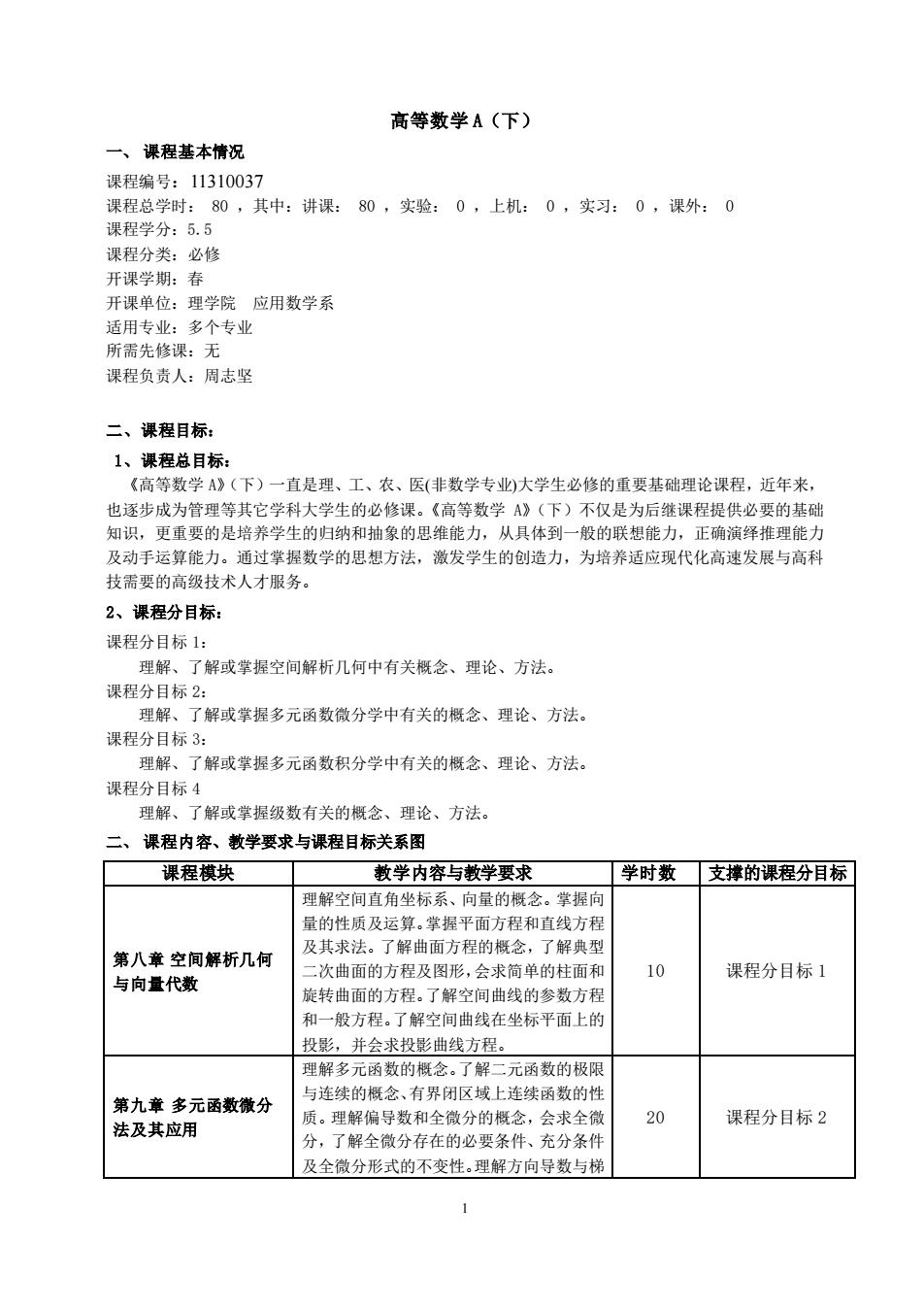
高等数学A(下)一、课程基本情况课程编号:11310037课程总学时:80,其中:讲课:80,实验:0,上机:0,实习:0,课外:0课程学分:5.5课程分类:必修开课学期:春开课单位:理学院应用数学系适用专业:多个专业所需先修课:无课程负责人:周志坚二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:《高等数学A》(下)一直是理、工、农、医(非数学专业)大学生必修的重要基础理论课程,近年来也逐步成为管理等其它学科大学生的必修课。《高等数学A》(下)不仅是为后继课程提供必要的基础知识,更重要的是培养学生的归纳和抽象的思维能力,从具体到一般的联想能力,正确演绎推理能力及动手运算能力。通过掌握数学的思想方法,激发学生的创造力,为培养适应现代化高速发展与高科技需要的高级技术人才服务。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:理解、了解或掌握空间解析几何中有关概念、理论、方法。课程分目标2:理解、了解或掌握多元函数微分学中有关的概念、理论、方法。课程分目标3:理解、了解或掌握多元函数积分学中有关的概念、理论、方法。课程分目标4理解、了解或掌握级数有关的概念、理论、方法。二、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块学时数教学内容与教学要求支撑的课程分目标理解空间直角坐标系、向量的概念。掌握向量的性质及运算。掌握平面方程和直线方程及其求法。了解曲面方程的概念,了解典型第八章空间解析几何10课程分目标1二次曲面的方程及图形,会求简单的柱面和与向量代数旋转曲面的方程。了解空间曲线的参数方程和一般方程。了解空间曲线在坐标平面上的投影,并会求投影曲线方程。理解多元函数的概念。了解二元函数的极限与连续的概念、有界闭区域上连续函数的性第九章多元函数微分20质。理解偏导数和全微分的概念,会求全微课程分目标2法及其应用分,了解全微分存在的必要条件、充分条件及全微分形式的不变性。理解方向导数与梯1
1 高等数学 A(下) 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号:11310037 课程总学时: 80 ,其中:讲课: 80 ,实验: 0 ,上机: 0 ,实习: 0 ,课外: 0 课程学分:5.5 课程分类:必修 开课学期:春 开课单位:理学院 应用数学系 适用专业:多个专业 所需先修课:无 课程负责人:周志坚 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标: 《高等数学 A》(下)一直是理、工、农、医(非数学专业)大学生必修的重要基础理论课程,近年来, 也逐步成为管理等其它学科大学生的必修课。《高等数学 A》(下)不仅是为后继课程提供必要的基础 知识,更重要的是培养学生的归纳和抽象的思维能力,从具体到一般的联想能力,正确演绎推理能力 及动手运算能力。通过掌握数学的思想方法,激发学生的创造力,为培养适应现代化高速发展与高科 技需要的高级技术人才服务。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1: 理解、了解或掌握空间解析几何中有关概念、理论、方法。 课程分目标 2: 理解、了解或掌握多元函数微分学中有关的概念、理论、方法。 课程分目标 3: 理解、了解或掌握多元函数积分学中有关的概念、理论、方法。 