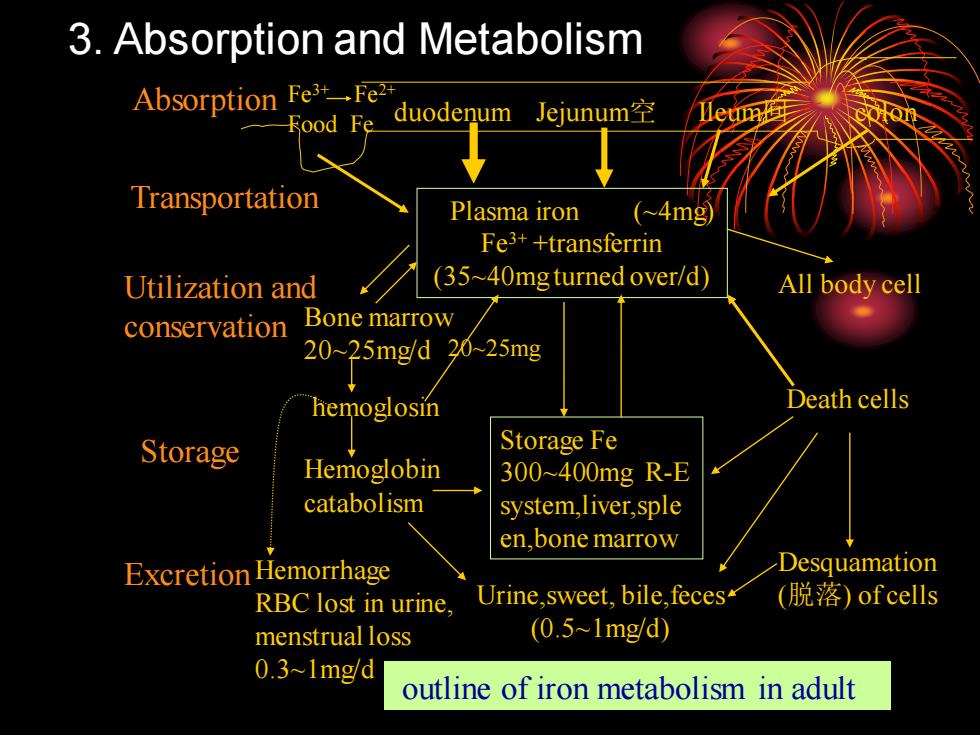
3. Absorption and Metabolism Absorption Fe3+ Fe2+ Food Fe duodenum Jejunum空 Ileum回 colon Plasma iron (~4mg) Fe3+ +transferrin (35~40mg turned over/d) Storage Fe 300~400mg R-E system,liver,sple en,bone marrow Bone marrow 20~25mg/d hemoglosin Hemoglobin catabolism Urine,sweet, bile,feces (0.5~1mg/d) Transportation Utilization and conservation Storage Hemorrhage RBC lost in urine, menstrual loss 0.3~1mg/d All body cell Death cells Desquamation (脱落) of cells 20~25mg Excretion outline of iron metabolism in adult
3. Absorption and Metabolism Absorption Fe3+ Fe2+ Food Fe duodenum Jejunum空 Ileum回 colon Plasma iron (~4mg) Fe3+ +transferrin (35~40mg turned over/d) Storage Fe 300~400mg R-E system,liver,sple en,bone marrow Bone marrow 20~25mg/d hemoglosin Hemoglobin catabolism Urine,sweet, bile,feces (0.5~1mg/d) Transportation Utilization and conservation Storage Hemorrhage RBC lost in urine, menstrual loss 0.3~1mg/d All body cell Death cells Desquamation (脱落) of cells 20~25mg Excretion outline of iron metabolism in adult
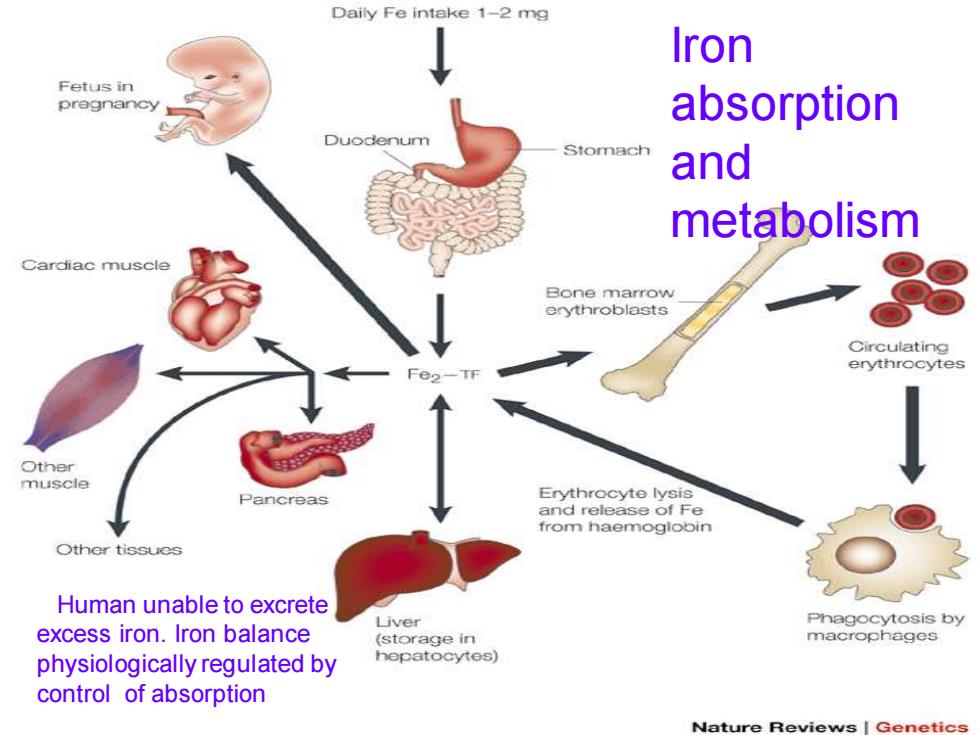
Iron absorption and metabolism Human unable to excrete excess iron. Iron balance physiologically regulated by control of absorption
Iron absorption and metabolism Human unable to excrete excess iron. Iron balance physiologically regulated by control of absorption

1) Absorption of nonheme iron(非血红素铁) Food Fe Gastric juice pH<4 Fe3+ Fe2+(Fe3+) Fe3+, Fe2+ or chelate VitC VitC,sugar,AA stomach Impaired abs in (achlorhydria and) gastrectomy apoferritin ferritin Mucosal cell transferrin β 1 -globulin Fe2+ desquamation Ingestion Duodeum (major place) pH>=7 Solubility of (Fe2+>Fe3+) Absorption Crypt at the base of villi Fe Transferrin desquamation villi Blood according to need Fe2+
