6.2.1 The essence and characteristics of covalent bond Chemical bonding: A chemical bonding is an interaction between atoms or molecules and allows the formation of polyatomic chemical compounds. The theory of chemical bonding consists of: 1)The ionic bond theory, 2)The metallic bond theory 3)The covalent bond theory
1)The ionic bond theory, 6.2.1 The essence and characteristics of covalent bond Chemical bonding: A chemical bonding is an interaction between atoms or molecules and allows the formation of polyatomic chemical compounds. The theory of chemical bonding consists of : 2) The metallic bond theory 3) The covalent bond theory

The covalent bond theory 1.The H-H covalent bond formation from isolated H atoms The two hydrogen atoms of different electronic spin come to each other,overlap resulting in 什H2排斥态 a large overlapped area of 0 electronic probability density. MH基态 The system's energy reduces and the hydrogen molecule is formed. 74 pm R The distance between two nuclei(核间距):R,=74pm Essence of covalent bond(共价键的本质)一The atomic orbits overlap to cause increasing electronic probability density which attract the two atomic nuclei
1.The H-H covalent bond formation from isolated H atoms The two hydrogen atoms of different electronic spin come to each other, overlap resulting in a large overlapped area of electronic probability density. The system’s energy reduces and the hydrogen molecule is formed. The distance between two nuclei (核间距): R0 = 74 pm Essence of covalent bond(共价键的本质)——The atomic orbits overlap to cause increasing electronic probability density which attract the two atomic nuclei. The covalent bond theory
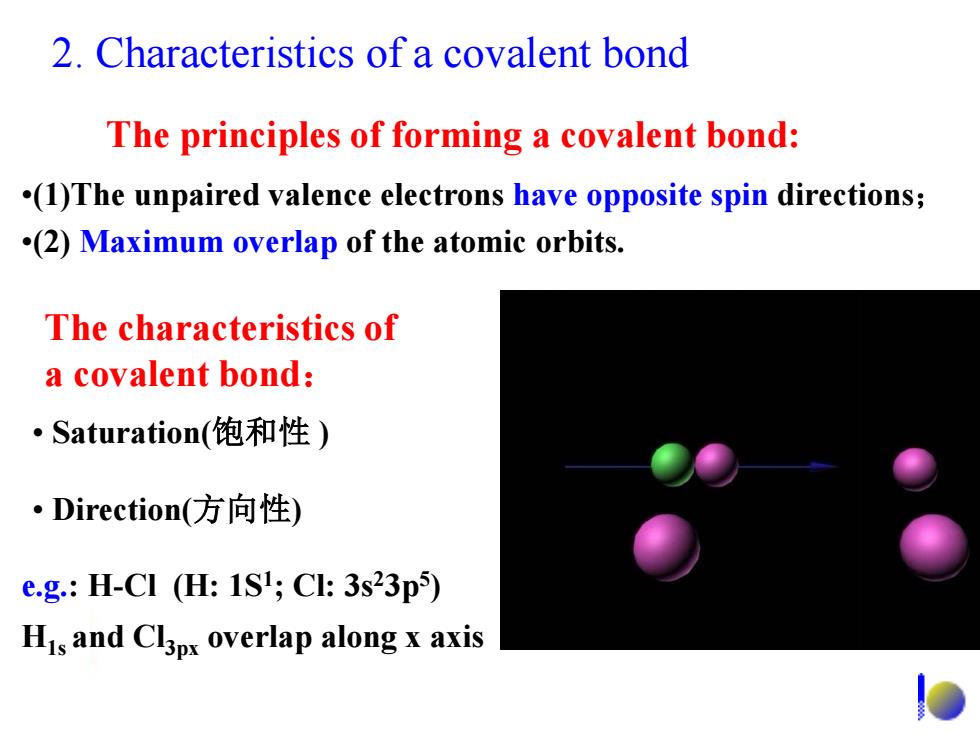
2.Characteristics of a covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: (1)The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; (2)Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of a covalent bond: ·Saturation(饱和性) ·Direction(方向性) e.g.:H-C1(H:1S;Cl:3s23p5) His and Cl3px overlap along x axis
2. Characteristics of a covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: •(1)The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; •(2) Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of a covalent bond: • Direction(方向性) • Saturation(饱和性 ) e.g.: H-Cl (H: 1S1 ; Cl: 3s23p5 ) H1s and Cl3px overlap along x axis
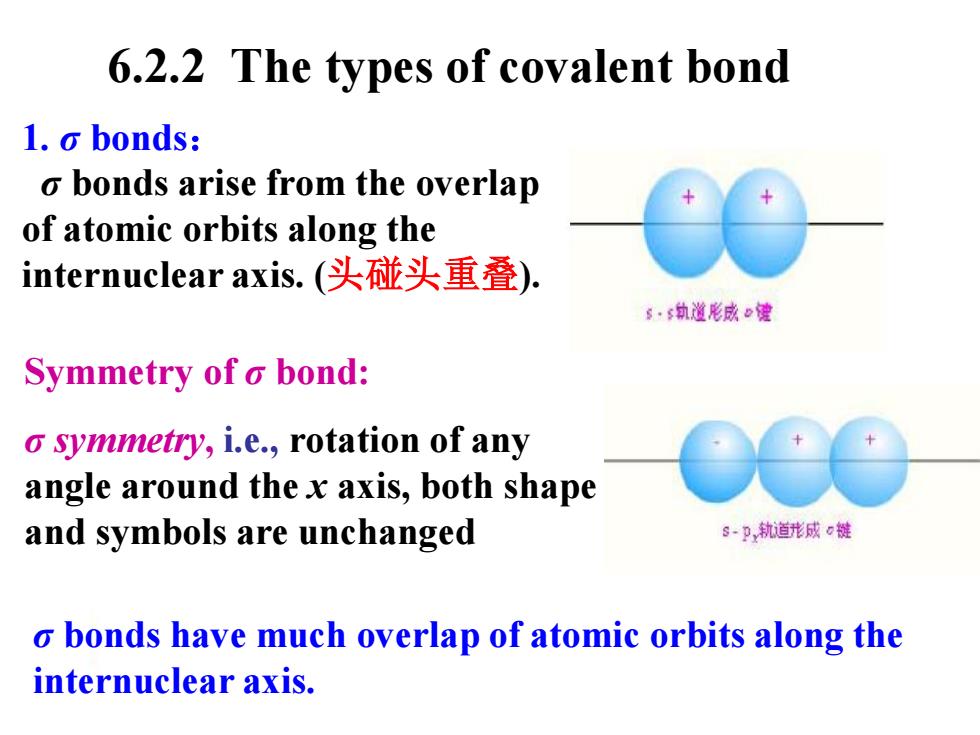
6.2.2 The types of covalent bond 1.o bonds: o bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis.(头碰头重叠). g·轨道形成健 Symmetry of o bond: o symmetry,i.e.,rotation of any angle around the x axis,both shape and symbols are unchanged s-P轨道形威c键 o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis
1. σ bonds: σ bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. (头碰头重叠). Symmetry of σ bond: σ symmetry, i.e., rotation of any angle around the x axis, both shape and symbols are unchanged σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. 6.2.2 The types of covalent bond

S-S s-P Px-Px o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis
σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. s s px s px px