
高等数学A上一、课程基本情况课程编号:11310036课程总学时:80+8,(其中80为讲课学时数,8为习题课学时数)5.5课程学分:必修课程分类:开课学期:秋开课单位:理学院应用数学系适用专业:全校工科类、管理类、资源与环境学院各专业及生命科学试验班所需先修课:无课程负责人:周志坚二、课程目标:1、课程总目标:通过本课程的学习,使学生能够获得相关专业课程必备的基础知识、基本的数学思想方法和必要的应用技能,为其今后的可持续发展奠定基础:培养学生的归纳、抽象思维的能力,逻辑推理、运算能力,从具体到一般的联想能力和提出问题分析问题解决问题的能力。增进学生对数学的理解和兴趣,激发学生的创造力,为培养适应现代化高速发展与高科技需要的高级技术人才服务。2、课程分目标:课程分目标1:理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性质。理解极限的概念,掌握极限的性质、法则及计算方法。课程分目标2:理解一元函数微分的基本概念,掌握一元函数微分的基本理论、基本运算及其应用。课程分目标3:理解不定积分及定积分的基本概念,掌握不定积分及定积分的基本理论和基本运算,掌握元素法、定积分的几何与物理应用。课程分目标4:理解常微分方程的基本概念、性质,掌握几类常微分方程的求解方法。课程分目标5:培养学生的抽象思维能力、逻辑推理能力、计算能力及发现问题并运用所学知识分析问题和解决问题的能力。课程分目标6:培养学生的数学应用意识、创新精神,提高数学文化素养和自主学习能力。三、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图课程模块教学内容与教学要求学时数支撑的课程分目标理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性质。理解复合函数、分段函数、反函数及隐函数的概念。掌握基本初等函数的性质及其图形。能建立简单的实际问题的函数关课程分目标第一章:函数与极限系。了解极限的“-8”、“e-N”定16+21、5、6义,并逐步加深对极限思想的理解。掌握极限的性质、四则运算法则及两个极限存在准则,掌握两个重要极限。理解无穷小和无穷大的概念,掌握无穷小的比较方1
1 高等数学 A 上 一、 课程基本情况 课程编号:11310036 课程总学时:80+8,(其中 80 为讲课学时数,8 为习题课学时数) 课程学分: 5.5 课程分类: 必修 开课学期: 秋 开课单位: 理学院应用数学系 适用专业: 全校工科类、管理类、资源与环境学院各专业及生命科学试验班 所需先修课: 无 课程负责人:周志坚 二、课程目标: 1、课程总目标:通过本课程的学习,使学生能够获得相关专业课程必备的基础知识、基本的数学思 想方法和必要的应用技能,为其今后的可持续发展奠定基础;培养学生的归纳、抽象思维的能力,逻 辑推理、运算能力,从具体到一般的联想能力和提出问题分析问题解决问题的能力。增进学生对数学 的理解和兴趣,激发学生的创造力,为培养适应现代化高速发展与高科技需要的高级技术人才服务。 2、课程分目标: 课程分目标 1:理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性质。理解极限的概念,掌握极限的性质、法则及计 算方法。 课程分目标 2:理解一元函数微分的基本概念,掌握一元函数微分的基本理论、基本运算及其应用。 课程分目标 3:理解不定积分及定积分的基本概念,掌握不定积分及定积分的基本理论和基本运算,掌 握元素法、定积分的几何与物理应用。 课程分目标 4:理解常微分方程的基本概念、性质,掌握几类常微分方程的求解方法。 课程分目标 5:培养学生的抽象思维能力、逻辑推理能力、计算能力及发现问题并运用所学知识分析问 题和解决问题的能力。 课程分目标 6:培养学生的数学应用意识、创新精神,提高数学文化素养和自主学习能力。 三、课程内容、教学要求与课程目标关系图 课程模块 教学内容与教学要求 学时数 支撑的课程分目标 第一章:函数与极限 理解函数的概念,掌握函数的基本性质。 理解复合函数、分段函数、反函数及隐函 数的概念。掌握基本初等函数的性质及其 图形。能建立简单的实际问题的函数关 系。了解极限的“ε-δ”、“ε-N”定 义,并逐步加深对极限思想的理解。掌握 极限的性质、四则运算法则及两个极限存 在准则,掌握两个重要极限。理解无穷小 和无穷大的概念,掌握无穷小的比较方 16+2 课程分目标 1、5、6
