
Chapter 9 Molecular Structure ק9.1 Lewis structure Theory ק9.2 Valence Bond Theory ק9.3 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)Theory x§9.4 Molecular Orbital Theory ק9.5 Bond Parameters
Chapter 9 Molecular Structure §9.2 Valence Bond Theory §9.5 Bond Parameters §9.4 Molecular Orbital Theory §9.3 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory §9.1 Lewis structure Theory
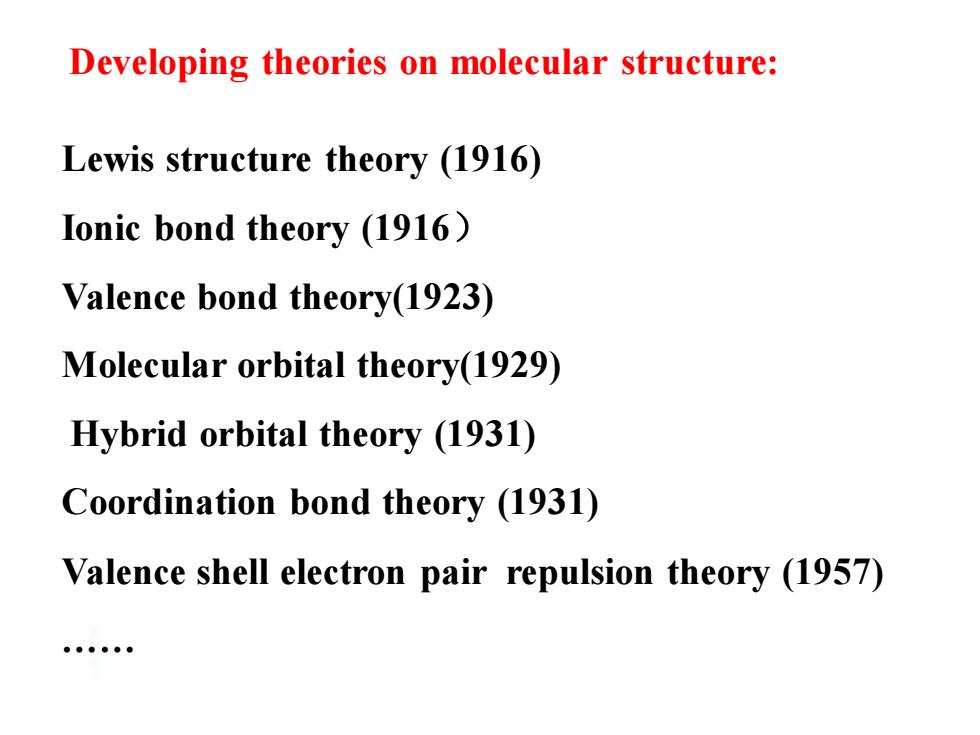
Developing theories on molecular structure: Lewis structure theory (1916) Ionic bond theory (1916) Valence bond theory(1923) Molecular orbital theory(1929) Hybrid orbital theory (1931) Coordination bond theory (1931) Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1957)
Developing theories on molecular structure: Lewis structure theory (1916) Ionic bond theory (1916) Valence bond theory(1923) Molecular orbital theory(1929) Hybrid orbital theory (1931) Coordination bond theory (1931) Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1957) ……
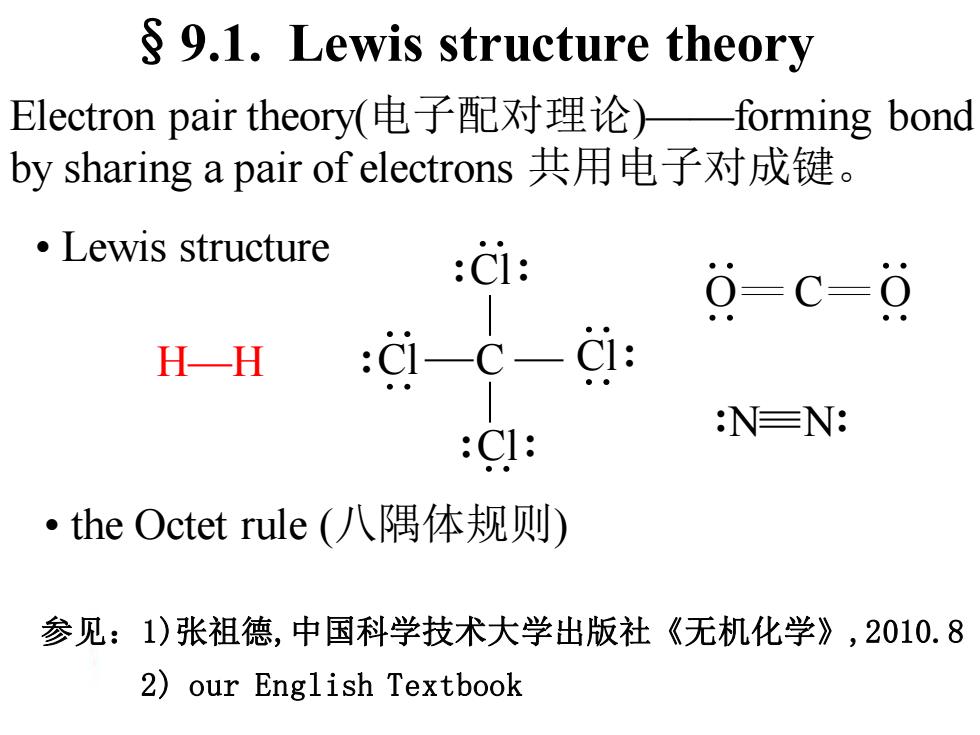
9.1.Lewis structure theory Electron pair theory(电子配对理论)一forming bond by sharing a pair of electrons共用电子对成键。 ·Lewis structure :C1: 0=c-9 H-H :i一C-i: NEN: :CI: ·he Octet rule(八隅体规则) 参见:1)张祖德,中国科学技术大学出版社《无机化学》,2010.8 2)our English Textbook
§9.1. Lewis structure theory Electron pair theory(电子配对理论)——forming bond by sharing a pair of electrons 共用电子对成键。 • Lewis structure • the Octet rule (八隅体规则) H—H :Cl Cl: :Cl: :Cl: C :N N: O C O 参见:1)张祖德,中国科学技术大学出版社《无机化学》,2010.8 2) our English Textbook

F Basic steps to write Lewis structure N F 1.Write the skeletal structure of the compound,using chemical symbols and placing bonded atoms next to one another.In general,the least electronegative atom occupies the central position.H and F usually occupy the terminal (end)positions in the Lewis structure 2.Count the total number of valence electrons present. For polyatomic anions,add the number of negative charges to that total;For polycations,substract the number of positive charges from this total