1) Absorption of nonheme iron(非血红素铁) Food Fe Gastric juice pH<4 Fe3+ Fe2+(Fe3+) Fe3+, Fe2+ or chelate VitC VitC,sugar,AA stomach Impaired abs in (achlorhydria and) gastrectomy apoferritin ferritin Mucosal cell transferrin β 1 -globulin Fe2+ desquamation Ingestion Duodeum (major place) pH>=7 Solubility of (Fe2+>Fe3+) Absorption Crypt at the base of villi Fe Transferrin desquamation villi Blood according to need Fe2+
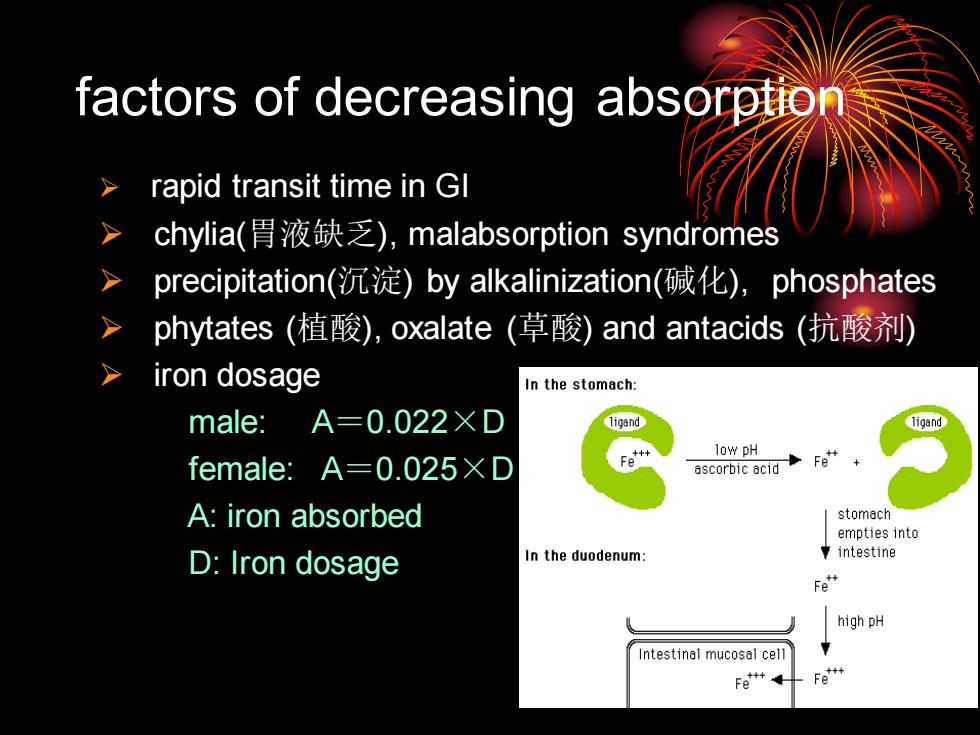
➢ rapid transit time in GI ➢ chylia(胃液缺乏), malabsorption syndromes ➢ precipitation(沉淀) by alkalinization(碱化), phosphates ➢ phytates (植酸), oxalate (草酸) and antacids (抗酸剂) ➢ iron dosage male: A=0.022×D female: A=0.025×D A: iron absorbed D: Iron dosage factors of decreasing absorption
➢ rapid transit time in GI ➢ chylia(胃液缺乏), malabsorption syndromes ➢ precipitation(沉淀) by alkalinization(碱化), phosphates ➢ phytates (植酸), oxalate (草酸) and antacids (抗酸剂) ➢ iron dosage male: A=0.022×D female: A=0.025×D A: iron absorbed D: Iron dosage factors of decreasing absorption

➢ factors of increasing absorption ❖ iron dosage ❖ vit.C, B2; amino acids: cysteine(半胱氨酸) ❖ MFP factor (meat fish poultry factor,肉鱼禽因子) ❖ Ca, Fe help each other to diminish the inhibitors;Zn, Fe have competitive absorption. 2) absorption of heme iron(血红素铁) heme iron enzyme duodenum cell blood(transferring) The absorption of heme iron is not influenced by inhibitors which decrease the absorption of nonheme iron
➢ factors of increasing absorption ❖ iron dosage ❖ vit.C, B2; amino acids: cysteine(半胱氨酸) ❖ MFP factor (meat fish poultry factor,肉鱼禽因子) ❖ Ca, Fe help each other to diminish the inhibitors;Zn, Fe have competitive absorption. 2) absorption of heme iron(血红素铁) heme iron enzyme duodenum cell blood(transferring) The absorption of heme iron is not influenced by inhibitors which decrease the absorption of nonheme iron