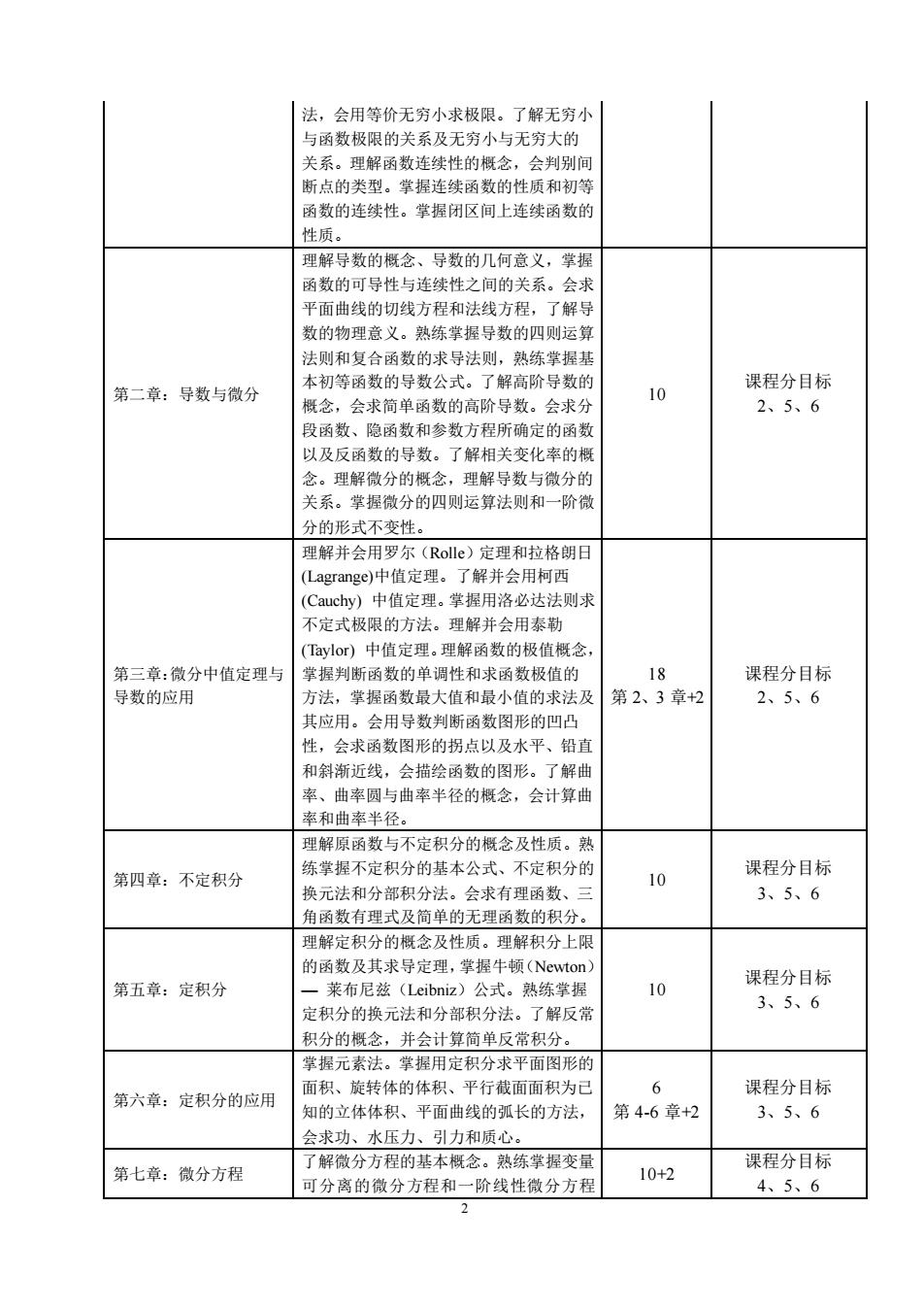
法,会用等价无穷小求极限。了解无穷小与函数极限的关系及无穷小与无穷大的关系。理解函数连续性的概念,会判别间断点的类型。掌握连续函数的性质和初等函数的连续性。掌握闭区间上连续函数的性质。理解导数的概念、导数的几何意义,掌握函数的可导性与连续性之间的关系。会求平面曲线的切线方程和法线方程,了解导数的物理意义。熟练掌握导数的四则运算法则和复合函数的求导法则,熟练掌握基课程分目标本初等函数的导数公式。了解高阶导数的第二章:导数与微分102、5、6概念,会求简单函数的高阶导数。会求分段函数、隐函数和参数方程所确定的函数以及反函数的导数。了解相关变化率的概念。理解微分的概念,理解导数与微分的关系。掌握微分的四则运算法则和一阶微分的形式不变性。理解并会用罗尔(Rolle)定理和拉格朗日(Lagrange)中值定理。了解并会用柯西(Cauchy)中值定理。掌握用洛必达法则求不定式极限的方法。理解并会用泰勒(Taylor)中值定理。理解函数的极值概念,第三章:微分中值定理与18课程分目标掌握判断函数的单调性和求函数极值的导数的应用方法,掌握函数最大值和最小值的求法及第2、3章+22、5、6其应用。会用导数判断函数图形的凹凸性,会求函数图形的拐点以及水平、铅直和斜渐近线,会描绘函数的图形。了解曲率、曲率圆与曲率半径的概念,会计算曲率和曲率半径。理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性质。熟课程分目标练掌握不定积分的基本公式、不定积分的10第四章:不定积分换元法和分部积分法。会求有理函数、三3、5、6角函数有理式及简单的无理函数的积分。理解定积分的概念及性质。理解积分上限的函数及其求导定理,掌握牛顿(Newton)课程分目标10第五章:定积分一莱布尼兹(Leibniz)公式。熟练掌握3、5、6定积分的换元法和分部积分法。了解反常积分的概念,并会计算简单反常积分。掌握元素法。掌握用定积分求平面图形的课程分目标面积、旋转体的体积、平行截面面积为已6第六章:定积分的应用知的立体体积、平面曲线的弧长的方法,第4-6章+23、5、6会求功、水压力、引力和质心。课程分目标了解微分方程的基本概念。熟练掌握变量第七章:微分方程10+2可分离的微分方程和一阶线性微分方程4、5、62
2 法,会用等价无穷小求极限。了解无穷小 与函数极限的关系及无穷小与无穷大的 关系。理解函数连续性的概念,会判别间 断点的类型。掌握连续函数的性质和初等 函数的连续性。掌握闭区间上连续函数的 性质。 第二章:导数与微分 理解导数的概念、导数的几何意义,掌握 函数的可导性与连续性之间的关系。会求 平面曲线的切线方程和法线方程,了解导 数的物理意义。熟练掌握导数的四则运算 法则和复合函数的求导法则,熟练掌握基 本初等函数的导数公式。了解高阶导数的 概念,会求简单函数的高阶导数。会求分 段函数、隐函数和参数方程所确定的函数 以及反函数的导数。了解相关变化率的概 念。理解微分的概念,理解导数与微分的 关系。掌握微分的四则运算法则和一阶微 分的形式不变性。 10 课程分目标 2、5、6 第三章:微分中值定理与 导数的应用 理解并会用罗尔(Rolle)定理和拉格朗日 (Lagrange)中值定理。了解并会用柯西 (Cauchy) 中值定理。掌握用洛必达法则求 不定式极限的方法。理解并会用泰勒 (Taylor) 中值定理。理解函数的极值概念, 掌握判断函数的单调性和求函数极值的 方法,掌握函数最大值和最小值的求法及 其应用。