
Chapter 1TheProcessPlanningofmechanicalmanufacturingAbstractThe purpose of mechanical machining is to turn a kind of raw material into the finished parts that meetthe requirement of the product.Under given manufactureconditions, how to applyboth an economicaland efficient method, as well as a rational process routine,to achieve the desired parts is the concern ofthis chapter.Thechapterbeginswith someimportantconcepts suchasworkingprocedure,process step,cutting inone continuous feed, setup,machining position, reference datum,manufacturing process and so on1.1 Process of product1.1.1Processofproduct(生产过程)Manufacturing is the utilization and management of materials, people, equipment, and money toproduce products. For successful and economical manufacturing to be achieved, planning must start at thedesign stage and continue through the selection of materials, processes, equipment, and the scheduling ofproductionThese related processes constitute the so-called production process Process of productinvolve:Productdesign、prepare、transport of rawandprocessedmaterials、roughmanufacture、mechanicalmachining、heattreatment、assembly、deburring、test、paintingandpackingThese related processes constitutethe so-called productionprocess.Itis usually completed by thecoordinated work of different factories or workshops.1.1.2 Process of Part(工艺过程)Process of Part:The process by which the shape, dimensions and performance of raw material or rough casting arechanged directly by mechanical manufacturing into desired parts is called component manufactured partproduction, or process route.When parts areassembled intoa product, it is called the assemblyprocess.1.1.2.1 part production2001.61.6Partproduction consists of one or several operations inVsequence.Arough casting can be turned into a finished二1*DOteor semi-finished product by the operations.e(1)operations(工序)150300Whenoneoperator(oragroupofoperators)worksB590inadefiniteposition(onemachinetoolorclippingtable)toachieve thecontinuousmanufacturing of one orFig 1-1 is the engineering drawing of a shaftseveralparts simultaneously.Anoperationisthebasicelement of process procedureas well as oftheproductionschedule and of cost estimation.If the number of the parts in a batch is small, the manufacturing process can be completed through 5operations, whichare shown in table 1-1.Table1-1the process of shaft manufacturingWorkplaceOperationNoOperationnamefacing end , center drlling endsEnginelathe2Cylindrical TurningEngine lathe3Key way millingUpright milling machineCylindrical grindingGrinding machinedeburringClipping table
Chapter 1 The Process Planning of mechanical manufacturing Abstract The purpose of mechanical machining is to turn a kind of raw material into the finished parts that meet the requirement of the product. Under given manufacture conditions, how to apply both an economical and efficient method, as well as a rational process routine, to achieve the desired parts is the concern of this chapter. The chapter begins with some important concepts such as working procedure, process step, cutting in one continuous feed, setup, machining position, reference datum, manufacturing process and so on. 1.1 Process of product 1.1.1 Process of product (生产过程) Manufacturing is the utilization and management of materials, people, equipment, and money to produce products. For successful and economical manufacturing to be achieved, planning must start at the design stage and continue through the selection of materials, processes, equipment, and the scheduling of production. These related processes constitute the so-called production process Process of product involve:Product design 、 prepare、transport of raw and processed materials、rough manufacture、 mechanical machining 、heat treatment 、assembly、 deburring、test 、painting and packing. These related processes constitute the so-called production process. It is usually completed by the coordinated work of different factories or workshops. 