
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure 5.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen x 5.2 The atomic structure of many-electron atoms x 5.3 Periodic law of elements
5.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen 5.2 The atomic structure of many-electron atoms 5.3 Periodic law of elements Chapter 5 Atomic Structure

5.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen -5.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr's theory 5.1.2 The dual nature of the electron 5.1.3 Schrodinger equation and quantum numbers 5.1.4 The ground state of H atoms 5.1.5 The excited state of HAtoms 回
5.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr’s theory 5.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen 5.1.5 The excited state of H Atoms 5.1.4 The ground state of H atoms 5.1.3 Schrödinger equation and quantum numbers 5.1.2 The dual nature of the electron
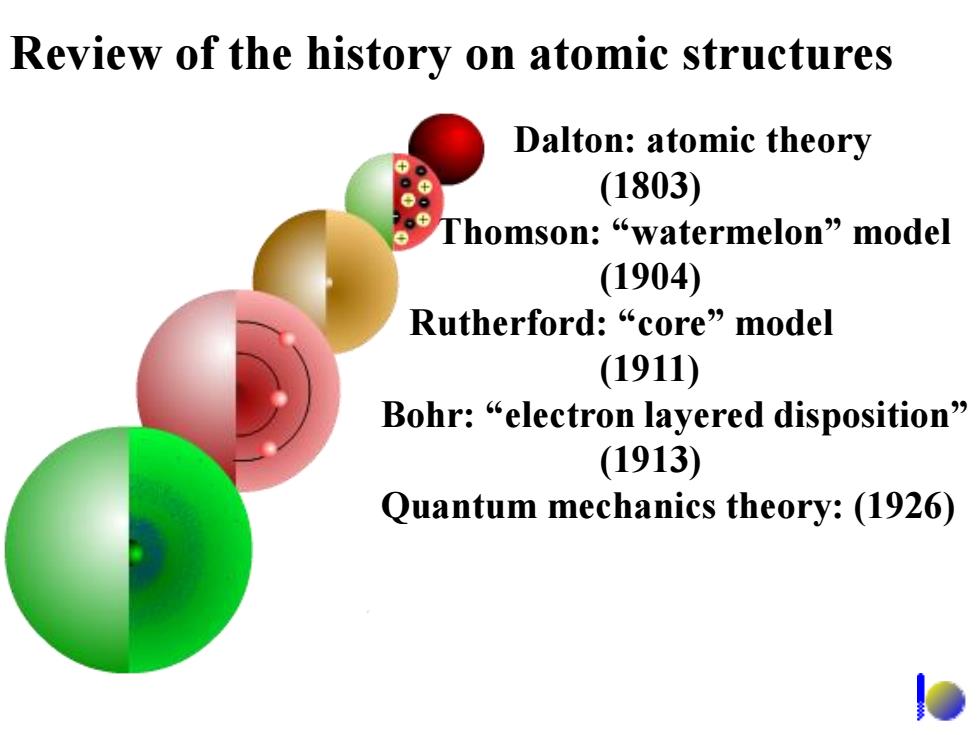
Review of the history on atomic structures Dalton:atomic theory (1803) Thomson:“watermelon”nodel (1904) Rutherford:“core”model (1911) Bohr:“electron layered disposition” (1913) Quantum mechanics theory:(1926)