会用导数判断函数图形的凹凸 性,会求函数图形的拐点以及水平、铅直 和斜渐近线,会描绘函数的图形。了解曲 率、曲率圆与曲率半径的概念,会计算曲 率和曲率半径。 18 第 2、3 章+2 课程分目标 2、5、6 第四章:不定积分 理解原函数与不定积分的概念及性质。熟 练掌握不定积分的基本公式、不定积分的 换元法和分部积分法。会求有理函数、三 角函数有理式及简单的无理函数的积分。 10 课程分目标 3、5、6 第五章:定积分 理解定积分的概念及性质。理解积分上限 的函数及其求导定理,掌握牛顿(Newton) — 莱布尼兹(Leibniz)公式。熟练掌握 定积分的换元法和分部积分法。了解反常 积分的概念,并会计算简单反常积分。 10 课程分目标 3、5、6 第六章:定积分的应用 掌握元素法。掌握用定积分求平面图形的 面积、旋转体的体积、平行截面面积为已 知的立体体积、平面曲线的弧长的方法, 会求功、水压力、引力和质心。 6 第 4-6 章+2 课程分目标 3、5、6 第七章:微分方程 了解微分方程的基本概念。熟练掌握变量 可分离的微分方程和一阶线性微分方程 10+2 课程分目标 4、5、6
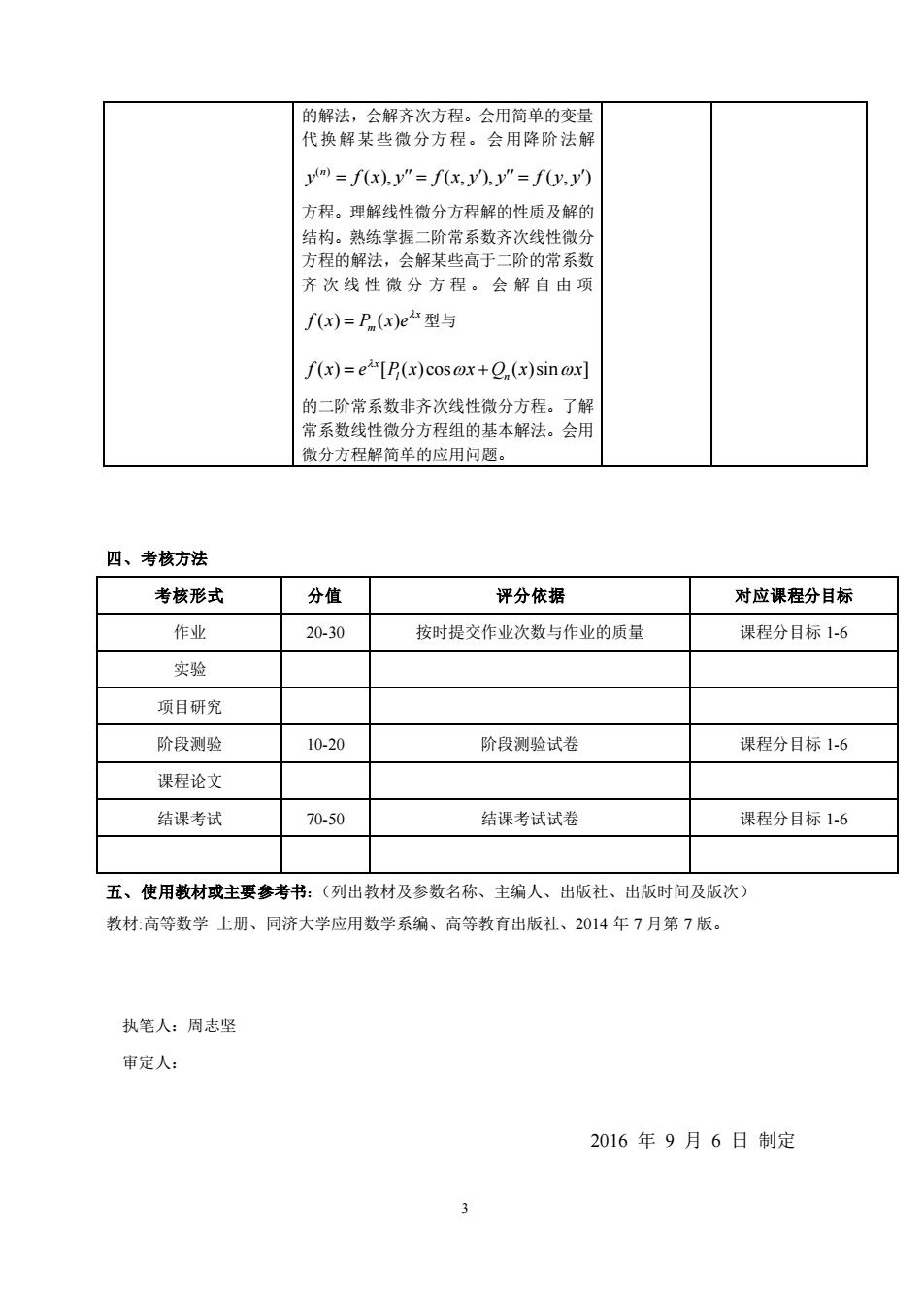
的解法,会解齐次方程。会用简单的变量代换解某些微分方程。会用降阶法解y(n) = f(x),j"= f(x,y),y"= f(y,y)方程。理解线性微分方程解的性质及解的结构。熟练掌握二阶常系数齐次线性微分方程的解法,会解某些高于二阶的常系数齐次线性微分方程。会解自由项f(x)= P(x)e型与f(x)=e[P(x) cos ox +O,(x)sin ox)的二阶常系数非齐次线性微分方程。了解常系数线性微分方程组的基本解法。会用微分方程解简单的应用问题。四、考核方法分值评分依据考核形式对应课程分目标作业20-30按时提交作业次数与作业的质量课程分目标1-6实验项目研究阶段测验10-20阶段测验试卷课程分目标1-6课程论文结课考试70-50结课考试试卷课程分目标1-6五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次)教材:高等数学上册、同济大学应用数学系编、高等教育出版社、2014年7月第7版。执笔人:周志坚审定人:2016年9月6日制定3
3 的解法,会解齐次方程。会用简单的变量 代换解某些微分方程。会用降阶法解 ( ) ( ), ( , ), ( , ) n y f x y f x y y f y y = = = 方程。理解线性微分方程解的性质及解的 结构。熟练掌握二阶常系数齐次线性微分 方程的解法,会解某些高于二阶的常系数 齐 次 线 性 微 分 方 程 。 会 解 自 由 项 ( ) ( ) x m f x P x e = 型与 ( ) [ ( )cos ( )sin ] x l n f x e P x x Q x x = + 的二阶常系数非齐次线性微分方程。了解 常系数线性微分方程组的基本解法。会用 微分方程解简单的应用问题。 四、考核方法 考核形式 分值 评分依据 对应课程分目标 作业 20-30 按时提交作业次数与作业的质量 课程分目标 1-6 实验 项目研究 阶段测验 10-20 阶段测验试卷 课程分目标 1-6 课程论文 结课考试 70-50 结课考试试卷 课程分目标 1-6 五、使用教材或主要参考书:(列出教材及参数名称、主编人、出版社、出版时间及版次) 教材:高等数学 上册、同济大学应用数学系编、高等教育出版社、2014 年 7 月第 7 版。 执笔人:周志坚 审定人: 2016 年 9 月 6 日 制定
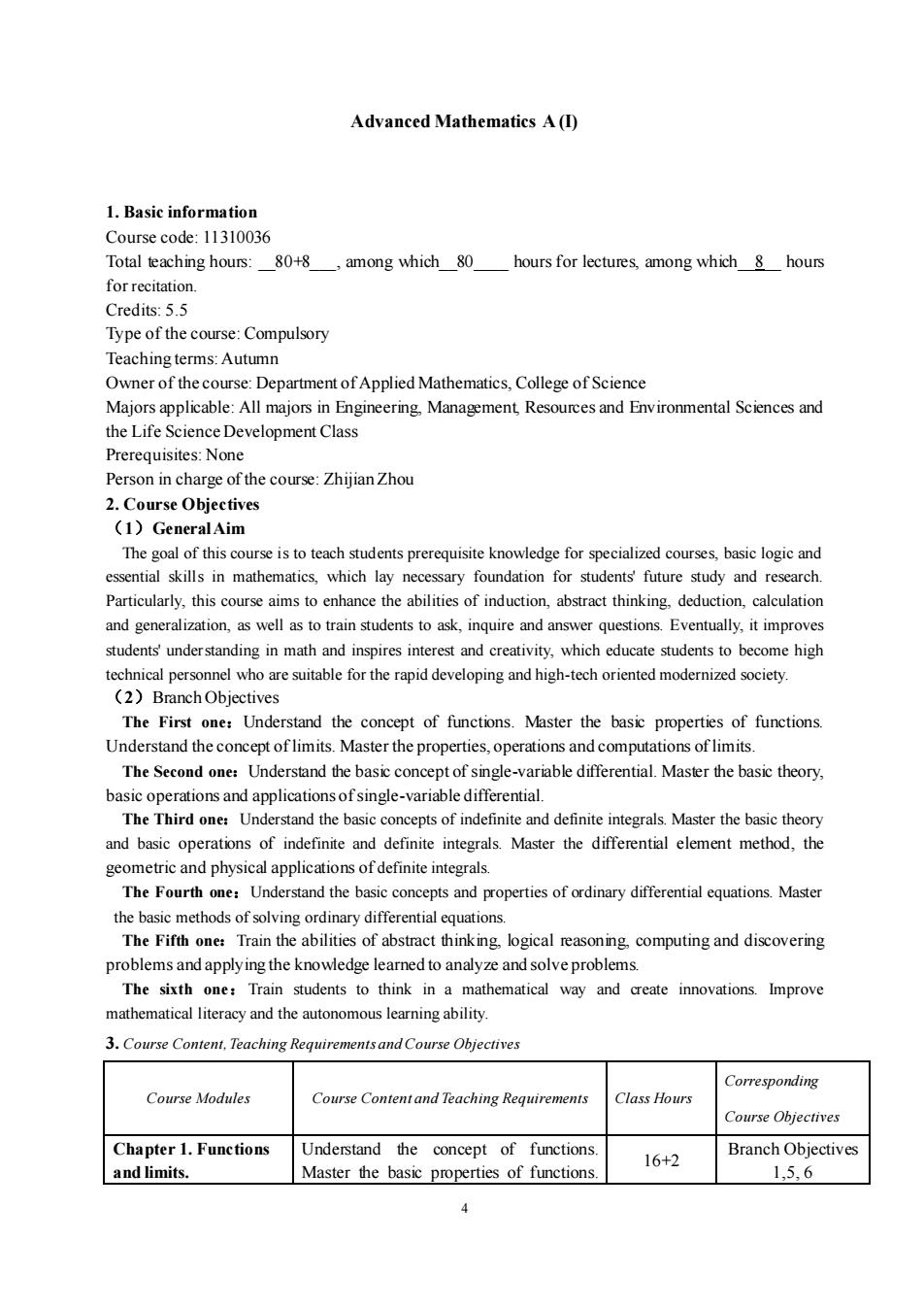
