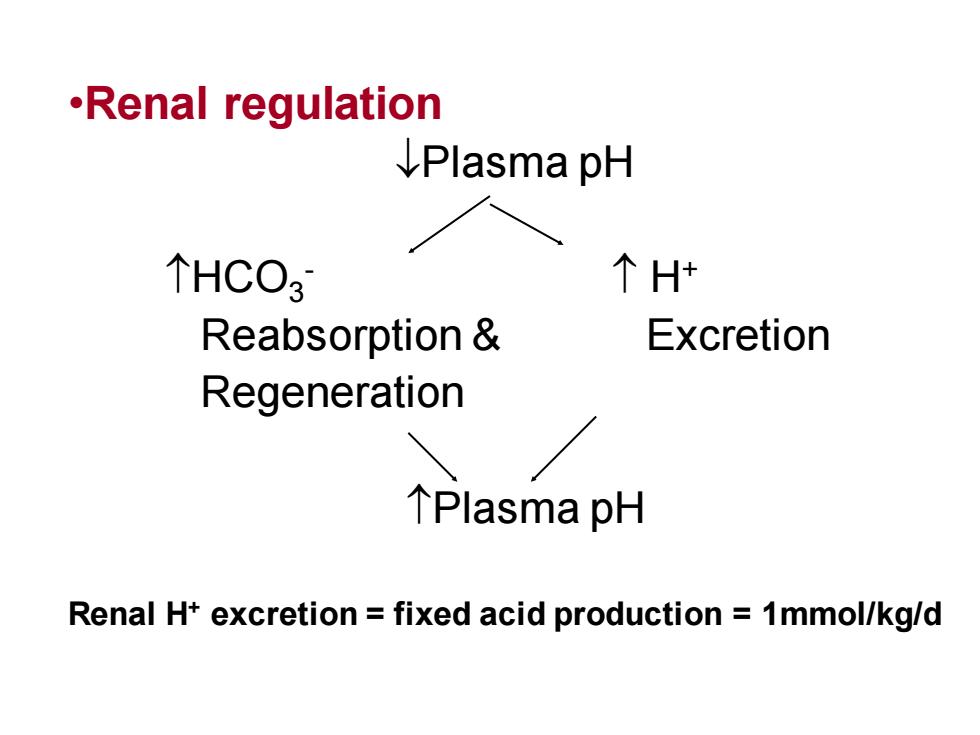
·RenalregulationIPlasmapH个 H+个HCO3ExcretionReabsorption&Regeneration个Plasma pHRenal H+ excretion=fixed acid production=1mmol/kg/d
•Renal regulation Plasma pH HCO3 - H+ Reabsorption & Excretion Regeneration Plasma pH Renal H+ excretion = fixed acid production = 1mmol/kg/d
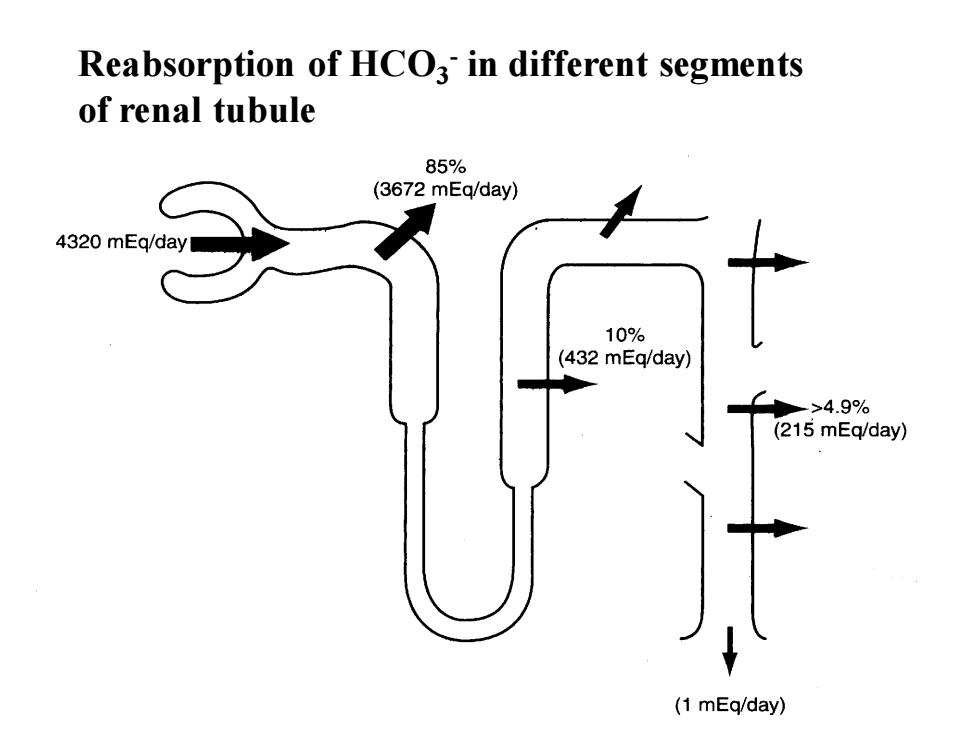
Reabsorption of HCO- in different segmentsof renal tubule85%(3672mEq/day)4320mEq/day10%(432mEq/day)>4.9%(215mEq/day)(1 mEq/day)
