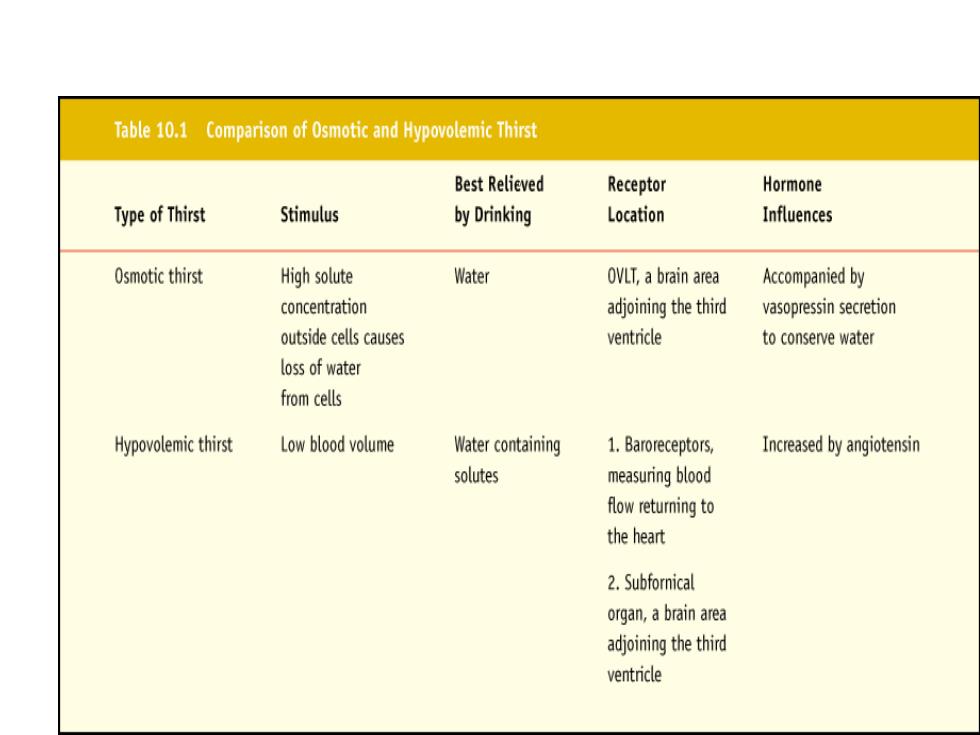
Table 10.1,Comparison of Osmotic and Hypovolemic ThirstReceptorHormoneBest RelievedStimulusType of Thirstby DrinkingLocationInfluencesHigh soluteWaterOsmoticthirstOVLT,a brain areaAccompanied byconcentrationadjoining the thirdvasopressin secretionoutsidecellscausesventricleto conservewaterloss of waterfrom cellsHypovolemic thirstLowblood volumeWater containing1.BaroreceptorsIncreasedbyangiotensinsolutesmeasuring bloodflow returning tothe heart2. Subfornicalorgan, a brain areaadjoining the thirdventricle
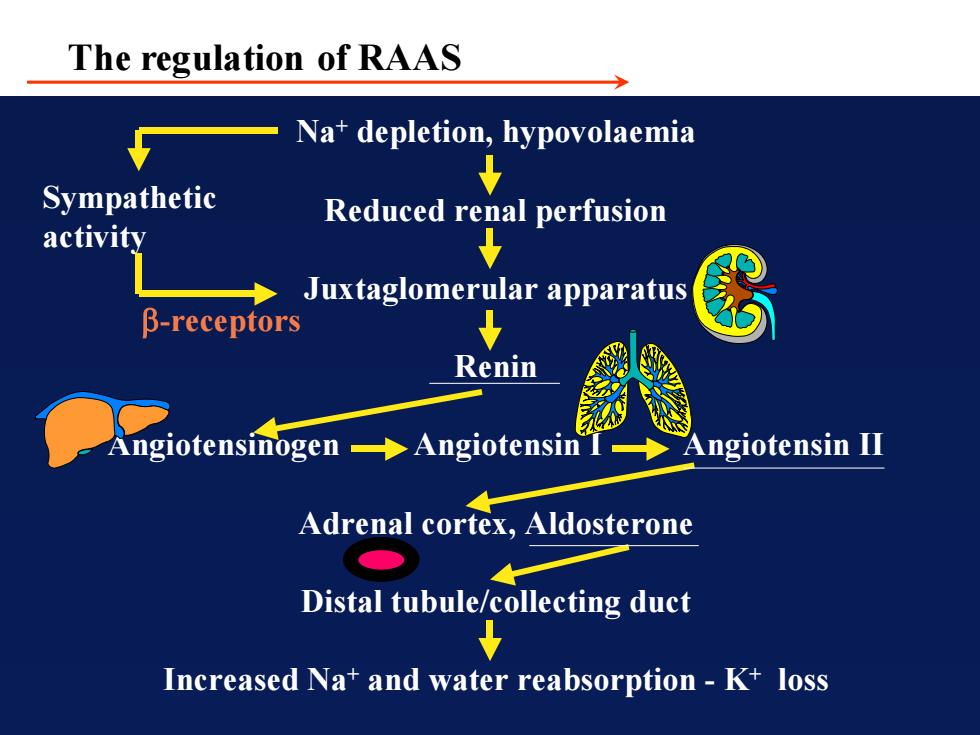
The regulation of RAASNa+depletion,hypovolaemiaSympatheticReduced renal perfusionactivityJuxtaglomerular apparatusβ-receptorsReninAngiotensinIAngiotensinAngiotensinogenAdrenal cortex,AldosteroneDistaltubule/collecting ductIncreased Na+ and waterreabsorption -K+ loss
Regulation of Na and water by the kidney This is achieved by the mineralocorticoid aldosterone acting on the DT/CD Na+ depletion, hypovolaemia Reduced renal perfusion Juxtaglomerular apparatus Renin Angiotensinogen Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Adrenal cortex, Aldosterone Distal tubule/collecting duct Increased Na+ and water reabsorption - K+ loss Sympathetic activity -receptors The regulation of RAAS