
高等数学B(上)一、课程基本情况课程编号:课程总学时:72课程学分:4.5课程分类:必修开课学期:秋开课单位:理学院应用数学系适用专业:生物与食品相关专业所需先修课:无课程负责人:王新平、邹辉二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:通过本课程的学习,使学生获得函数、极限与连续、一元函数微分学和积分学等方面的基本概念基本理论和基本运算技能。使学生掌握高等数学的基本理论知识的同时,培养学生的抽象思维能力、逻辑推理能力、运算能力、分析问题和解决问题的能力,提高学生用数学方法分析和处理本专业领域中数量关系的能力,为学习后继课程和进一步获取数学知识奠定必要的数学基础。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:函数与极限理解函数的概念和函数的极限与连续性的概念。掌握基本初等函数的性质,连续函数的性质和初等函数的连续性。课程分目标2:导数和微分理解导数和微分的概念和性质,掌握初等函数一阶、二阶导数的求法。课程分目标3:微分中值定理与导数的应用了解微分中值定理,掌握导数的应用。课程分目标4:不定积分理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性质,掌握不定积分的计算。课程分目标5:定积分理解定积分的概念及性质,掌握牛顿(Newton)一莱布尼兹(Leibniz)公式和定积分的计算。课程分目标6:定积分的应用理解定积分的元素法,掌握定积分在几何学上的应用。二、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块教学内容与教学要求学时数支撑的课程分目标1、理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性18第一章:函数与极限质,会建立简单实际问题中的函数关系课程分目标1式。1
1 高等数学 B(上) 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号: 课程总学时:72 课程学分:4.5 课程分类:必修 开课学期:秋 开课单位:理学院应用数学系 适用专业:生物与食品相关专业 所需先修课:无 课程负责人:王新平、邹辉 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标: 通过本课程的学习,使学生获得函数、极限与连续、一元函数微分学和积分学等方面的基本概念、 基本理论和基本运算技能。使学生掌握高等数学的基本理论知识的同时,培养学生的抽象思维能力、 逻辑推理能力、运算能力、分析问题和解决问题的能力,提高学生用数学方法分析和处理本专业领域 中数量关系的能力,为学习后继课程和进一步获取数学知识奠定必要的数学基础。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1:函数与极限 理解函数的概念和函数的极限与连续性的概念。掌握基本初等函数的性质,连续函数的性质和初 等函数的连续性。 课程分目标 2:导数和微分 理解导数和微分的概念和性质,掌握初等函数一阶、二阶导数的求法。 课程分目标 3:微分中值定理与导数的应用 了解微分中值定理,掌握导数的应用。 课程分目标 4:不定积分 理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性质,掌握不定积分的计算。 课程分目标 5:定积分 理解定积分的概念及性质,掌握牛顿(Newton)— 莱布尼兹(Leibniz)公式和定积分的计算。 课程分目标 6:定积分的应用 理解定积分的元素法,掌握定积分在几何学上的应用。 二、 课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第一章:函数与极限 1、理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性 质,会建立简单实际问题中的函数关系 式。 18 课程分目标 1
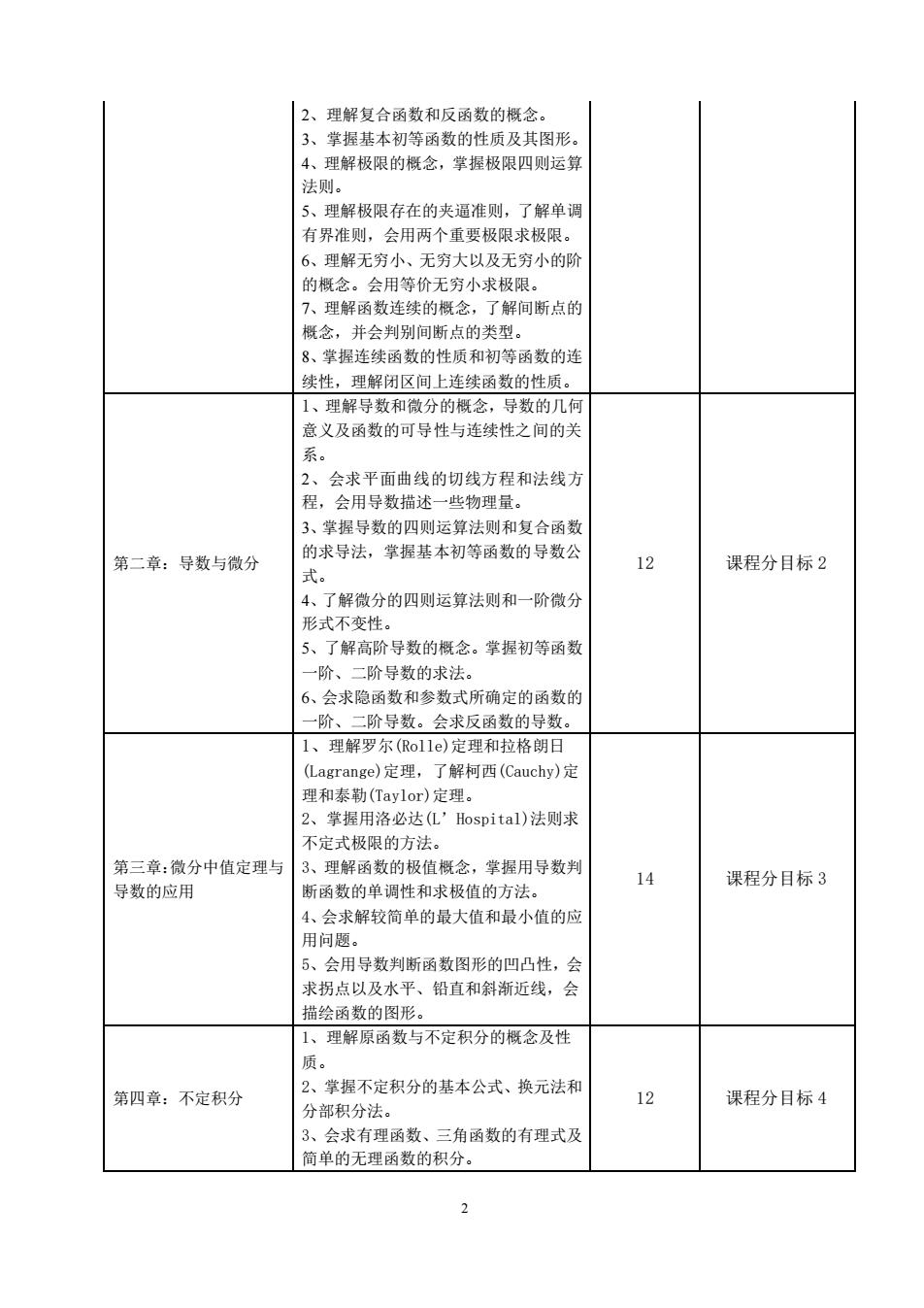
