
从溶液中析出配合物时,配离子常与带有相反电 荷的其它离子结合成盐,这类盐称为配盐(complex salt)。配盐的组成可以划分为内层(inner sphere)和外 层(outer sphere)。配离子属于内层,配离子以外的其 他离子属于外层。外层离子所带电荷总数等于配离子 的电荷数。 out sphere inner sphere K3[Fe(CN)6] ↑ 形成体 配配配 位体位 原子
从溶液中析出配合物时,配离子常与带有相反电 荷的其它离子结合成盐,这类盐称为配盐(complex salt)。配盐的组成可以划分为内层(inner sphere)和外 层(outer sphere)。配离子属于内层,配离子以外的其 他离子属于外层。外层离子所带电荷总数等于配离子 的电荷数。 形 成 体 配 位 原 子 配 体 配 位 数 K3[ Fe ( C N ) 6 ] out sphere inner sphere
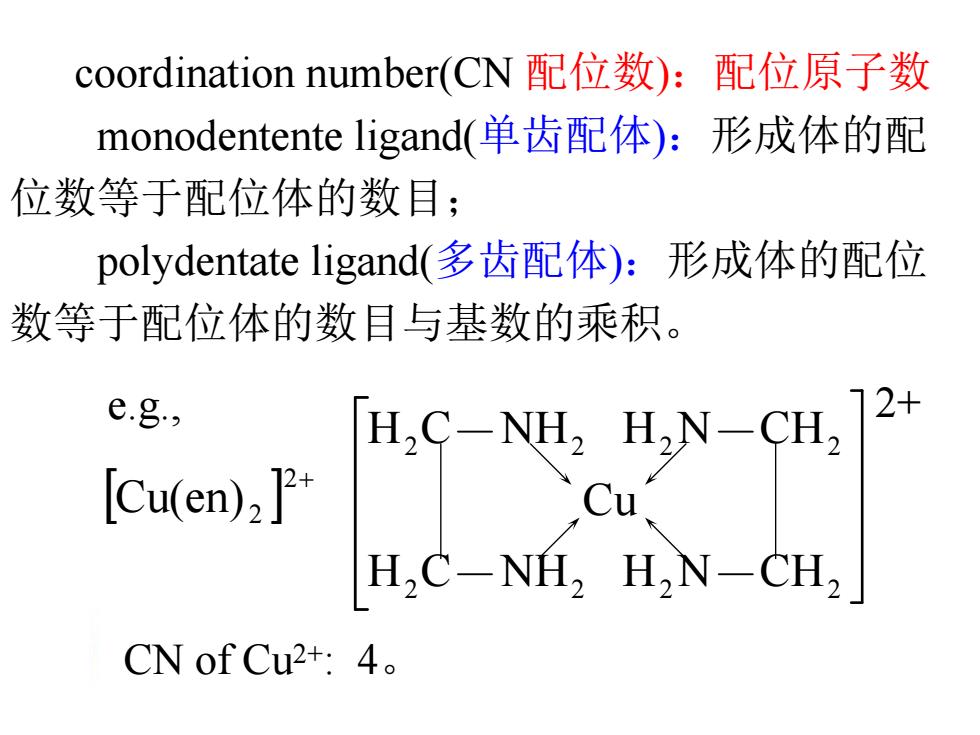
coordination number(CN配位数):配位原子数 monodentente ligand(单齿配体):形成体的配 位数等于配位体的数目; polydentate ligand(多齿配体):形成体的配位 数等于配位体的数目与基数的乘积。 e.g., [Cu(en)2] H.C-NEL.HN CU. Cu H,C-NH,H,N-CH, CN of Cu2+:4
coordination number(CN 配位数):配位原子数 monodentente ligand(单齿配体):形成体的配 位数等于配位体的数目; polydentate ligand(多齿配体):形成体的配位 数等于配位体的数目与基数的乘积。 Cu(en) 2 2 CN of Cu2+: 4。 e.g., H C NH H N CH Cu H C NH H N CH 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2+

[Ca(EDTA)2 or CaY2- CN of Ca2+:6, CH, the coordinating atoms are 4 O,2 N atoms respectively
[Ca(EDTA)]2- or CaY2- CN of Ca2+: 6, the coordinating atoms are 4 O,2 N atoms respectively

11.1.2.Names of complexes of various types l.The basic procedure for naming a complex(英语命名 法): 1When naming a complex ion,the ligands are named before the metal ion. 2Write the names of the ligands in alphabetical order. i)multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences:di-,tri-, tetra-,penta-,or hexa.Polydentate ligands (e.g., ethylenediamine,oxalate)receive bis-,tris-,tetrakis-,etc. ii)anions end in o.This replaces the final 'e'when the anion ends with '-ate',e.g.sulfate becomes sulfato.It replaces 'ide':cyanide becomes cyano
11.1.2. Names of complexes of various types 1. The basic procedure for naming a complex (英语命名 法): ①When naming a complex ion, the ligands are named before the metal ion. ②Write the names of the ligands in alphabetical order. ⅰ) multiple occurring monodentate ligands receive a prefix according to the number of occurrences: di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, or hexa. Polydentate ligands (e.g., ethylenediamine, oxalate) receive bis-, tris-, tetrakis-, etc. ⅱ) anions end in o. This replaces the final 'e' when the anion ends with '-ate', e.g. sulfate becomes sulfato. It replaces 'ide': cyanide becomes cyano

iii)neutral ligands are given their usual name,with some exceptions:NH3 becomes ammine;H2O becomes aqua or aquo;CO becomes carbonyl;NO becomes nitrosyl. 3 write the name of the central atom/ion.If the complex is an anion,the central atom's name will end in -ate,and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). 4If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible,or zero),write it as a Roman numeral (or 0)in parentheses. 5Name cation then anion as separate words(if applicable,as in last example)
ⅲ) neutral ligands are given their usual name, with some exceptions: NH3 becomes ammine; H2O becomes aqua or aquo; CO becomes carbonyl; NO becomes nitrosyl. ③ write the name of the central atom/ion. If the complex is an anion, the central atom's name will end in -ate, and its Latin name will be used if available (except for mercury). ④If the central atom's oxidation state needs to be specified (when it is one of several possible, or zero), write it as a Roman numeral (or 0) in parentheses. ⑤Name cation then anion as separate words (if applicable, as in last example)