课程分目标 4 理解、了解或掌握级数有关的概念、理论、方法。 二、 课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第八章 空间解析几何 与向量代数 理解空间直角坐标系、向量的概念。掌握向 量的性质及运算。掌握平面方程和直线方程 及其求法。了解曲面方程的概念,了解典型 二次曲面的方程及图形,会求简单的柱面和 旋转曲面的方程。了解空间曲线的参数方程 和一般方程。了解空间曲线在坐标平面上的 投影,并会求投影曲线方程。 10 课程分目标 1 第九章 多元函数微分 法及其应用 理解多元函数的概念。了解二元函数的极限 与连续的概念、有界闭区域上连续函数的性 质。理解偏导数和全微分的概念,会求全微 分,了解全微分存在的必要条件、充分条件 及全微分形式的不变性。理解方向导数与梯 20 课程分目标 2
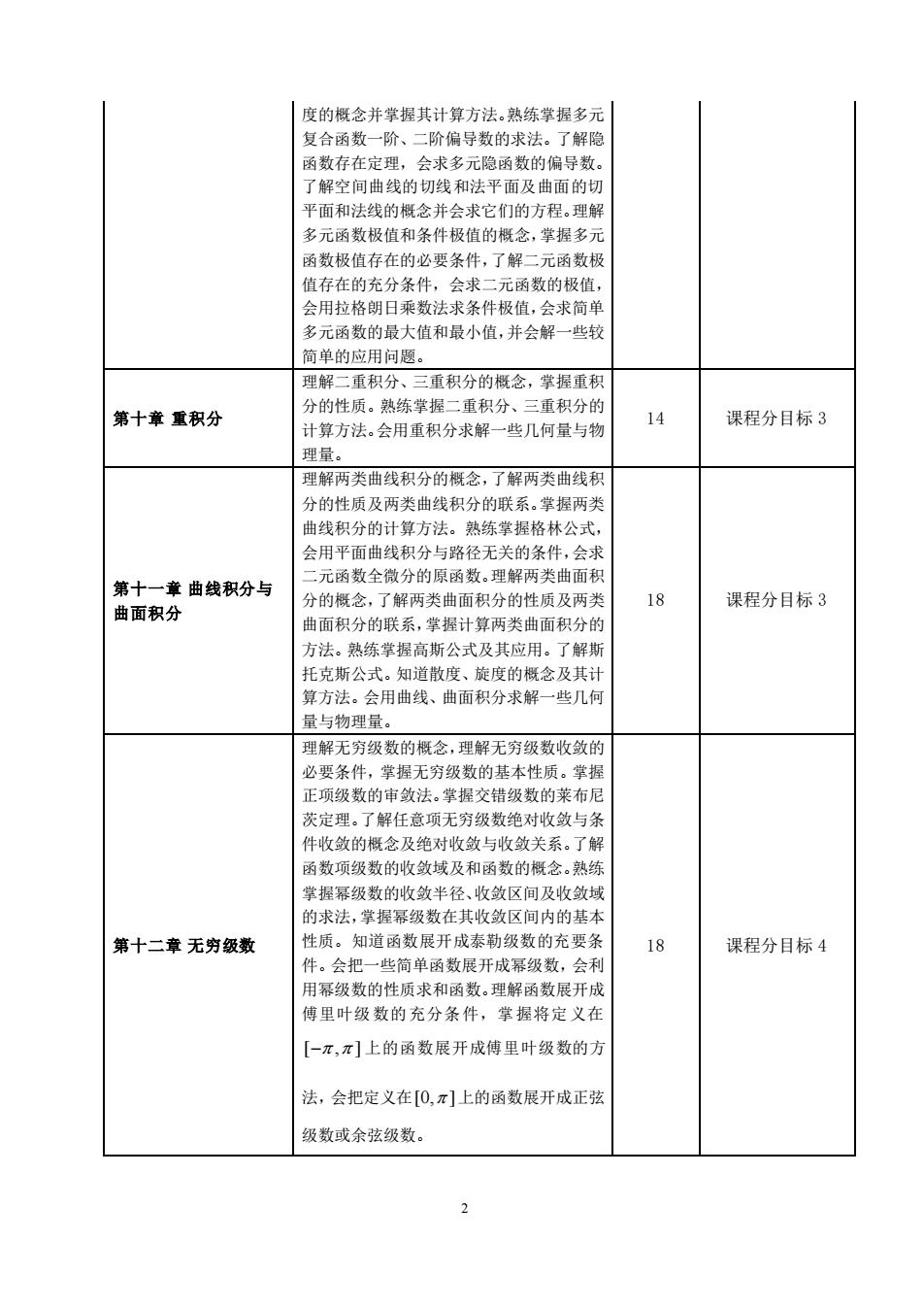
度的概念并掌握其计算方法。熟练掌握多元复合函数一阶、二阶偏导数的求法。了解隐函数存在定理,会求多元隐函数的偏导数。了解空间曲线的切线和法平面及曲面的切平面和法线的概念并会求它们的方程。理解多元函数极值和条件极值的概念,掌握多元函数极值存在的必要条件,了解二元函数极值存在的充分条件,会求二元函数的极值,会用拉格朗日乘数法求条件极值,会求简单多元函数的最大值和最小值,并会解一些较简单的应用问题。理解二重积分、三重积分的概念,掌握重积分的性质。熟练掌握二重积分、三重积分的14第十章重积分课程分目标3计算方法。会用重积分求解一些几何量与物理量。理解两类曲线积分的概念,了解两类曲线积分的性质及两类曲线积分的联系。掌握两类曲线积分的计算方法。熟练掌握格林公式,会用平面曲线积分与路径无关的条件,会求二元函数全微分的原函数。理解两类曲面积第十一章曲线积分与18分的概念,了解两类曲面积分的性质及两类课程分目标3曲面积分曲面积分的联系,掌握计算两类曲面积分的方法。熟练掌握高斯公式及其应用。了解斯托克斯公式。知道散度、旋度的概念及其计算方法。会用曲线、曲面积分求解一些几何量与物理量。理解无穷级数的概念,理解无穷级数收敛的必要条件,掌握无穷级数的基本性质。掌握正项级数的审敛法。掌握交错级数的莱布尼茨定理。了解任意项无穷级数绝对收敛与条件收敛的概念及绝对收敛与收敛关系。了解函数项级数的收敛域及和函数的概念。熟练掌握幂级数的收敛半径、收敛区间及收敛域的求法,掌握幂级数在其收敛区间内的基本性质。知道函数展开成泰勒级数的充要条18第十二章无穷级数课程分目标4件。会把一些简单函数展开成幂级数,会利用幂级数的性质求和函数。理解函数展开成傅里叶级数的充分条件,掌握将定义在[一元,元】上的函数展开成傅里叶级数的方法,会把定义在[0,元]上的函数展开成正弦级数或余弦级数。2
2 度的概念并掌握其计算方法。熟练掌握多元 复合函数一阶、二阶偏导数的求法。了解隐 函数存在定理,会求多元隐函数的偏导数。 了解空间曲线的切线和法平面及曲面的切 平面和法线的概念并会求它们的方程。理解 多元函数极值和条件极值的概念,掌握多元 函数极值存在的必要条件,了解二元函数极 值存在的充分条件,会求二元函数的极值, 会用拉格朗日乘数法求条件极值,会求简单 多元函数的最大值和最小值,并会解一些较 简单的应用问题。 第十章 重积分 理解二重积分、三重积分的概念,掌握重积 分的性质。熟练掌握二重积分、三重积分的 计算方法。会用重积分求解一些几何量与物 理量。 14 课程分目标 3 第十一章 曲线积分与 曲面积分 理解两类曲线积分的概念,了解两类曲线积 分的性质及两类曲线积分的联系。