1.1.2 Process of Part (工艺过程) Process of Part: The process by which the shape, dimensions and performance of raw material or rough casting are changed directly by mechanical manufacturing into desired parts is called component manufactured part production, or process route. When parts are assembled into a product, it is called the assembly process. 1.1.2.1 part production Part production consists of one or several operations in sequence. A rough casting can be turned into a finished or semi-finished product by the operations. (1) operations (工序) When one operator (or a group of operators) works in a definite position(one machine tool or clipping table) to achieve the continuous manufacturing of one or several parts simultaneously. An operation is the basic element of process procedure as well as of the production schedule and of cost estimation. If the number of the parts in a batch is small, the manufacturing process can be completed through 5 operations, which are shown in table 1-1. Table 1-1 the process of shaft manufacturing Operation No. Operation name Work place 1 facing end , center drilling ends Engine lathe 2 Cylindrical Turning Engine lathe 3 Key way milling Upright milling machine 4 Cylindrical grinding Grinding machine 6 deburring Clipping table Fig 1-1 is the engineering drawing of a shaft

For the manufacturing of the same part as Fig 1-1, if the number of parts is large, the operation 1 intable 1-1 can be divided into 2 operationsa)facing and centering one end in an engine latheby one operatorb) transferring to another engine lathe for facing and centering the another end by another operator(2)OperationStep(工步)An operationstepisthebasicelement of an operation.Oneoperationstep isdefined as anoperationthat is completed under the condition when the surface to be manufactured, the cutting parameters(includingcuttingspeed andfeed)and cuttingtool remain thesame.Whenany ofthecuttingparameters ischanged, it will become another operation step.When several surfaces of a part are manufacturedsimultaneously,it is called a composite operation step.The purpose of classifying an operation into steps is to make a complex operation more convenientand easy to analyze and describe, and to make it more efficient to organize the manufacturing and calculatethe operationtime.(3)cuttingpass(走刀)When the amount of metal to be removed is large, several cutting passes may need to be carried out.A cutting pass is a kind ofoperation step that is completed by a single type of tool to cut the samesurface under the same cutting parameters.(4)setup(安装)Before it can be machined, the part must have a proper position relative to the cutting tool, and beclamped by a fixture in the machine tool. This procedure is called the fixturing(clamping). The operationcompleted through one fixturing is called single setup.Each operation may have either single setup or several setups.In the same operation, the number of setups should be arranged to be as few as possible.If this isdone,not only can the production efficiency beraised, but also theproduction error caused by setups canbe reduced.(5)operation position(工位)In orderto reducethenumberof setups,a rotational worktableorfixture isusually used tomake sequential machiningin differentpositions possible from a single setup. The job performed in oneposition is called one operation position.Demonstration ofoperation,operation step,position and cuttingpass1.1.2.2 Impact of production type on process planningProcess planning arehighly affected by the production type.When the production type changes, the production organization and management, the layout ofworkshop and machinetools, the processmethod ofthe rawmaterial,the