2、理解复合函数和反函数的概念。3、掌握基本初等函数的性质及其图形。4、理解极限的概念,掌握极限四则运算法则。5、理解极限存在的夹逼准则,了解单调有界准则,会用两个重要极限求极限。6、理解无穷小、无穷大以及无穷小的阶的概念。会用等价无穷小求极限。7、理解函数连续的概念,了解间断点的概念,并会判别间断点的类型。8、掌握连续函数的性质和初等函数的连续性,理解闭区间上连续函数的性质。1、理解导数和微分的概念,导数的几何意义及函数的可导性与连续性之间的关系。2、会求平面曲线的切线方程和法线方程,会用导数描述一些物理量。3、掌握导数的四则运算法则和复合函数的求导法,掌握基本初等函数的导数公12第二章:导数与微分课程分目标2式。4、了解微分的四则运算法则和一阶微分形式不变性。5、了解高阶导数的概念。掌握初等函数一阶、二阶导数的求法。6、会求隐函数和参数式所确定的函数的一阶、二阶导数。会求反函数的导数。1、理解罗尔(Rolle)定理和拉格朗日(Lagrange)定理,了解柯西(Cauchy)定理和泰勒(Taylor)定理。2、掌握用洛必达(L’Hospital)法则求不定式极限的方法。第三章:微分中值定理与3、理解函数的极值概念,掌握用导数判14课程分目标3导数的应用断函数的单调性和求极值的方法。4、会求解较简单的最大值和最小值的应用问题。5、会用导数判断函数图形的凹凸性,会求拐点以及水平、铅直和斜渐近线,会描绘函数的图形。1、理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性质。2、掌握不定积分的基本公式、换元法和12课程分目标4第四章:不定积分分部积分法。3、会求有理函数、三角函数的有理式及简单的无理函数的积分。2
2 2、理解复合函数和反函数的概念。 3、掌握基本初等函数的性质及其图形。 4、理解极限的概念,掌握极限四则运算 法则。 5、理解极限存在的夹逼准则,了解单调 有界准则,会用两个重要极限求极限。 6、理解无穷小、无穷大以及无穷小的阶 的概念。会用等价无穷小求极限。 7、理解函数连续的概念,了解间断点的 概念,并会判别间断点的类型。 8、掌握连续函数的性质和初等函数的连 续性,理解闭区间上连续函数的性质。 第二章:导数与微分 1、理解导数和微分的概念,导数的几何 意义及函数的可导性与连续性之间的关 系。 2、会求平面曲线的切线方程和法线方 程,会用导数描述一些物理量。 3、掌握导数的四则运算法则和复合函数 的求导法,掌握基本初等函数的导数公 式。 4、了解微分的四则运算法则和一阶微分 形式不变性。 5、了解高阶导数的概念。掌握初等函数 一阶、二阶导数的求法。 6、会求隐函数和参数式所确定的函数的 一阶、二阶导数。会求反函数的导数。 12 课程分目标 2 第三章:微分中值定理与 导数的应用 1、理解罗尔(Rolle)定理和拉格朗日 (Lagrange)定理,了解柯西(Cauchy)定 理和泰勒(Taylor)定理。 2、掌握用洛必达(L’Hospital)法则求 不定式极限的方法。 3、理解函数的极值概念,掌握用导数判 断函数的单调性和求极值的方法。 4、会求解较简单的最大值和最小值的应 用问题。 5、会用导数判断函数图形的凹凸性,会 求拐点以及水平、铅直和斜渐近线,会 描绘函数的图形。 14 课程分目标 3 第四章:不定积分 1、理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性 质。 2、掌握不定积分的基本公式、换元法和 分部积分法。 3、会求有理函数、三角函数的有理式及 简单的无理函数的积分。 12 课程分目标 4
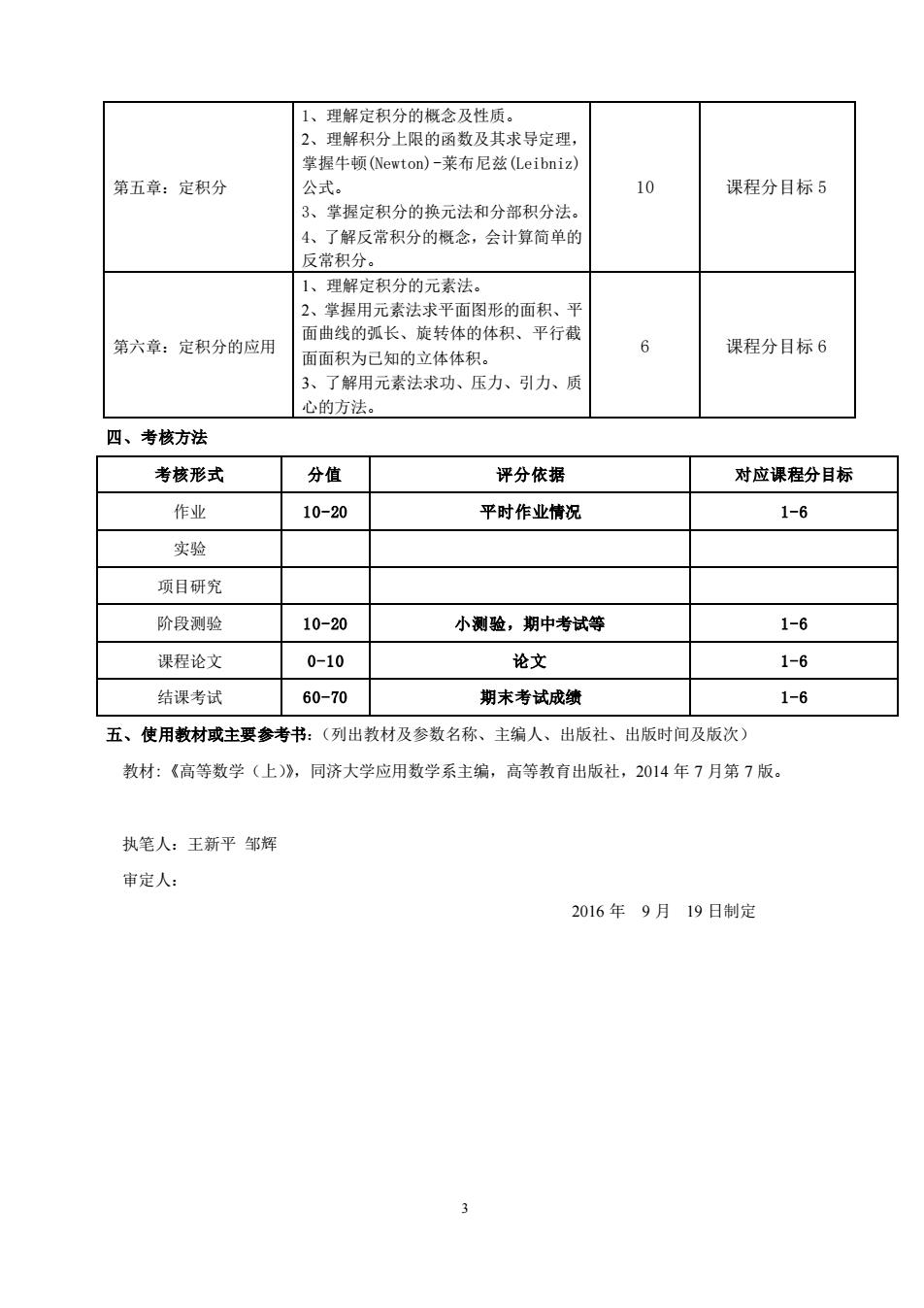
