
第二节蛋白质的定性测定 考马斯亮蓝法(Stain with Coomassie blue)):考马斯亮蓝法 灵敏度比氨基黑高玉倍,尤基适用手D电泳的微量军三质的 九品 在549nm有最大吸值蛋白质在1~10g线性笑系 奇检测出0.1ug的金当廣累带.苣银染法可以检测屈2ng的 蛋白质条带. Casting stand Casting frame and glass plate sandwich wwwwwww Clamping frame Plastic combs and electrode assembly Glass plates with Sample loading integrated spacers guides
第二节 蛋白质的定性测定 考马斯亮蓝法 (Stain with Coomassie blue):考马斯亮蓝法 灵敏度比氨基黑高五倍,尤其适用于SDS电泳的微量蛋白质的 染色。在549nm有最大吸收值,蛋白质在1~10μg呈线性关系。 可以检测出0.1 ug 的蛋白质条带. 但银染法可以检测出 2 ng的 蛋白质条带
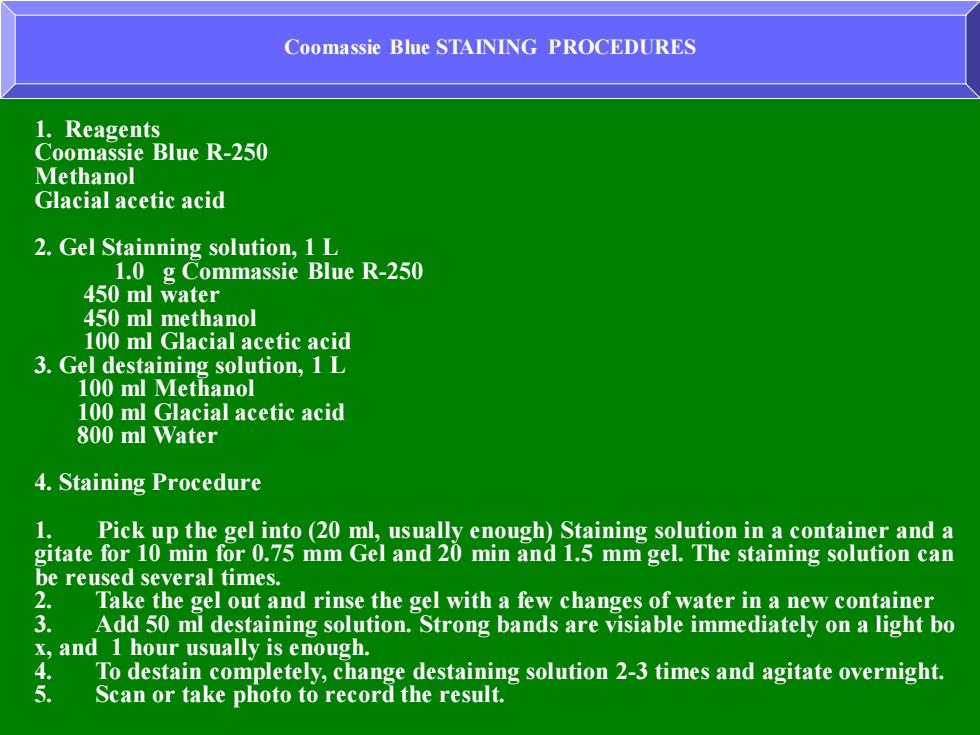
Coomassie Blue STAINING PROCEDURES 1.Reagents Coomassie Blue R-250 Methanol Glacial acetic acid 2.Gel Stainning solution,1L 1.0 g Commassie Blue R-250 450 ml water 450 ml methanol 100 ml Glacial acetic acid 3.Gel destaining solution,1 L 100 ml Methanol 100 ml Glacial acetic acid 800 ml Water 4.Staining Procedure 1. Pick up the gel into (20 ml,usually enough)Staining solution in a container and a gitate for 10 min for 0.75 mm Gel and 20 min and 1.5 mm gel.The staining solution can be reused several times. 2. Take the gel out and rinse the gel with a few changes of water in a new container 3. Add 50 ml destaining solution.Strong bands are visiable immediately on a light bo x,and 1 hour usually is enough. To destain completely,change destaining solution 2-3 times and agitate overnight. 5. Scan or take photo to record the result
Coomassie Blue STAINING PROCEDURES 1. Reagents Coomassie Blue R-250 Methanol Glacial acetic acid 2. Gel Stainning solution, 1 L 1.0 g Commassie Blue R-250 450 ml water 450 ml methanol 100 ml Glacial acetic acid 3. Gel destaining solution, 1 L 100 ml Methanol 100 ml Glacial acetic acid 800 ml Water 4. Staining Procedure 1. Pick up the gel into (20 ml, usually enough) Staining solution in a container and a gitate for 10 min for 0.75 mm Gel and 20 min and 1.5 mm gel. The staining solution can be reused several times. 