
Chapter 4Chemical equilibria 4.1 The state of a chemical reaction at equilibrium X 4.2 Direction of a chemical reaction 4.3 The relationship between standard equilibrium constant Ke and A,G X 4.4 The shift of a chemical equilibrium
Chapter 4 Chemical equilibria §4.3 The relationship between standard equilibrium constant K and rGm §4.2 Direction of a chemical reaction §4.1 The state of a chemical reaction at equilibrium §4.4 The shift of a chemical equilibrium
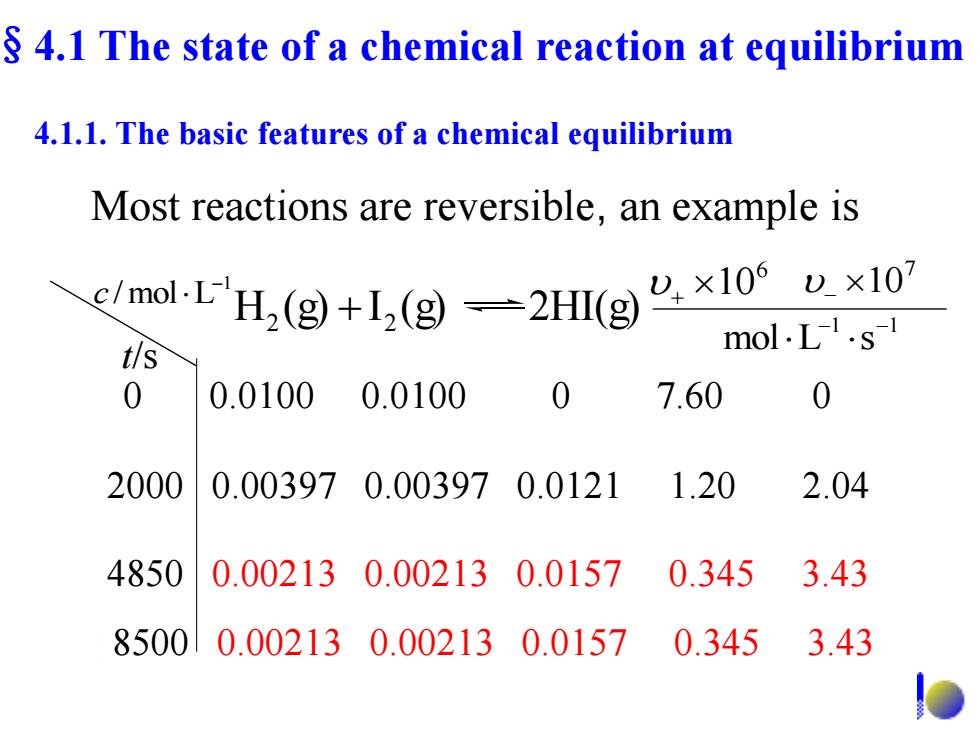
4.1 The state of a chemical reaction at equilibrium 4.1.1.The basic features of a chemical equilibrium Most reactions are reversible,an example is molH(x1x1 mol.L.s- t/s 0 0.01000.0100 0 7.60 0 2000 0.003970.003970.0121 1.20 2.04 4850 0.002130.002130.0157 0.3453.43 85000.002130.002130.01570.345 3.43 多
0 0.0100 0.0100 0 7.60 0 2000 0.00397 0.00397 0.0121 1.20 2.04 4850 0.00213 0.00213 0.0157 0.345 3.43 Most reactions are reversible, an example is t/s 1 /mol L c 6 10 7 10 1 1 mol L s H (g) I (g) 2HI(g) 2 2 8500 0.00213 0.00213 0.0157 0.345 3.43 §4.1 The state of a chemical reaction at equilibrium 4.1.1. The basic features of a chemical equilibrium

Initially,concentrations of H,and I,are large,only the forward reaction occurs;As time passes,the concentrations of H,and I, decrease and in result the forward reaction slows down.The concentrations of HI increase and in result the reverse reaction speeds up. The reaction mixture is at equilibrium until the forward and reverse reactions go at the same rate