1、理解定积分的概念及性质。2、理解积分上限的函数及其求导定理,掌握牛顿(Newton)-莱布尼兹(Leibniz)10第五章:定积分公式。课程分目标53、掌握定积分的换元法和分部积分法。4、了解反常积分的概念,会计算简单的反常积分。1、理解定积分的元素法。2、掌握用元素法求平面图形的面积、平面曲线的弧长、旋转体的体积、平行截6第六章:定积分的应用课程分目标6面面积为已知的立体体积。3、了解用元素法求功、压力、引力、质心的方法。四、考核方法分值考核形式评分依据对应课程分目标作业10-201-6平时作业情况实验项目研究1-6阶段测验10-20小测验,期中考试等0-10论文1-6课程论文60-70期末考试成绩1-6结课考试五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次)教材:《高等数学(上)》,同济大学应用数学系主编,高等教育出版社,2014年7月第7版。执笔人:王新平邹辉审定人:2016年9月19日制定en
3 第五章:定积分 1、理解定积分的概念及性质。 2、理解积分上限的函数及其求导定理, 掌握牛顿(Newton)-莱布尼兹(Leibniz) 公式。 3、掌握定积分的换元法和分部积分法。 4、了解反常积分的概念,会计算简单的 反常积分。 10 课程分目标 5 第六章:定积分的应用 1、理解定积分的元素法。 2、掌握用元素法求平面图形的面积、平 面曲线的弧长、旋转体的体积、平行截 面面积为已知的立体体积。 3、了解用元素法求功、压力、引力、质 心的方法。 6 课程分目标 6 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 10-20 平时作业情况 1-6 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 10-20 小测验,期中考试等 1-6 课程论文 0-10 论文 1-6 结课考试 60-70 期末考试成绩 1-6 五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次) 教材:《高等数学(上)》,同济大学应用数学系主编,高等教育出版社,2014 年 7 月第 7 版。 执笔人:王新平 邹辉 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 19 日制定
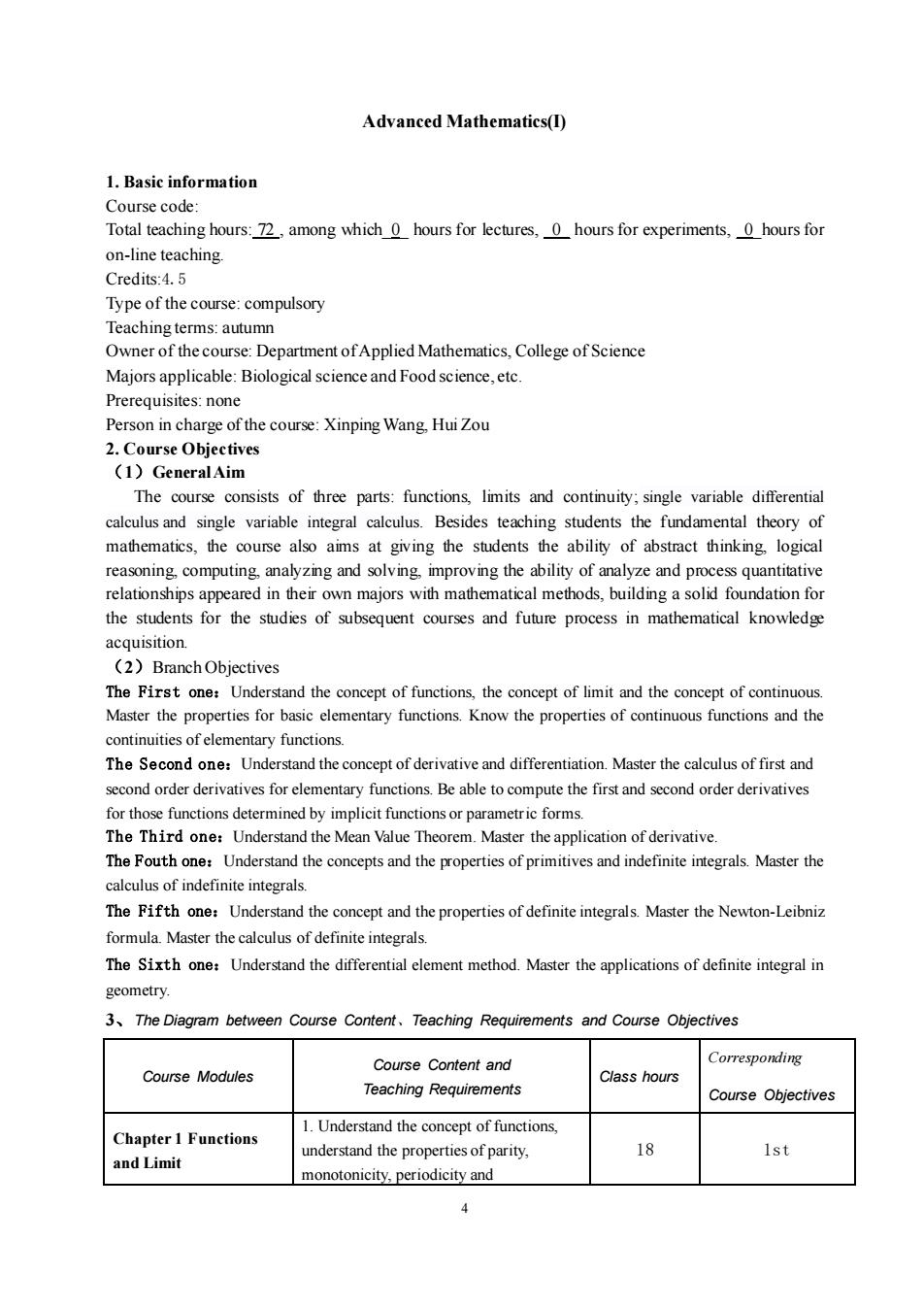
Advanced Mathematics()1. Basic informationCourse code:Totalteachinghours:72,amongwhich Qhoursforlectures,ohoursforexperiments,Qhoursforon-line teaching.Credits:4.5Type of the course: compulsoryTeaching terms: autumnOwnerofthecourse:DepartmentofAppliedMathematics,CollegeofScienceMajors applicable:Biological scienceandFood science,etc.Prerequisites: nonePerson in charge of the course: Xinping Wang, Hui Zou2.Course Objectives(1)GeneralAimThe course consists of three parts:functions,limits and continuitysingle variable differentialcalculus and single variable integral calculus.Besides teaching students the fundamental theory ofmathematics, the course also aims at giving the students the ability of abstract thinking, logicalreasoning, computing, analyzing and solving. improving the ability of analyze and process quantitativerelationships appeared in their own majors with mathematical methods, building