2. Take the gel out and rinse the gel with a few changes of water in a new container 3. Add 50 ml destaining solution. Strong bands are visiable immediately on a light bo x, and 1 hour usually is enough. 4. To destain completely, change destaining solution 2-3 times and agitate overnight. 5. Scan or take photo to record the result
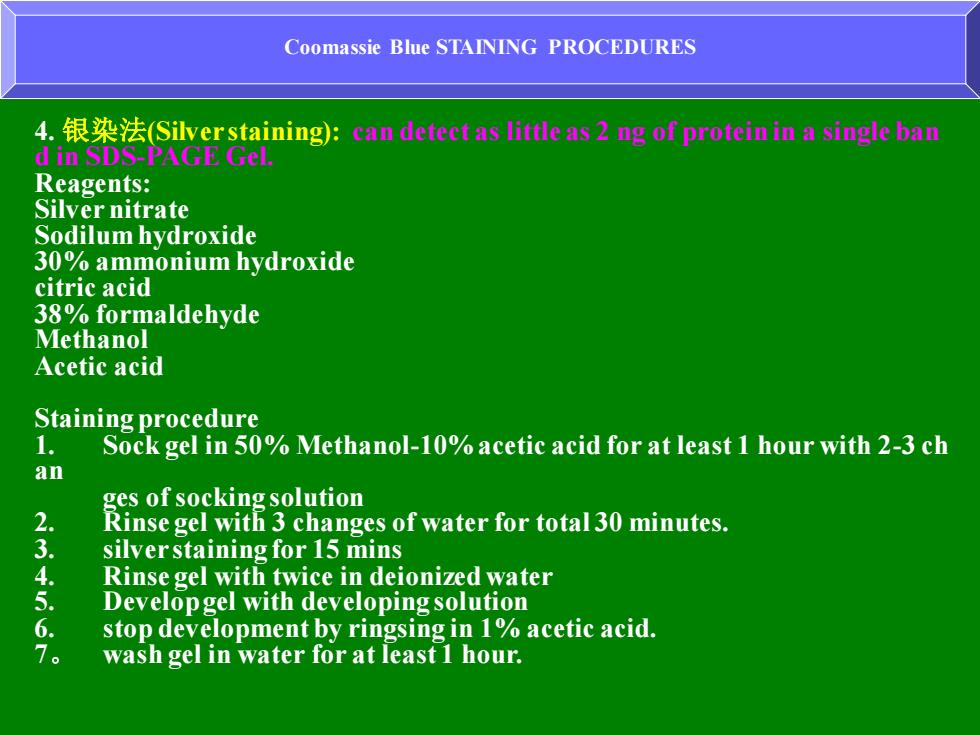
Coomassie Blue STAINING PROCEDURES 4.银染法(Silver staining):an dete1 as little as2 g of protein in a single ba di山SDSA Reagents: Silver nitrate Sodilum hydroxide 30%ammonium hydroxide citric acid 38%formaldehyde Methanol Acetic acid Staining procedure 1. Sock gel in 50%Methanol-10%acetic acid for at least 1 hour with 2-3 ch an ges of socking solution 2. Rinse gel with 3 changes of water for total 30 minutes. 3 silver staining for 15 mins Rinse gel with twice in deionized water 5 Developgel with developing solution stop development by ringsing in 1%acetic acid. 。 wash gel in water for at least 1 hour
Coomassie Blue STAINING PROCEDURES 4. 银染法(Silver staining): can detect as little as 2 ng of protein in a single ban d in SDS-PAGE Gel. Reagents: Silver nitrate Sodilum hydroxide 30% ammonium hydroxide citric acid 38% formaldehyde Methanol Acetic acid Staining procedure 1. Sock gel in 50% Methanol-10% acetic acid for at least 1 hour with 2-3 ch an ges of socking solution 2. Rinse gel with 3 changes of water for total 30 minutes. 3. silver staining for 15 mins 4. Rinse gel with twice in deionized water 5. Develop gel with developing solution 6. stop development by ringsing in 1% acetic acid. 7。 wash gel in water for at least 1 hour