Advanced Mathematics A (l)1.Basic informationCoursecode:11310036Total teaching hours:80+8,amongwhich80hoursforlectures,amongwhich8hoursforrecitation.Credits: 5.5Type of the course:CompulsoryTeachingterms:AutumnOwnerofthecourse:DepartmentofAppliedMathematics,CollegeofScienceMajors applicable: All majors in Engineering,Management Resources and Environmental Sciences andthe Life Science Development ClassPrerequisites:NonePerson in charge ofthe course:Zhijian Zhou2.Course Objectives(1)GeneralAimThe goal of this course is to teach students prerequisite knowledge for specialized courses, basic logic andessential skills in mathematics, which lay necessary foundation for studentsfuture study and researchParticularly,this course aims to enhance the abilities of induction, abstract thinking,deduction, calculationand generalization, as well as to train students to ask,inquireand answer questions.Eventually,it improvesstudents understanding in math and inspires interest and creativity, which educate students to become hightechnical personnel who are suitablefortherapiddeveloping and high-tech oriented modernized society(2)BranchObjectivesThe First one: Understand the concept of functions. Master the basic properties of functions.Understand the concept of limits. Master the properties,operations and computations of limitsThe Second one:Understand the basic concept of single-variable differential.Master thebasic theory,basicoperationsandapplicationsofsingle-variabledifferential.The Third one:Understand the basic concepts of indefinite and definite integrals.Master the basic theoryand basic operations of indefinite and definite integrals.Master the differential element method, thegeometric and physical applications of definite integrals.The Fourth one:Understand the basic concepts and properties of ordinary differential equations.Masterthebasic