
Chapter 8 Atomic Structure 8.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen x 8.2 The atomic structure of many-electron atoms x 8.3 Periodic law of elements
8.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen 8.2 The atomic structure of many-electron atoms 8.3 Periodic law of elements Chapter 8 Atomic Structure

8.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen 8.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr's theory 8.1.2 The dual nature of the electron 8.1.3 Schrodinger equation and quantum numbers 8.1.4 The ground state of H atoms 8.1.5 The excited state of HAtoms 回
8.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr’s theory 8.1 The atomic structure of hydrogen 8.1.5 The excited state of H Atoms 8.1.4 The ground state of H atoms 8.1.3 Schrödinger equation and quantum numbers 8.1.2 The dual nature of the electron
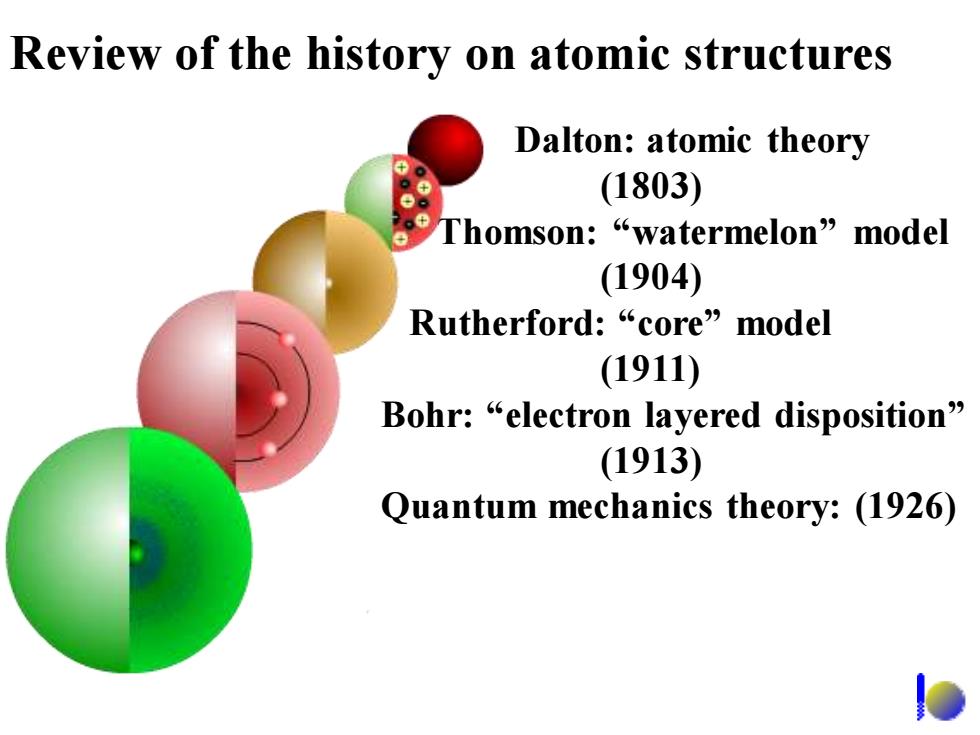
Review of the history on atomic structures Dalton:atomic theory (1803) Thomson:“watermelon”nodel (1904) Rutherford:“core”model (1911) Bohr:“electron layered disposition'” (1913) Quantum mechanics theory:(1926)