2DE 2-DE:the technique to separate proteins in the first dimension according to t heir isoelectric point,by Isoelectric Focusing(IEF),and in the second dimensi on according to their molecular weight,by SDS-PAGE.2-DE combined with protein identification basing on microsequencing,amino acid composition an d Mass spectrometry,provides an invaluable tool for proteomic studies. Step 1-Sample Prep Step 2-First-Dimension(IEF)Separation Step 3-Second-Dimension(SDS-PAGE)Separation Step 4-Protein Detection by Staining/Destaining +3-0 -59 ◆310W
2DE 2-DE: the technique to separate proteins in the first dimension according to t heir isoelectric point, by Isoelectric Focusing(IEF), and in the second dimensi on according to their molecular weight, by SDS-PAGE. 2-DE combined with protein identification basing on microsequencing, amino acid composition an d Mass spectrometry, provides an invaluable tool for proteomic studies. Step 1 — Sample Prep Step 2 — First-Dimension (IEF) Separation Step 3 — Second-Dimension (SDS-PAGE) Separation Step 4 — Protein Detection by Staining /Destaining

凯氏定氮法 凯氏定氮法是先测定总氮量,然后乘以蛋白质换算系数,即可 得到粗蛋白质含量。可用于所有动、植物食品的蛋白质含量测 定。但因样品中常含有核酸、生物碱、含氮类脂、卟啉以及含 氮色素等非蛋白质的含氮化合物,故结果称为粗蛋白质含量。 凯氏定氮法由Kieldahl于1833年首先提出,经过长期改进,迄今已演变成 常量法、微量法、自动定氮仪法、半微量法及改良凯氏法等多种,至今仍 被作为标准检验方法。在此主要介绍常量凯氏定氮法的原理及步骤。 原理: 样品与浓硫酸和催化剂一同加热消化,使蛋白质分解,其中碳 和氢被氧化成二氧化碳和水逸出,而部分硫酸被还原成二氧化 硫,样品中的有机氨转化为氨与过量的硫酸结合成硫酸铵;然 后加碱蒸馏,使氨蒸出,用弱酸硼酸吸收后再以标准强酸如盐 酸或硫酸溶液滴定,根据标准酸消耗量可计算出蛋白质的含量
凯氏定氮法 凯氏定氮法是先测定总氮量, 然后乘以蛋白质换算系数,即可 得到粗蛋白质含量。可用于所有动、植物食品的蛋白质含量测 定。但因样品中常含有核酸、生物碱、含氮类脂、卟啉以及含 氮色素等非蛋白质的含氮化合物,故结果称为粗蛋白质含量。 凯氏定氮法由Kieldahl于1833年首先提出,经过长期改进,迄今已演变成 常量法、微量法、自动定氮仪法、半微量法及改良凯氏法等多种,至今仍 被作为标准检验方法。在此主要介绍常量凯氏定氮法的原理及步骤。 原理: 样品与浓硫酸和催化剂一同加热消化,使蛋白质分解,其中碳 和氢被氧化成二氧化碳和水逸出,而部分硫酸被还原成二氧化 硫,样品中的有机氮转化为氨与过量的硫酸结合成硫酸铵; 然 后加碱蒸馏,使氨蒸出,用弱酸硼酸吸收后再以标准强酸如盐 酸或硫酸溶液滴定,根据标准酸消耗量可计算出蛋白质的含量