methodsofsolving ordinarydifferential equations.The Fifth one: Train the abilities of abstract thinking, logical reasoning. computing and discoveringproblems and applying the knowledge learned to analyze and solve problems.The sixth one:Train students to think in a mathematical way and create innovations.Improvemathematical literacyandtheautonomouslearningability3.CourseContent,TeachingRequirementsandCourseObjectivesCorrespondingCourse ModulesCourse Contentand Teaching RequirementsClass HoursCourse ObjectivesChapter1.FunctionsUnderstand the concept of functions.BranchObjectives16+2and limits.1,5, 6Master the basic properties of functions4
4 Advanced Mathematics A (I) 1. Basic information Course code: 11310036 Total teaching hours: _80+8_, among which_80_ hours for lectures, among which_8_ hours for recitation. Credits: 5.5 Type of the course: Compulsory Teaching terms: Autumn Owner of the course: Department of Applied Mathematics, College of Science Majors applicable: All majors in Engineering, Management, Resources and Environmental Sciences and the Life Science Development Class Prerequisites: None Person in charge of the course: Zhijian Zhou 2. Course Objectives (1)General Aim The goal of this course is to teach students prerequisite knowledge for specialized courses, basic logic and essential skills in mathematics, which lay necessary foundation for students' future study and research. Particularly, this course aims to enhance the abilities of induction, abstract thinking, deduction, calculation and generalization, as well as to train students to ask, inquire and answer questions. Eventually, it improves students' understanding in math and inspires interest and creativity, which educate students