掌握两类 曲线积分的计算方法。熟练掌握格林公式, 会用平面曲线积分与路径无关的条件,会求 二元函数全微分的原函数。理解两类曲面积 分的概念,了解两类曲面积分的性质及两类 曲面积分的联系,掌握计算两类曲面积分的 方法。熟练掌握高斯公式及其应用。了解斯 托克斯公式。知道散度、旋度的概念及其计 算方法。会用曲线、曲面积分求解一些几何 量与物理量。 18 课程分目标 3 第十二章 无穷级数 理解无穷级数的概念,理解无穷级数收敛的 必要条件,掌握无穷级数的基本性质。掌握 正项级数的审敛法。掌握交错级数的莱布尼 茨定理。了解任意项无穷级数绝对收敛与条 件收敛的概念及绝对收敛与收敛关系。了解 函数项级数的收敛域及和函数的概念。熟练 掌握幂级数的收敛半径、收敛区间及收敛域 的求法,掌握幂级数在其收敛区间内的基本 性质。知道函数展开成泰勒级数的充要条 件。会把一些简单函数展开成幂级数,会利 用幂级数的性质求和函数。理解函数展开成 傅里叶级数的充分条件,掌握将定义在 [− , ] 上的函数展开成傅里叶级数的方 法,会把定义在 [0, ] 上的函数展开成正弦 级数或余弦级数。 18 课程分目标 4
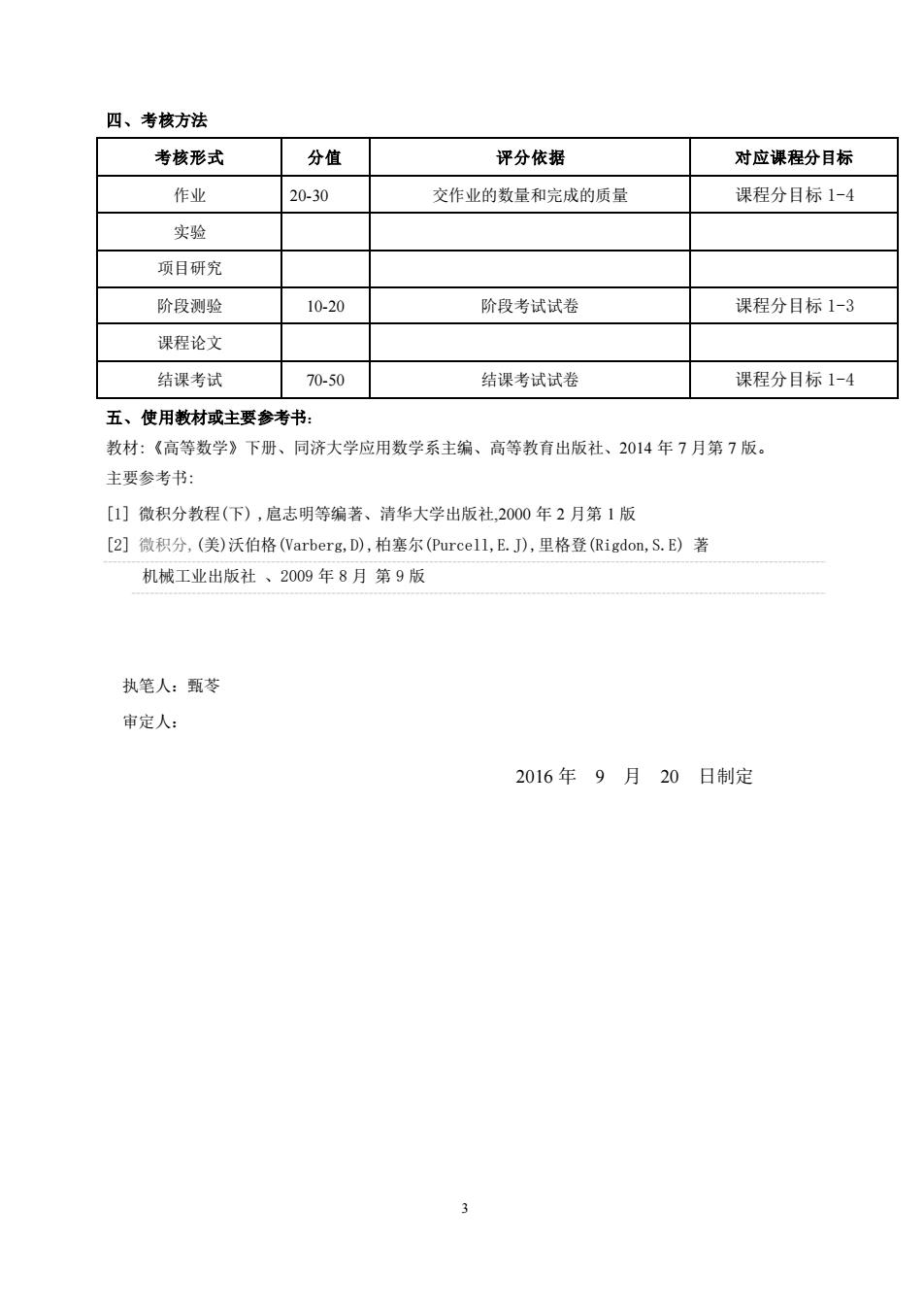
四、考核方法考核形式分值评分依据对应课程分目标作业20-30交作业的数量和完成的质量课程分目标1-4实验项目研究课程分目标1-3阶段测验10-20阶段考试试卷课程论文结课考试70-50结课考试试卷课程分目标1-4五、使用教材或主要参考书:教材:《高等数学》下册、同济大学应用数学系主编、高等教育出版社、2014年7月第7版。主要参考书:[1】微积分教程(下),扈志明等编著、清华大学出版社,2000年2月第1版[2】微积分,(美)沃伯格(Varberg,D,柏塞尔(Purcel1,E.J),里格登(Rigdon,S.E)著机械工业出版社、2009年8月第9版执笔人:甄苓审定人:2016年9月20日制定3
3 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 20-30 交作业的数量和完成的质量 课程分目标 1-4 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 10-20 阶段考试试卷 课程分目标 1-3 课程论文 结课考试 70-50 结课考试试卷 课程分目标 1-4 五、使用教材或主要参考书: 教材:《高等数学》下册、同济大学应用数学系主编、高等教育出版社、2014 年 7 月第 7 版。 主要参考书: [1] 微积分教程(下) ,扈志明等编著、清华大学出版社,2000 年 2 月第 1 版 [2] 微积分,(美)沃伯格(Varberg,D),柏塞尔(Purcell,E.J),里格登(Rigdon,S.E) 著 机械工业出版社 、2009 年 8 月 第 9 版 执笔人:甄苓 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 20 日制定