a solid foundation forthe students for the studies of subsequent courses and future process in mathematical knowledgeacquisition(2)BranchObjectivesThe First one: Understand the concept of functions, the concept of limit and the concept of continuous.Master theproperties for basic elementary functions.Know the properties of continuous functions and thecontinuitiesofelementaryfunctionsThe Second one:Understand the concept of derivative and differentiation.Master thecalculus of first andsecond order derivativesfor elementaryfunctions.Beable to compute the first and second order derivativesforthosefunctions determinedbyimplicitfunctionsorparametricforms.The Third one:Understand theMean Value Theorem.Master theapplication of derivativeThe Fouth one:Understand the concepts and the properties of primitives and indefinite integrals. Master thecalculus of indefiniteintegralsThe Fifth one:Understand the concept and the properties of definite integrals. Master the Newton-Leibnizformula.Masterthecalculusofdefiniteintegrals.The Sixth one:Understand the differential element method.Master the applications of definite integral ingeometry.3、TheDiagram between Course Content,TeachingRequirements andCourse ObjectivesCorrespondingCourse Content andClass hoursCourse ModulesTeaching RequirementsCourse Objectives1.Understand the concept of functions,Chapter1 Functions18lstunderstand the properties of parity,and Limitmonotonicity,periodicityand4
4 Advanced Mathematics(I) 1. Basic information Course code: Total teaching hours: 72 , among which_0_ hours for lectures, _0_ hours for experiments, _0_hours for on-line teaching. Credits:4.5 Type of the course: compulsory Teaching terms: autumn Owner of the course: Department of Applied Mathematics, College of Science Majors applicable: Biological