
膳食成分对钙吸收利用的影响 提高吸收利用 降低吸收利用 无作用 乳糖 植酸盐 磷 某些氨基酸 膳食纤维 蛋白质 Vit D 草酸盐 Vit C 脂肪(脂肪泻时) 柠檬酸 乙醇 果胶
膳食成分对钙吸收利用的影响 提高吸收利用 降低吸收利用 无作用 乳糖 植酸盐 磷 某些氨基酸 膳食纤维 蛋白质 Vit D 草酸盐 Vit C 脂肪(脂肪泻时) 柠檬酸 乙醇 果胶

3) Excretion Fecal Ca : 194 ± 73 mg/d in the American men from unabsorbed Ca and endogenous (内源性) Ca Urine Ca: diets containing 600-800 mg/d ranges between 80-250mg in urine. Sweat Ca: 20-30mg/d; 1g/d at high temp. Milk Ca: 150-300mg/d Renal tubular reabsorption of Ca is increased by parathyroid hormone(甲状旁腺素), a fall in plasma Ca, metabolic alkolosis(代谢性碱中 毒), and diuretics(利尿剂). Increased by saline diureses(含盐多尿症), carbohydrate ingestion, phosphate deprivation(丧失), metabolic acidosis (代谢性酸中毒), cortisal, thyroid and growth hormones, diets rich in protein and magnesium(镁). fecal
3) Excretion Fecal Ca : 194 ± 73 mg/d in the American men from unabsorbed Ca and endogenous (内源性) Ca Urine Ca: diets containing 600-800 mg/d ranges between 80-250mg in urine. Sweat Ca: 20-30mg/d; 1g/d at high temp. Milk Ca: 150-300mg/d Renal tubular reabsorption of Ca is increased by parathyroid hormone(甲状旁腺素), a fall in plasma Ca, metabolic alkolosis(代谢性碱中 毒), and diuretics(利尿剂). Increased by saline diureses(含盐多尿症), carbohydrate ingestion, phosphate deprivation(丧失), metabolic acidosis (代谢性酸中毒), cortisal, thyroid and growth hormones, diets rich in protein and magnesium(镁). fecal
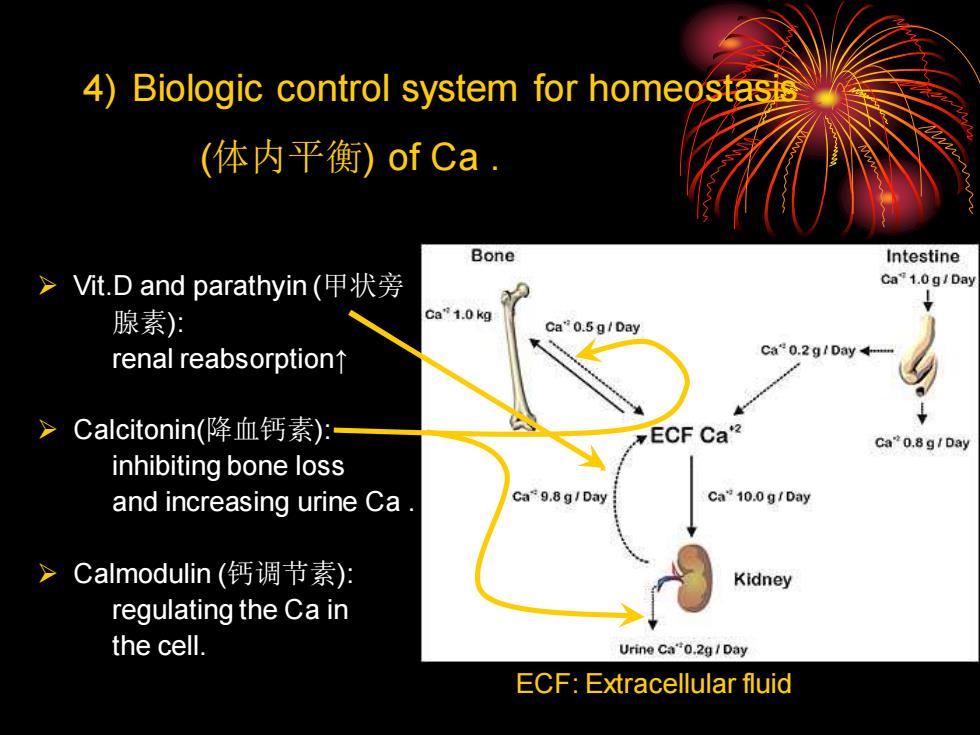
➢ Vit.D and parathyin (甲状旁 腺素): renal reabsorption↑ ➢ Calcitonin(降血钙素): inhibiting bone loss and increasing urine Ca . ➢ Calmodulin (钙调节素): regulating the Ca in the cell. 4) Biologic control system for homeostasis (体内平衡) of Ca . ECF: Extracellular fluid