Review of the history on atomic structures Dalton: atomic theory (1803) Thomson: “watermelon” model (1904) Rutherford: “core” model (1911) Bohr: “electron layered disposition” (1913) Quantum mechanics theory: (1926)
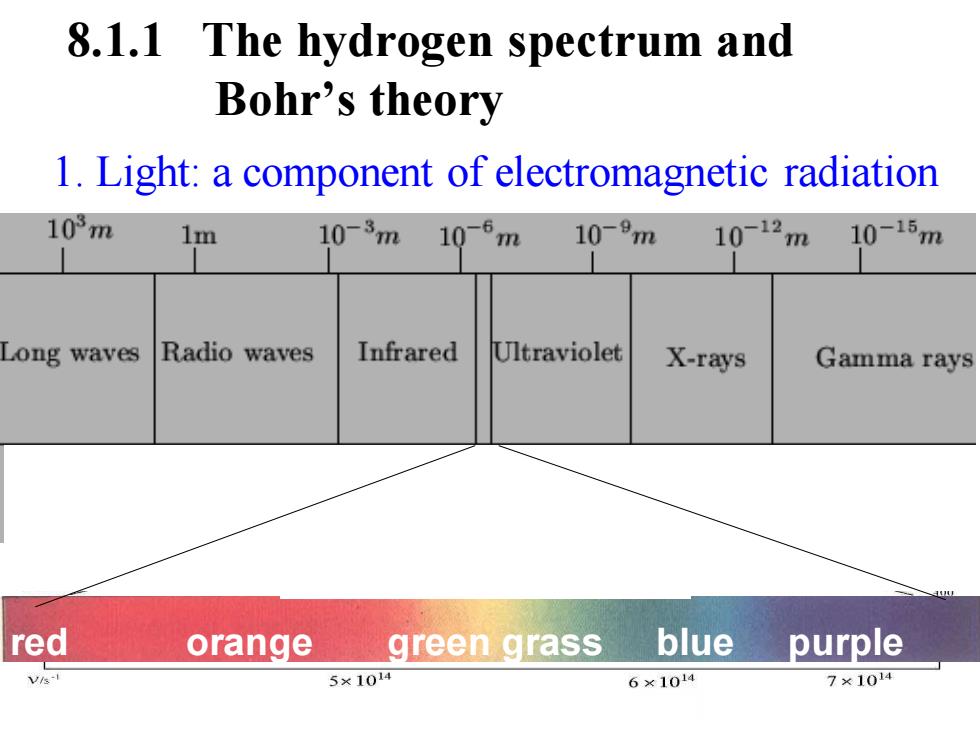
8.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr's theory 1.Light:a component of electromagnetic radiation 103m 1m 10-3m 10-6m 10-9m 10-12m 10-15m Long waves Radio waves Infrared Ultraviolet X-rays Gamma rays red orange green grass blue purple v⅓ 5×1014 6×1014 7×1014
1. Light: a component of electromagnetic radiation 8.1.1 The hydrogen spectrum and Bohr’s theory red orange green grass blue purple
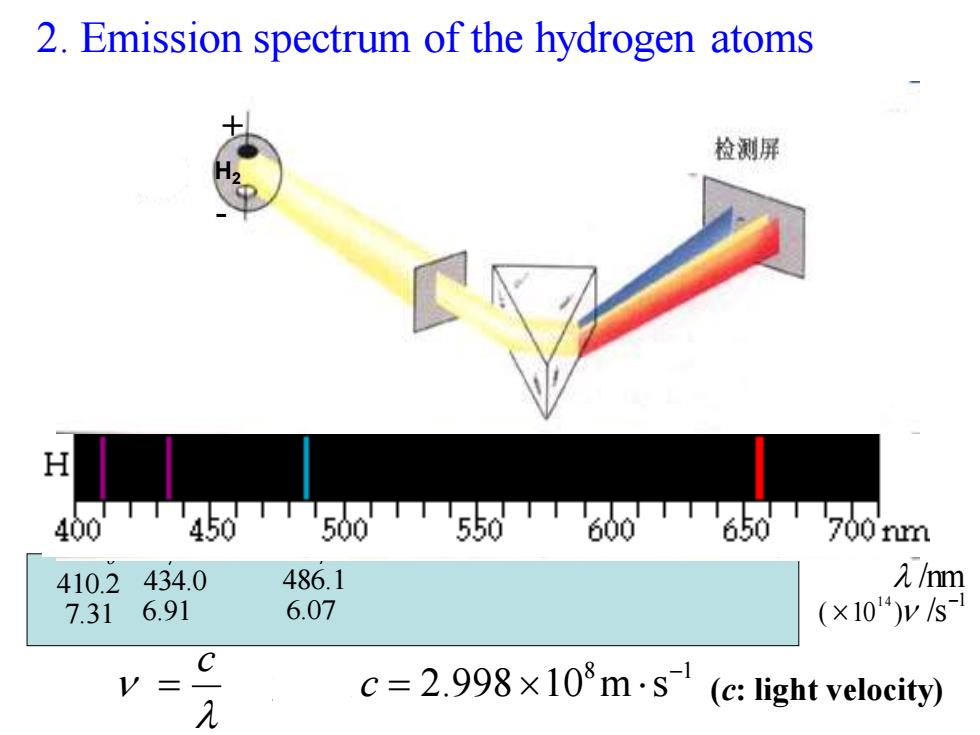
2.Emission spectrum of the hydrogen atoms 检测屏 H 400TTT450T500550T600T650700nm 410.2434.0 486.1 1/m 7.31 6.91 6.07 (×104)ys- C V= 元 c=2.998×103m·s(c:light velocity))
2. Emission spectrum of the hydrogen atoms 8 1 2.998 10 m s − = c = c 光速 Hα 656.3 4.57 Hβ 486.1 6.07 Hγ 434.0 6.91 Hδ 410.2 7.31 /nm1 ( 10 ) /s 1 4 − H2 + - (c: light velocity)