AdvancedMathematicsA(I)1.Basic informationCoursecode:11310037Total teaching hours:80, among which o hours for lectures, hours for experiments, o hours for on-lineteaching.Credits: 5.5Type of the course:CompulsoryTeachingterms: SpringOwner of the course:Department ofApplied Mathematics, School of ScienceMajorsapplicable:SeveralmajorsPrerequisites: NonePersoninchargeofthecourse:2.CourseObjectives(1) GeneralAimAdvanced Mathematics is always an important compulsory fundamental theoretical course forundergraduate students majoringin science, engineering,agriculture and medicines. In recent years, italso becomes a compulsory course for students majoring in management and other fields. AdvancedMathematics not only provides necessary basic knowledge for subsequent courses, but also builds theabilities of induction and abstraction, the abilities of imaginingfrom the specific to thegeneral, theabilities of correct deductive and reasoning and the abilities of calculations.By providing themathematical methods of thinking,it will inspire students'creativities.It servesfor the education ofseniortechnical personnel who are suitablefortherapid development ofmodemization and thedemandsof high-tech.(2)BranchObjectivesThe First one:Students are required to understand or master the concepts,theories,methods of Analytic geometry andvectoralgebrasThe Second one:Students are required tounderstand or master the concepts,theories,methods of thedifferential calculusin n-Space.The Third one:Students arerequired to understand ormastertheconcepts,theories,methodsofthe integral in n-SpaceThe Fourth one:Students are required to understand or master the concepts, theories,methods ofInfinite series3,The Diagram between Course Content,Teaching Requirements and Course ObjectivesClassCorrespondingCourse ModulesCourseContentandTeachingRequirementshourCourse Objectives