➢ Vit.D and parathyin (甲状旁 腺素): renal reabsorption↑ ➢ Calcitonin(降血钙素): inhibiting bone loss and increasing urine Ca . ➢ Calmodulin (钙调节素): regulating the Ca in the cell. 4) Biologic control system for homeostasis (体内平衡) of Ca . ECF: Extracellular fluid
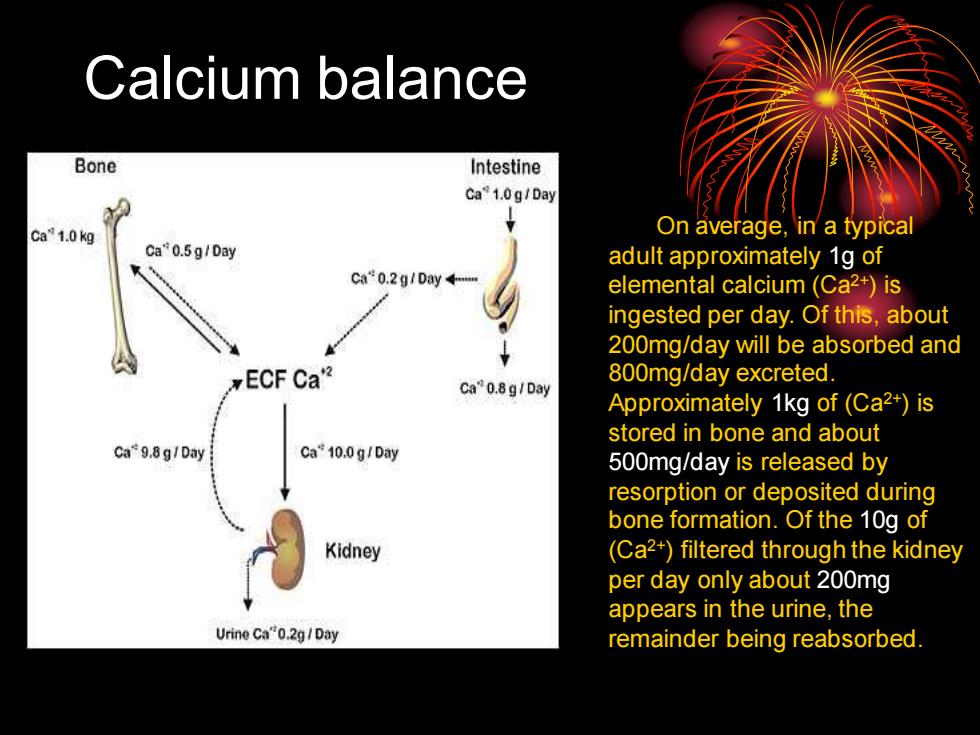
Calcium balance On average, in a typical adult approximately 1g of elemental calcium (Ca2+) is ingested per day. Of this, about 200mg/day will be absorbed and 800mg/day excreted. Approximately 1kg of (Ca2+) is stored in bone and about 500mg/day is released by resorption or deposited during bone formation. Of the 10g of (Ca2+) filtered through the kidney per day only about 200mg appears in the urine, the remainder being reabsorbed
Calcium balance On average, in a typical adult approximately 1g of elemental calcium (Ca2+) is ingested per day. Of this, about 200mg/day will be absorbed and 800mg/day excreted. Approximately 1kg of (Ca2+) is stored in bone and about 500mg/day is released by resorption or deposited during bone formation. Of the 10g of (Ca2+) filtered through the kidney per day only about 200mg appears in the urine, the remainder being reabsorbed

4. DRIs of Ca (1) Estimation of DRIs(膳食参考摄入量) ➢ Infants: mean intake of breast milk(母乳) ➢ Others: Ca balance test(平衡试验) ➢ Direct measure (2) DRIs (mg/d ) y: 0~ 0.5~ 1~ 4~ 11~ 18~ 50~ AI: 300 400 600 800 1000 800 1000 Y: pregnant women wet nurse(乳母) AI: 1000(中期) 1200(晚期) 1200 UL(tolerable upper intake level,): 2000mg NOAEL: 1500mg
4. DRIs of Ca (1) Estimation of DRIs(膳食参考摄入量) ➢ Infants: mean intake of breast milk(母乳) ➢ Others: Ca balance test(平衡试验) ➢ Direct measure (2) DRIs (mg/d ) y: 0~ 0.5~ 1~ 4~ 11~ 18~ 50~ AI: 300 400 600 800 1000 800 1000 Y: pregnant women wet nurse(乳母) AI: 1000(中期) 1200(晚期) 1200 UL(tolerable upper intake level,): 2000mg NOAEL: 1500mg