
2.元bonds: x bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits. (肩并肩重叠)。p.-p或p,-P, Symmetry ofπbond(r键的对称性):π对称,i.e.,绕x轴旋转180°, 形状不变,符号变。或者说对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 T π键
2. π bonds: π bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits. (肩并肩重叠)。 pz pz 或py py Symmetry of π bond (π 键的对称性):π对称 , i.e.,绕 x 轴旋转180 , 形状不变,符号变。或者说对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 σ π π
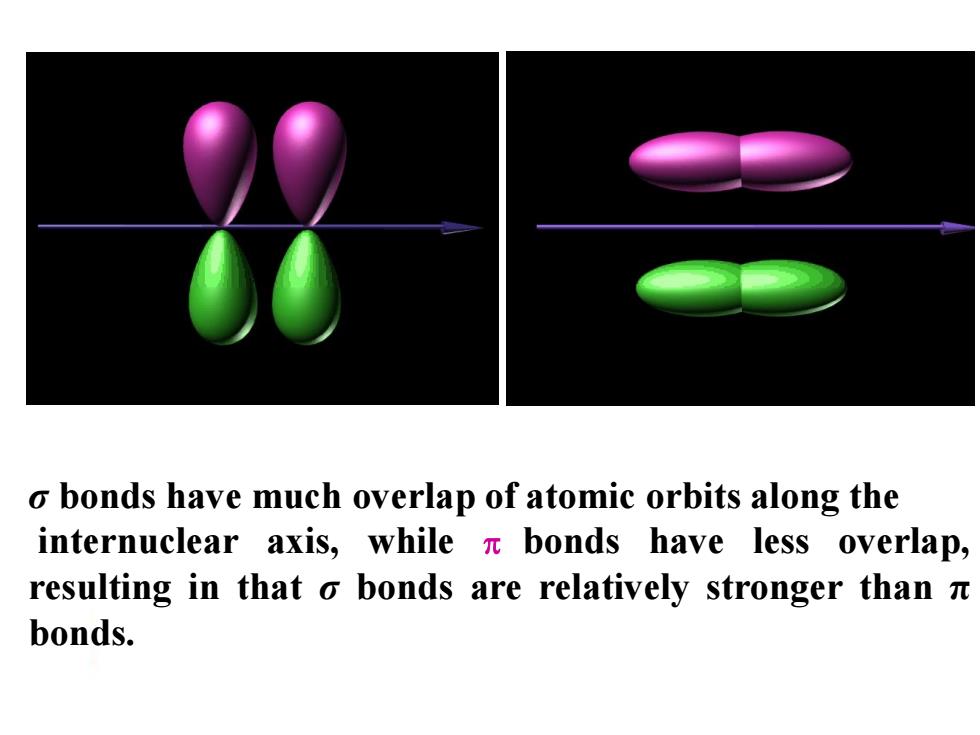
o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis,while bonds have less overlap, resulting in that o bonds are relatively stronger than n bonds
σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis, while bonds have less overlap, resulting in that σ bonds are relatively stronger than π bonds
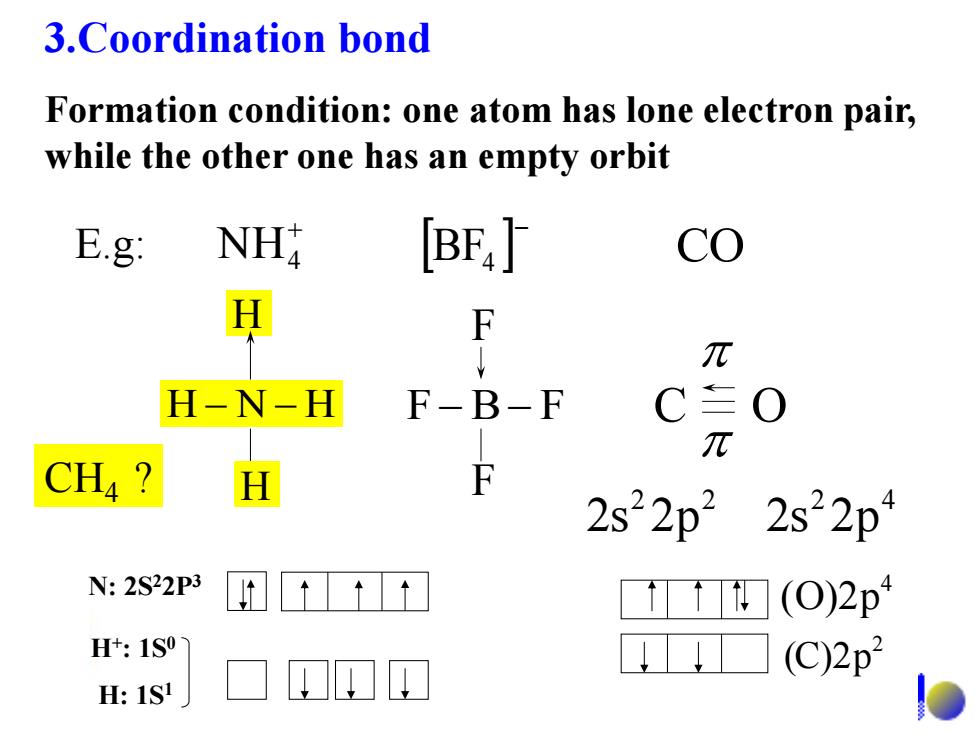
3.Coordination bond Formation condition:one atom has lone electron pair, while the other one has an empty orbit E.g: NH [BE4] co H F π H-N-H F-B -F C O π CH4 H F 2s22p22s22p4 N:2S22P3 ☐(O)2p1 H+:1S0 (C)2p2 H:1S!
3.Coordination bond Formation condition: one atom has lone electron pair, while the other one has an empty orbit NH4 BF4 CO 2 2 2s 2p 2 4 2s 2p H N H H H FB F F F E.g: C O N: 2S22P3 H+ : 1S0 H: 1S1 2 (C)2p 4 (O)2p CH4 ?

6.3 Hybrid orbits Theory -6.3.1 Concept of hybrid orbits 6.3.2 The types of hybrid orbits e6.3.2元bond and extended元bond 返回
6.3.1 Concept of hybrid orbits §6.3 Hybrid orbits Theory 6.3.2 The types of hybrid orbits 6.3.2 bond and extended bond
6.3.1 Concept of hybrid orbits The principles of the hybrid orbit theory: .Hybridization is the mixing of nonequivalent atomic orbits with matching energies in an atom to generate a set of hybrid orbits. .The number of hybrid orbits generated is equal to the number of pure atomic orbits that participate in the hybridization process. .Hybrid orbits and pure atomic orbits have very different shapes
The principles of the hybrid orbit theory: •Hybridization is the mixing of nonequivalent atomic orbits with matching energies in an atom to generate a set of hybrid orbits. •The number of hybrid orbits generated is equal to the number of pure atomic orbits that participate in the hybridization process. •Hybrid orbits and pure atomic orbits have very different shapes. 6.3.1 Concept of hybrid orbits