science and Food science, etc. Prerequisites: none Person in charge of the course: Xinping Wang, Hui Zou 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim The course consists of three parts: functions, limits and continuity; single variable differential calculus and single variable integral calculus. Besides teaching students the fundamental theory of mathematics, the course also aims at giving the students the ability of abstract thinking, logical reasoning, computing, analyzing and solving, improving the ability of analyze and process quantitative relationships appeared in their own majors with mathematical methods, building a solid foundation for the students for the studies of subsequent courses and future process in mathematical knowledge acquisition. (2)Branch Objectives The First one:Understand the concept of functions, the concept of limit and the concept of continuous. Master the properties for basic elementary functions. Know the properties of continuous functions and the continuities of elementary functions. The Second one:Understand the concept of derivative and differentiation. Master the calculus of first and second order derivatives for elementary functions. Be able to compute the first and second order derivatives for those functions determined by implicit functions or parametric forms. The Third one:Understand the Mean Value Theorem. Master the application of derivative. The Fouth one:Understand the concepts and the properties of primitives and indefinite integrals. Master the calculus of indefinite integrals. The Fifth one:Understand the concept and the properties of definite integrals. Master the Newton-Leibniz formula. Master the calculus of definite integrals. The Sixth one:Understand the differential element method. Master the applications of definite integral in geometry. 