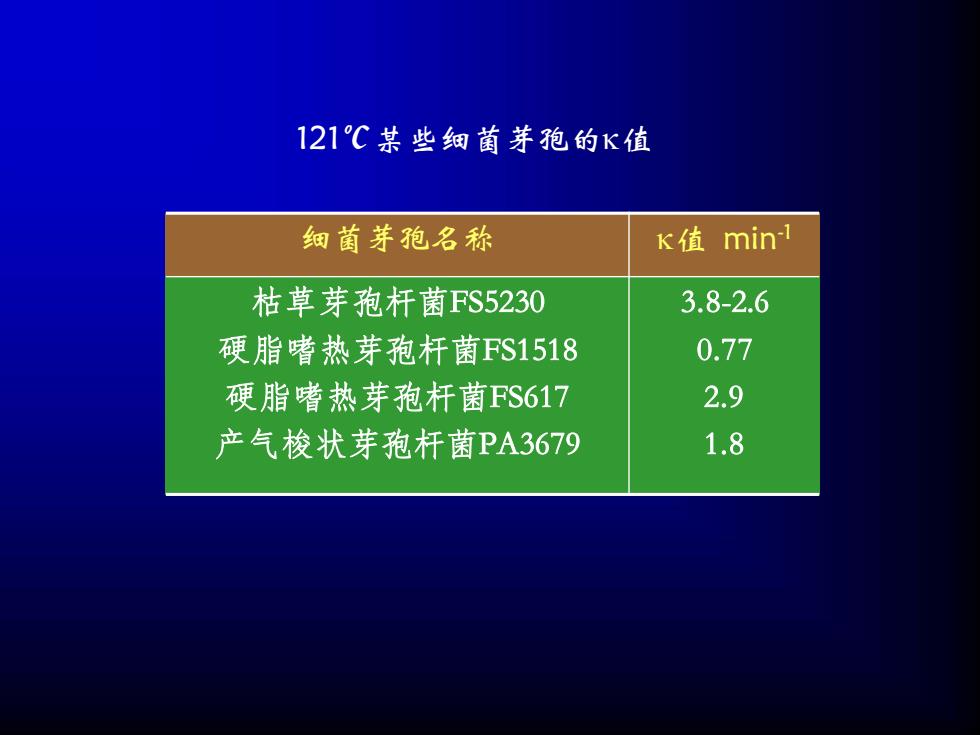
细菌芽孢名称 值 min-1 枯草芽孢杆菌FS5230 硬脂嗜热芽孢杆菌FS1518 硬脂嗜热芽孢杆菌FS617 产气梭状芽孢杆菌PA3679 3.8-2.6 0.77 2.9 1.8 121℃某些细菌芽孢的值
细菌芽孢名称 值 min-1 枯草芽孢杆菌FS5230 硬脂嗜热芽孢杆菌FS1518 硬脂嗜热芽孢杆菌FS617 产气梭状芽孢杆菌PA3679 3.8-2.6 0.77 2.9 1.8 121℃某些细菌芽孢的值

4、培养基灭菌温度的选择 ◆ 培养基灭菌过程中,除微生物被杀死外,还伴随着培养基 成分被破坏,在加热下氨基酸、维生素等受破坏。 ◆ 培养基灭菌时,必须选择既能达到灭菌目的,又能使培养 基成分破坏减至最少的条件。 ◆ 灭菌过程微生物死亡属于一级反应动力学类型(从对数残 留定律表达式可知)。 ◆ 在其它条件不变时,比死亡速率与温度的关系可用阿仑尼 乌斯方程式表示
4、培养基灭菌温度的选择 ◆ 培养基灭菌过程中,除微生物被杀死外,还伴随着培养基 成分被破坏,在加热下氨基酸、维生素等受破坏。 ◆ 培养基灭菌时,必须选择既能达到灭菌目的,又能使培养 基成分破坏减至最少的条件。 ◆ 灭菌过程微生物死亡属于一级反应动力学类型(从对数残 留定律表达式可知)。 ◆ 在其它条件不变时,比死亡速率与温度的关系可用阿仑尼 乌斯方程式表示

Svante August Arrhenius was a Swedish physical chemist best known for his theory that electrolytes, certain substances that dissolve in water to yield a solution that conducts electricity, are separated, or dissociated, into electrically charged particles, or ions, even when there is no current flowing through the solution. In 1903 he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry
Svante August Arrhenius was a Swedish physical chemist best known for his theory that electrolytes, certain substances that dissolve in water to yield a solution that conducts electricity, are separated, or dissociated, into electrically charged particles, or ions, even when there is no current flowing through the solution. In 1903 he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry

= A e R T -—E Arrhenius equation A — 比例常数; E — 杀死细菌所需的活化能,(E)(×4.18 J/mol); T — 绝对温度,(K) R — 气体常数,[1.978×4.18 J/(mol·K)] e — 2.71 (exp)
= A e R T -—E Arrhenius equation A — 比例常数; E — 杀死细菌所需的活化能,(E)(×4.18 J/mol); T — 绝对温度,(K) R — 气体常数,[1.978×4.18 J/(mol·K)] e — 2.71 (exp)
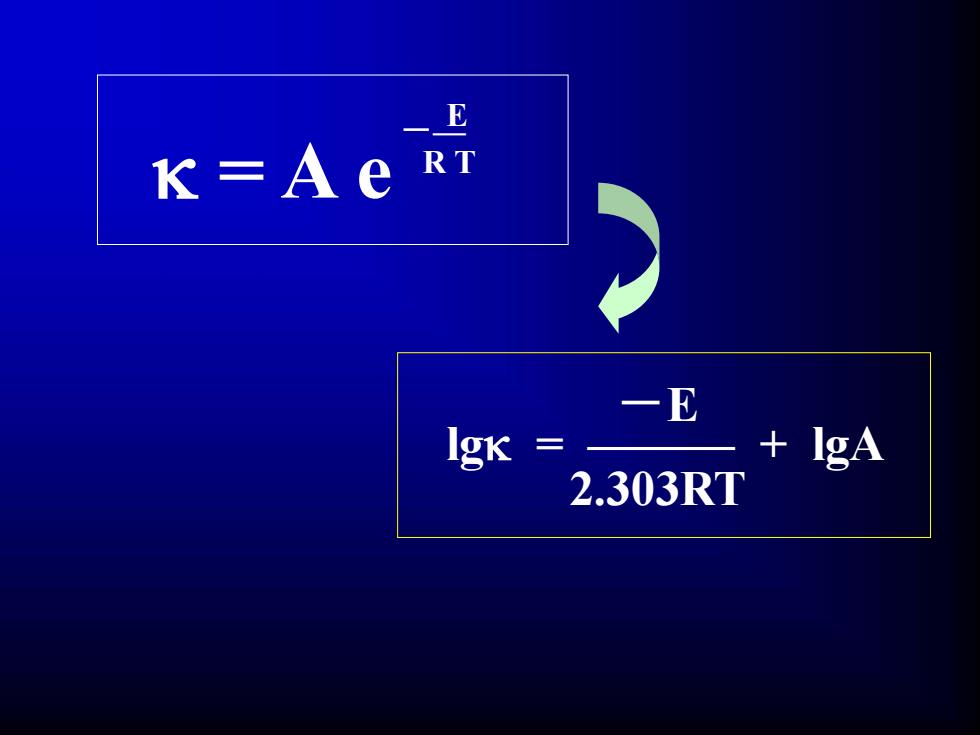
= A e R T -—E lg = ——— + lgA -E 2.303RT
= A e R T -—E lg = ——— + lgA -E 2.303RT