to become high technical personnel who are suitable for the rapid developing and high-tech oriented modernized society. (2)Branch Objectives The First one:Understand the concept of functions. Master the basic properties of functions. Understand the concept of limits. Master the properties, operations and computations of limits. The Second one:Understand the basic concept of single-variable differential. Master the basic theory, basic operations and applications of single-variable differential. The Third one:Understand the basic concepts of indefinite and definite integrals. Master the basic theory and basic operations of indefinite and definite integrals. Master the differential element method, the geometric and physical applications of definite integrals. The Fourth one:Understand the basic concepts and properties of ordinary differential equations. Master the basic methods of solving ordinary differential equations. The Fifth one:Train the abilities of abstract thinking, logical reasoning, computing and discovering problems and applying the knowledge learned to analyze and solve problems. The sixth one:Train students to think in a mathematical way and create innovations. Improve mathematical literacy and the autonomous learning ability. 3. Course Content, Teaching Requirements and Course Objectives Course Modules Course Content and Teaching Requirements Class Hours Corresponding Course Objectives Chapter 1. Functions and limits. Understand the concept of functions. Master the basic properties of functions. 16+2 Branch Objectives 1,5, 6
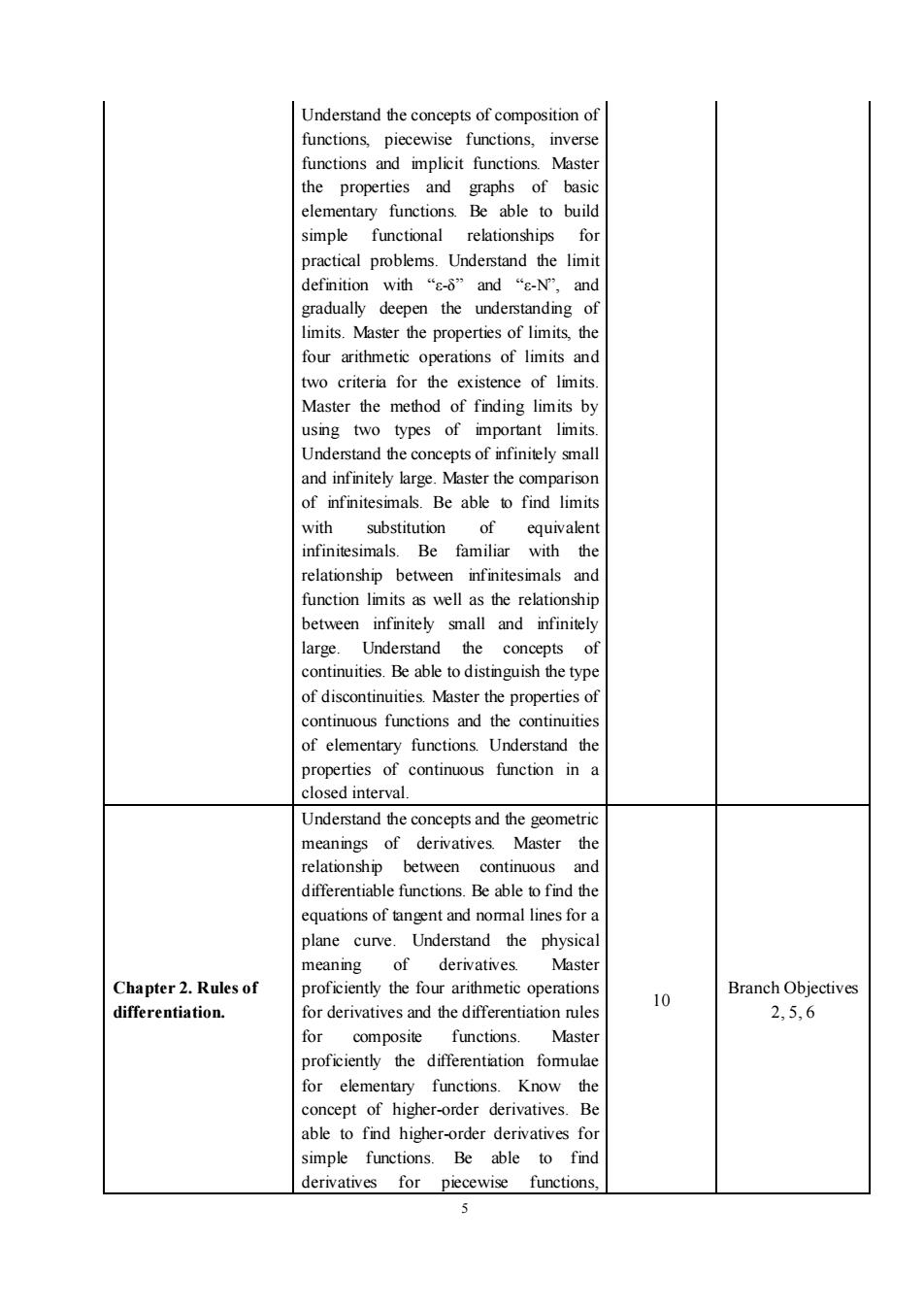