3、The Diagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class hours Corresponding Course Objectives Chapter 1 Functions and Limit 1. Understand the concept of functions, understand the properties of parity, monotonicity, periodicity and 18 1st

boundedness,be able toestablishfunctionrelationsforsimplerealproblems2.Understandtheconceptsof compositefunction and inverse function.3.Master the properties and graphs forbasic elementary functions3.Understand the concept of limit, masterfour arithmetic operationsfor limits.4.Understand the squeeze rule for theexistence oflimits,know themonotonousboundedcriteria,andbeableto computelimits by usingtwo important limits5.Understand the concept of the infinitelysmall and infinitely large and the order ofinfinitesimals6.Be able to find limits by the substitutionofequivalent infinitesimals.7.Knowthe concept of continuous at onepoint and continuous in an interval,understand the concept of discontinuity,and determine the types of discontinuity8.Know the continuities of elementaryfunctions and the properties of continuousfunctions in a closed interval1.Understand theconcept ofderivativeand differentiation.Understand thegeometric meanings for derivative and therelationship between differentiability andcontinuity2. Be able to find the equations oftangent and normal lines fora planecurve,Be able to describe some quantitiesin physics by derivatives.3.Master the differentiation rules forChapter2 Derivative122ndarithmeticoperationsand compositeand differentialfunctions. Master the differentiationformulae for basic elementary functionsand hyperbolic functions.4.Understand the arithmetic laws fordifferential, and understand the invarianceof first-order differential forms.5.Know the concept of higher orderderivatives.Master the calculus of firstand second orderderivativesforelementary functions.5