Review of the history on atomic structures Dalton: atomic theory (1803) Thomson: “watermelon” model (1904) Rutherford: “core” model (1911) Bohr: “electron layered disposition” (1913) Quantum mechanics theory: (1926)
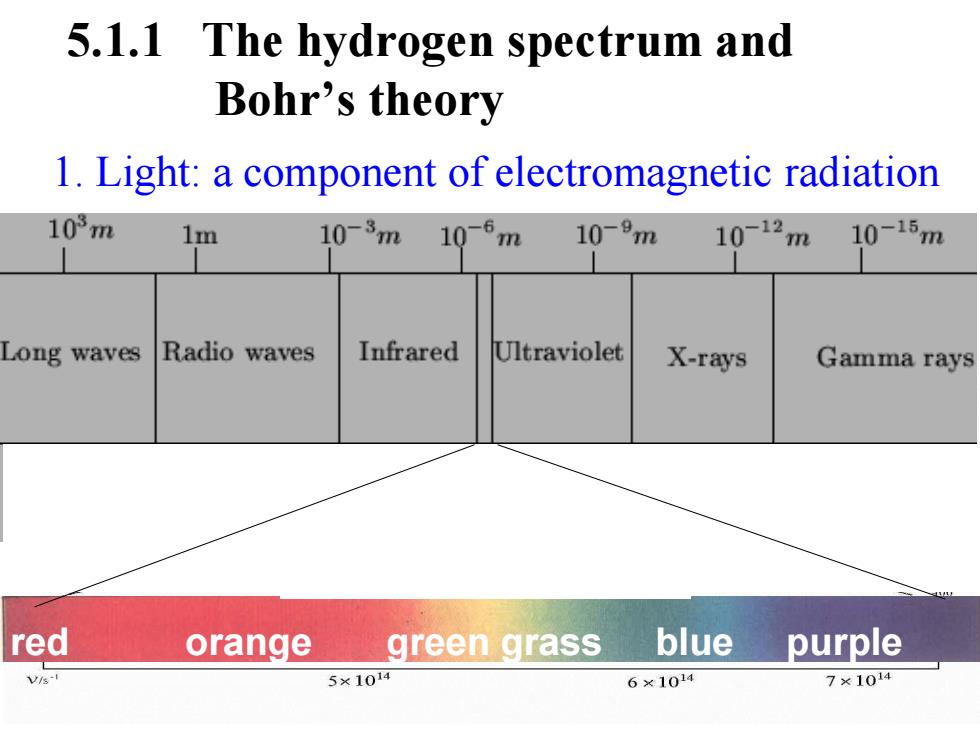
5.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr's theory 1.Light:a component of electromagnetic radiation 103m 1m 10-3m 10-6m 10-9m 10-12m 10-15m Long waves Radio waves Infrared Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma rays red orange green grass blue purple Vi-I 5×1014 6×1014 7×1014
1. Light: a component of electromagnetic radiation 5.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr’s theory red orange green grass blue purple
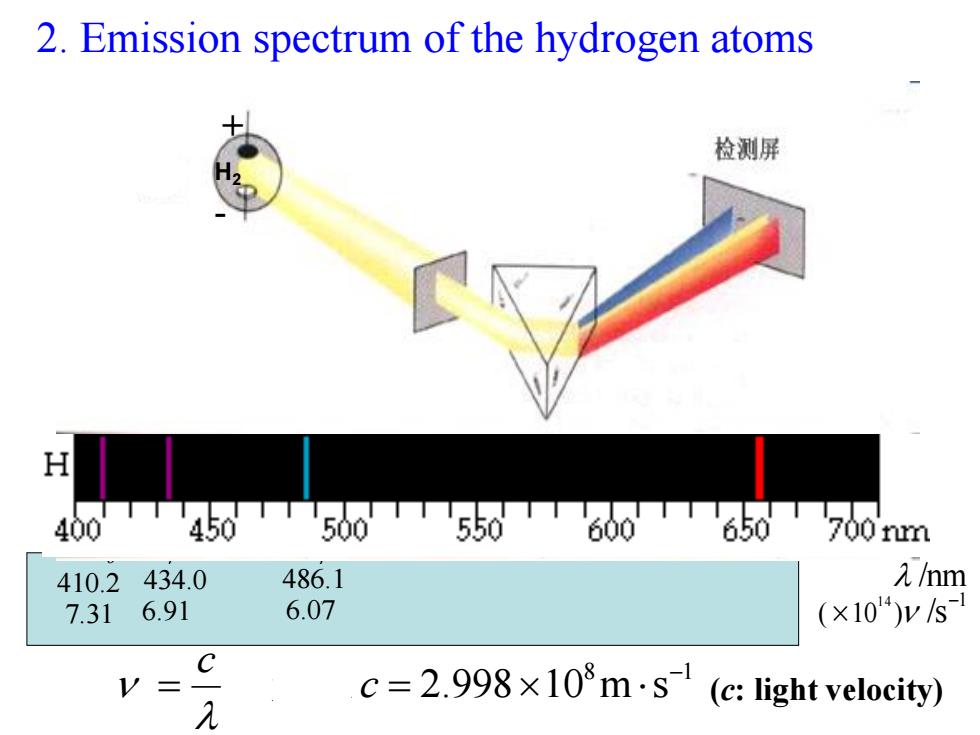
2.Emission spectrum of the hydrogen atoms 检测屏 H 400T450T500550T600T650T700m 410.2434.0 486.1 元/hm 7.31 6.91 6.07 (×10)ys C V= 元 c=2.998×108m·s(c:light velocity)
2. Emission spectrum of the hydrogen atoms 8 1 2.998 10 m s c c 光速 Hα 656.3 4.57 Hβ 486.1 6.07 Hγ 434.0 6.91 Hδ 410.2 7.31 /nm1 ( 10 ) /s 1 4 H2 + - (c: light velocity)