Understand the concepts of composition offunctions,piecewise functions,inversefunctions and implicit functions. Masterthe properties and graphs of basicelementary functions. Be able to buildrelationshipsforsimplefunctional1practical problems. Understand the limitdefinition with“g-8" and "s-N", andgradually deepen the understanding oflimits.Master the properties of limits, thefour arithmetic operations of limits andtwo criteria for the existence of limits.Master the method of finding limits byusing two types of important limitsUnderstand the concepts of infinitely smalland infinitely large. Master the comparisonof infinitesimals.Be able to find limitswithsubstitutionofequivalentinfinitesimals.Be familiar with therelationship between infinitesimals andfunction limits as well as the relationshipbetween infinitely small and infinitelylarge.Understandthe conceptsofcontinuities. Be able to distinguish the typeof discontinuities. Master the properties ofcontinuous functions and the continuitiesof elementary functions. Understand theproperties of continuous function in aclosed intervalUnderstand the concepts and the geometricmeanings of derivatives. Master therelationship between continuous anddifferentiablefunctions.Beabletofindtheequationsof tangentandnormal linesforaplane curve. Understand the physicalmeaningof derivatives.MasterBranch ObjectivesChapter 2. Rules ofproficiently the four arithmetic operations102,5,6differentiation.for derivatives and the differentiation rulesforcompositefunctions.Masterproficiently the differentiation fomulaefor elementaryfunctions.Knowttheconcept of higher-order derivatives.Beable to find higher-order derivatives forBeabletofindsimple functions.functions,derivativesforpiecewise5