4 Advanced Mathematics A(Ⅱ) 1. Basic information Course code: 11310037 Total teaching hours:80, among which 0 hours for lectures,0 hours for experiments, 0 hours for on-line teaching. Credits: 5.5 Type of the course: Compulsory Teaching terms: Spring Owner of the course: Department of Applied Mathematics, School of Science Majors applicable: Several majors Prerequisites: None Person in charge of the course: 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim Advanced Mathematics is always an important compulsory fundamental theoretical course for undergraduate students majoring in science, engineering, agriculture and medicines. In recent years, it also becomes a compulsory course for students majoring in management and other fields. Advanced Mathematics not only provides necessary basic knowledge for subsequent courses, but also builds the abilities of induction and abstraction, the abilities of imagining from the specific to the general, the abilities of correct deductive and reasoning and the abilities of calculations. By providing the mathematical methods of thinking, it will inspire students’ creativities. It serves for the education of senior technical personnel who are suitable for the rapid development of modernization and the demands of high-tech. (2)Branch Objectives The First one: Students are required to understand or master the concepts,theories,methods of Analytic geometry and vector algebras The Second one: Students are required to understand or master the concepts,theories,methods of the differential calculus in n-Space. The Third one: Students are required to understand or master the concepts, theories, methods of the integral in n-Space. The Fourth one: Students are required to understand or master the concepts, theories ,methods of Infinite series. 3、The Diagram between Course Content、Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class hour s Corresponding Course Objectives
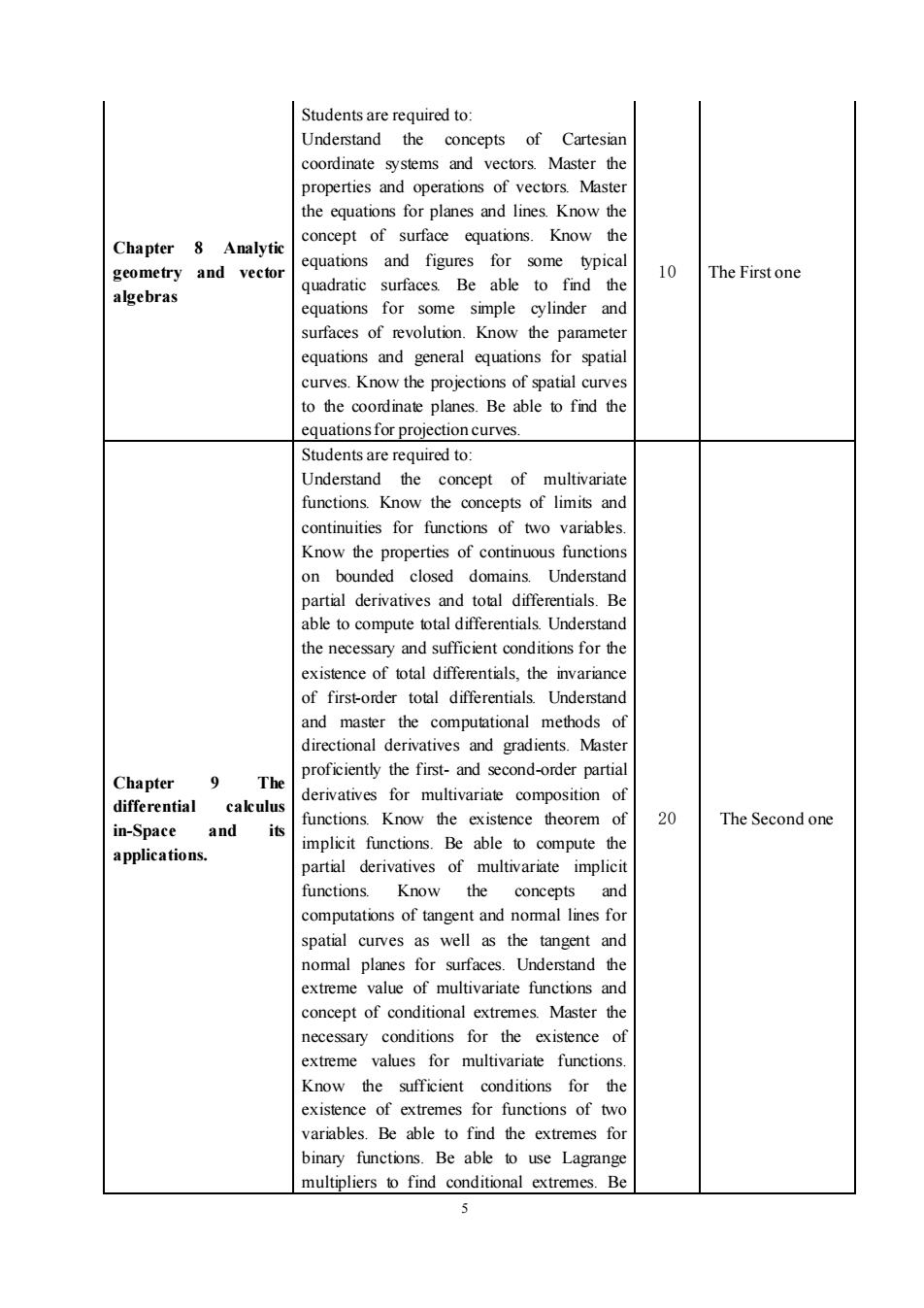
Students are required to:Understand theconcepts ofCartesiancoordinate systems and vectors. Master theproperties and operations of vectors. Masterthe equations for planes and lines. Know theKnowtheconceptof surfaceeequations.Chapter8Analyticequations and figures for some typical10geometryandvectorTheFirstonequadratic surfaces Be able to find thealgebrasequations for some simple cylinder andsurfaces of revolution. Know the parameterequations and general equations for spatialcurves. Know the projections of spatial curvesto the coordinate planes.Be able to find theequationsfor projectioncurvesStudents are required to:Understandtheconceptofmultivariatefunctions.Know theconcepts of limits andcontinuities for functions of two variables.Know the properties of continuous functionsonbounded closeddomains.Understandpartial derivatives and total differentials.Beabletocomputetotal differentials.Understandthe necessary and sufficient