Reabsorption of HCO3 - in different segments of renal tubule
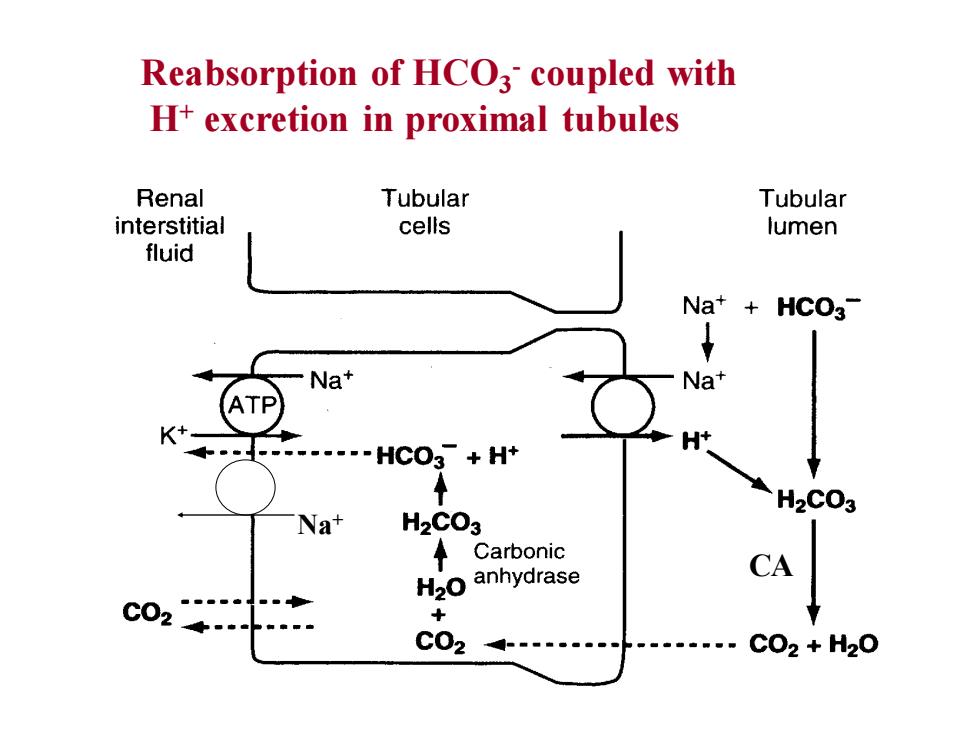
Reabsorption ofHCOcoupled withH+ excretion in proximal tubulesRenalTubularTubularinterstitialcellslumenfluidNa+ + HCO3Na*NatHCO3- + H+H2CO3H2CO3NatCarbonicCAH2o anhydraseCO2+CO2CO2 + H2O
Reabsorption of HCO3 - coupled with H+ excretion in proximal tubules CA Na+