5 Understand the concepts of composition of functions, piecewise functions, inverse functions and implicit functions. Master the properties and graphs of basic elementary functions. Be able to build simple functional relationships for practical problems. Understand the limit definition with “ε-δ” and “ε-N”, and gradually deepen the understanding of limits. Master the properties of limits, the four arithmetic operations of limits and two criteria for the existence of limits. Master the method of finding limits by using two types of important limits. Understand the concepts of infinitely small and infinitely large. Master the comparison of infinitesimals. Be able to find limits with substitution of equivalent infinitesimals. Be familiar with the relationship between infinitesimals and function limits as well as the relationship between infinitely small and infinitely large. Understand the concepts of continuities. Be able to distinguish the type of discontinuities. Master the properties of continuous functions and the continuities of elementary functions. Understand the properties of continuous function in a closed interval. Chapter 2. Rules of differentiation. Understand the concepts and the geometric meanings of derivatives. Master the relationship between continuous and differentiable functions. Be able to find the equations of tangent and normal lines for a plane curve. Understand the physical meaning of derivatives. Master proficiently the four arithmetic operations for derivatives and the differentiation rules for composite functions. Master proficiently the differentiation formulae for elementary functions. Know the concept of higher-order derivatives. Be able to find higher-order derivatives for simple functions. Be able to find derivatives for piecewise functions, 10 Branch Objectives 2, 5, 6