conditions for theexistenceof total differentials,the invarianceof first-order total differentials. Understandand master the computational methods ofdirectional derivatives and gradients. Masterproficiently the fist- and second-order partial9TheChapterderivatives for multivariate composition ofdifferentialcalculusfunctions. Know the existence theorem of20The Second onein-Spaceanditsimplicit functions. Be able to compute theapplications.partial derivatives of multivariate implicitfunctions.andKnowtheconceptscomputations of tangentandnormal linesforspatial curves as well as the tangent andnomal planes for surfaces. Understand theextreme value of multivariate functions andconcept of conditional extremes.Master thenecessary conditions for the existence ofextreme values for multivariate functions.Knowthesufficientconditions fortheexistence of extremes for functions of twovariables,Be able tofind the extremes forbinary functions. Be able to use Lagrangemultipliers to find conditional extremes. Be5
5 Chapter 8 Analytic geometry and vector algebras Students are required to: Understand the concepts of Cartesian coordinate systems and vectors. Master the properties and operations of vectors. Master the equations for planes and lines. Know the concept of surface equations. Know the equations and figures for some typical quadratic surfaces. Be able to find the equations for some simple cylinder and surfaces of revolution. Know the parameter equations and general equations for spatial curves. Know the projections of spatial curves to the coordinate planes. Be able to find the equations for projection curves. 10 The First one Chapter 9 The differential calculus in-Space and its applications. Students are required to: Understand the concept of multivariate functions. Know the concepts of limits and continuities for functions of two variables. Know the properties of continuous functions on bounded closed domains. Understand partial derivatives and total differentials. Be able to compute total differentials. Understand the necessary and sufficient conditions for the existence of total differentials, the invariance of first-order total differentials. Understand and master the computational methods of directional derivatives and gradients. Master proficiently the first- and second-order partial derivatives for multivariate composition of functions. Know the existence theorem of implicit functions. Be able to compute the partial derivatives of multivariate implicit functions. Know the concepts and computations of tangent and normal lines for spatial curves as well as the tangent and normal planes for surfaces. Understand the extreme value of multivariate functions and concept of conditional extremes. Master the necessary conditions for the existence of extreme values for multivariate functions. Know the sufficient conditions for the existence of extremes for functions of two variables. Be able to find the extremes for binary functions. Be able to use Lagrange multipliers to find conditional extremes. Be 20 The Second one