5 boundedness, be able to establish function relations for simple real problems. 2.Understand the concepts of composite function and inverse function. 3.Master the properties and graphs for basic elementary functions. 3.Understand the concept of limit, master four arithmetic operations for limits. 4.Understand the squeeze rule for the existence of limits, know the monotonous bounded criteria, and be able to compute limits by using two important limits. 5.Understand the concept of the infinitely small and infinitely large and the order of infinitesimals. 6.Be able to find limits by the substitution of equivalent infinitesimals. 7.Know the concept of continuous at one point and continuous in an interval, understand the concept of discontinuity, and determine the types of discontinuity. 8.Know the continuities of elementary functions and the properties of continuous functions in a closed interval. Chapter 2 Derivative and differential 1.Understand the concept of derivative and differentiation. Understand the geometric meanings for derivative and the relationship between differentiability and continuity. 2. Be able to find the equations of tangent and normal lines for a plane curve. Be able to describe some quantities in physics by derivatives. 3.Master the differentiation rules for arithmetic operations and composite functions. Master the differentiation formulae for basic elementary functions and hyperbolic functions. 4.Understand the arithmetic laws for differential, and understand the invariance of first-order differential forms. 5.Know the concept of higher order derivatives. Master the calculus of first and second order derivatives for elementary functions. 12 2nd