Basic steps to write Lewis structure 1. Write the skeletal structure of the compound, using chemical symbols and placing bonded atoms next to one another. In general, the least electronegative atom occupies the central position. H and F usually occupy the terminal (end) positions in the Lewis structure 2. Count the total number of valence electrons present. For polyatomic anions, add the number of negative charges to that total; For polycations, substract the number of positive charges from this total. F N F F
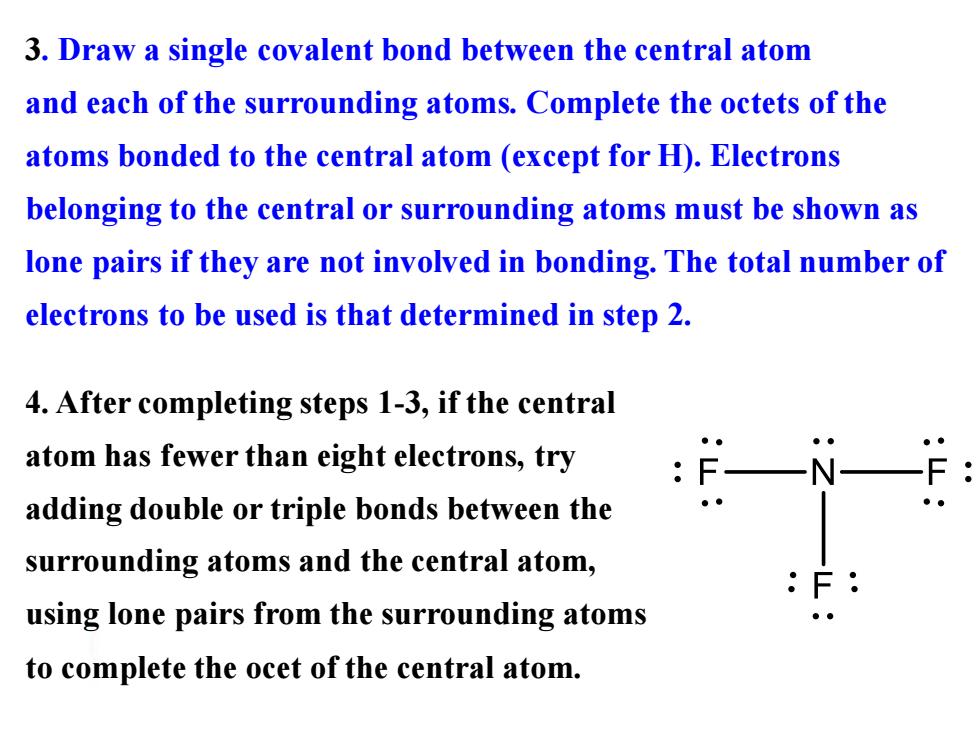
3.Draw a single covalent bond between the central atom and each of the surrounding atoms.Complete the octets of the atoms bonded to the central atom (except for H).Electrons belonging to the central or surrounding atoms must be shown as lone pairs if they are not involved in bonding.The total number of electrons to be used is that determined in step 2. 4.After completing steps 1-3,if the central atom has fewer than eight electrons,try adding double or triple bonds between the surrounding atoms and the central atom, using lone pairs from the surrounding atoms to complete the ocet of the central atom
3. Draw a single covalent bond between the central atom and each of the surrounding atoms. Complete the octets of the atoms bonded to the central atom (except for H). Electrons belonging to the central or surrounding atoms must be shown as lone pairs if they are not involved in bonding. The total number of electrons to be used is that determined in step 2. 4. After completing steps 1-3, if the central atom has fewer than eight electrons, try adding double or triple bonds between the surrounding atoms and the central atom, using lone pairs from the surrounding atoms to complete the ocet of the central atom