Initially, concentrations of H2 and I2 are large, only the forward reaction occurs; As time passes, the concentrations of H2 and I2 decrease and in result the forward reaction slows down. The concentrations of HI increase and in result the reverse reaction speeds up. The reaction mixture is at equilibrium until the forward and reverse reactions go at the same rate
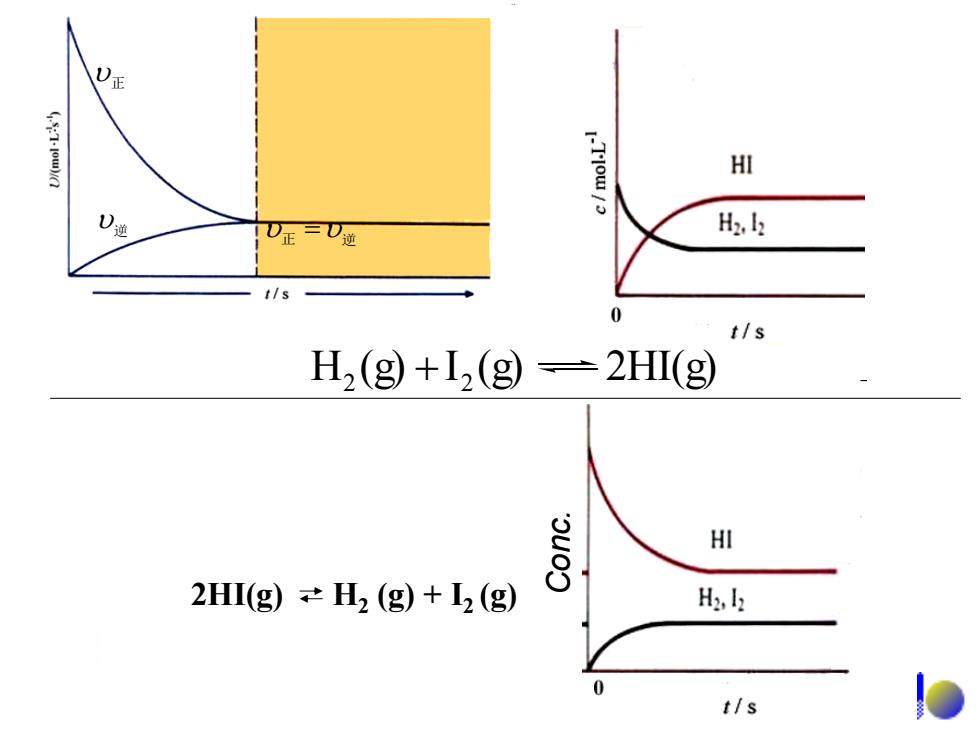
(57-1ow)ia I-Tlow/ HI )通 H2. t/s t/s H2(g)+I,(g)=2HI(g) HI 2HI(g))≠H2(g)+2(g) H2,k t/s
正 逆 正 逆 H (g) I (g) 2HI(g) 2 2 2HI(g) H2 (g) + I2 (g) Conc
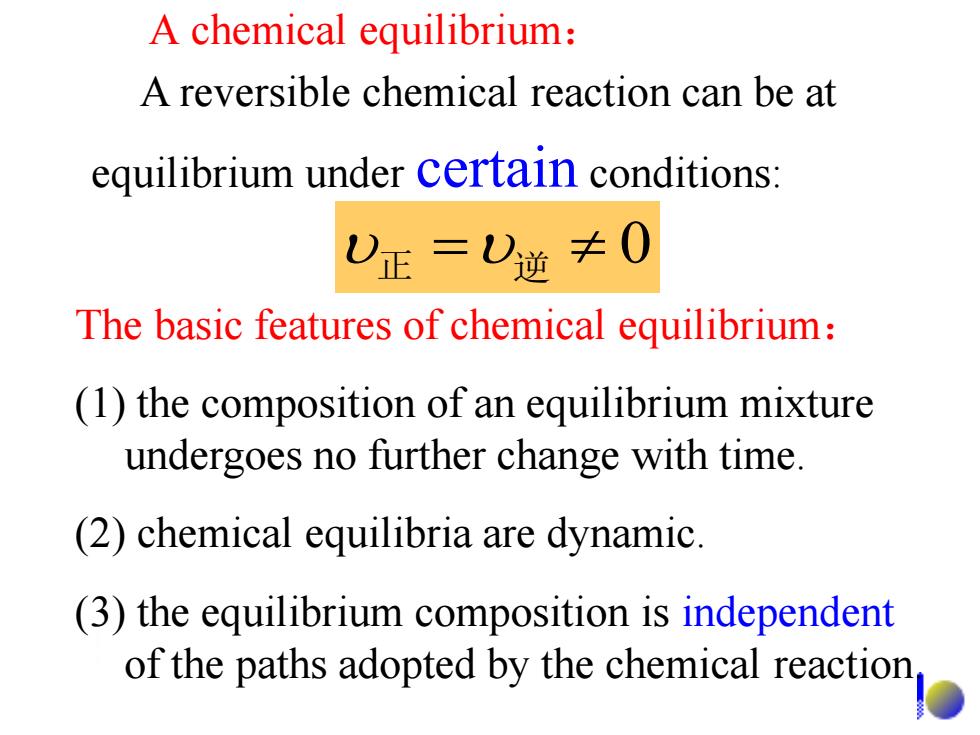
A chemical equilibrium: A reversible chemical reaction can be at equilibrium under certain conditions: 0正=)逆≠0 The basic features of chemical equilibrium: (1)the composition of an equilibrium mixture undergoes no further change with time. (2)chemical equilibria are dynamic. (3)the equilibrium composition is independent of the paths adopted by the chemical reaction
A chemical equilibrium: 正 逆 0 A reversible chemical reaction can be at equilibrium under certain conditions: The basic features of chemical equilibrium: (1) the composition of an equilibrium mixture undergoes no further change with time. (2) chemical equilibria are dynamic. (3) the equilibrium composition is independent of the paths adopted by the chemical reaction