manufacturing equipment, suchas kinds ofcutting tool, fixture and inspection tools and the technical level ofthe operators will also variedaccordingly.Therefore,before process planning,a concise explanation of the effect of production batchsize will be given.Production type refers to the specialized classification of an enterprise in respect of a workshop,manufacturinglineorgroup,work place,and soon Generally,itcan be classified into3tys,which are,(1) Single productionThe number of workpieces with different structure or different dimensions is only one at a time, oronly in small quantity
For the manufacturing of the same part as Fig 1-1, if the number of parts is large, the operation 1 in table 1-1 can be divided into 2 operations: a) facing and centering one end in an engine lathe by one operator b)transferring to another engine lathe for facing and centering the another end by another operator (2)Operation Step (工步) An operation step is the basic element of an operation. One operation step is defined as an operation that is completed under the condition when the surface to be manufactured, the cutting parameters (including cutting speed and feed) and cutting tool remain the same. When any of the cutting parameters is changed, it will become another operation step. When several surfaces of a part are manufactured simultaneously, it is called a composite operation step. The purpose of classifying an operation into steps is to make a complex operation more convenient and easy to analyze and describe, and to make it more efficient to organize the manufacturing and calculate the operation time. (3)cutting pass (走刀) When the amount of metal to be removed is large, several cutting passes may need to be carried out. A cutting pass is a kind of operation step that is completed by a single type of tool to cut the same surface under the same cutting parameters. (4) setup (安装) Before it can be machined, the part must have a proper position relative to the cutting tool, and be clamped by a fixture in the machine tool. This procedure is called the fixturing(clamping). The operation completed through one fixturing is called single setup. Each operation may have either single setup or several setups. In the same operation, the number of setups should be arranged to be as few as possible. If this is done, not only can the production efficiency be raised, but also the production error caused by setups can be reduced. (5)operation position(工位) In order to reduce the number of setups, a rotational worktable or fixture is usually used to make sequential machining in different positions possible from a single setup. The job performed in one position is called one operation position. Demonstration of operation, operation step,position and cutting pass 1.1.2.2 Impact of production type on process planning Process planning are highly affected by the production type. When the production type changes, the production organization and management, the layout of workshop and machine tools, the process method of the raw material, the manufacturing equipment, such as kinds of cutting tool, fixture and inspection tools and the technical level of the operators will also varied accordingly. Therefore, before process planning, a concise explanation of the effect of production batch size will be given. Production type refers to the specialized classification of an enterprise in respect of a workshop, manufacturing line or group, work place, and so on. Generally, it can be classified into 3 types, which are, (1)Single production The number of workpieces with different structure or different dimensions is only one at a time, or only in small quantity
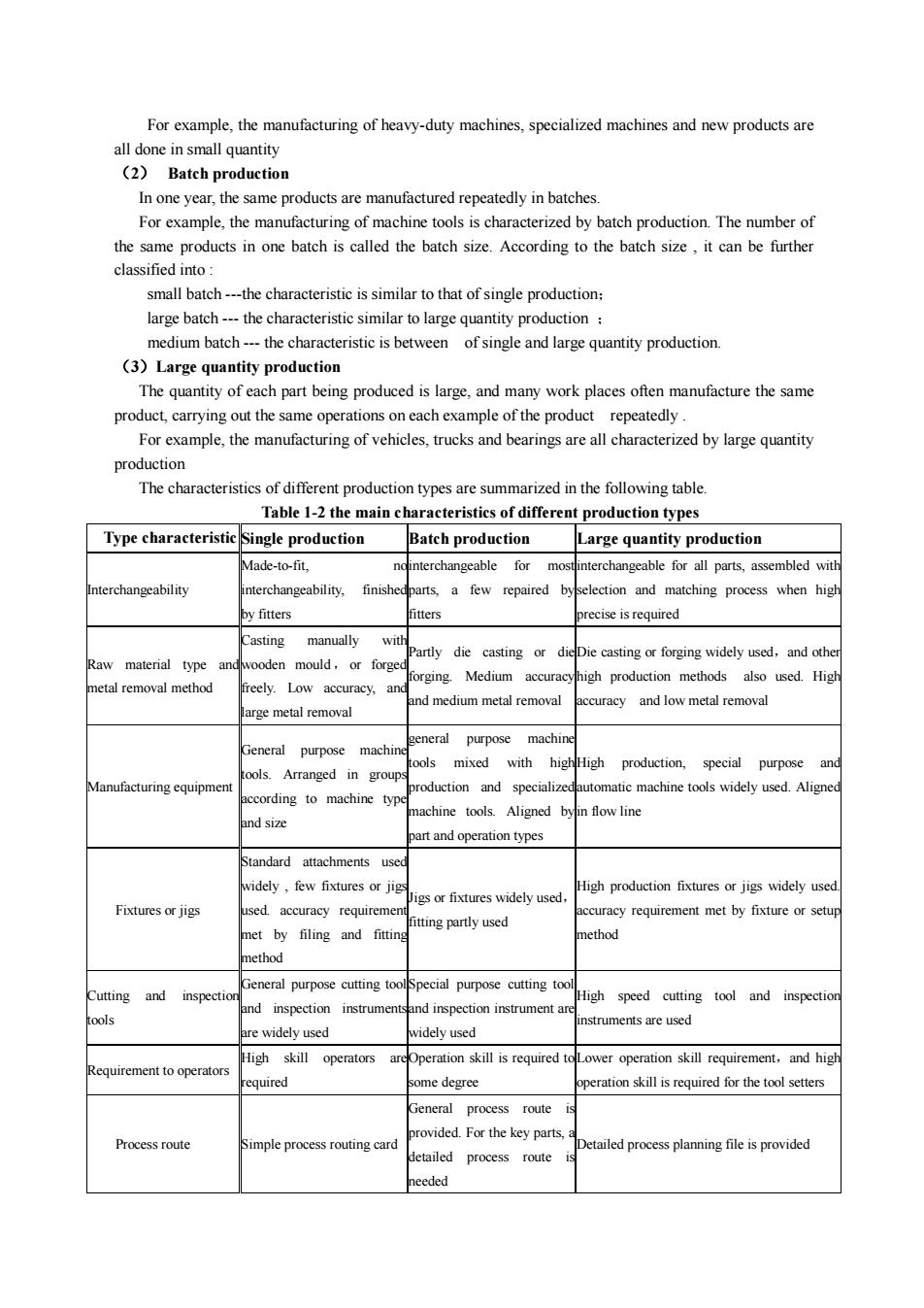
For example,themanufacturing ofheavy-duty machines, specialized machines and newproducts areall done in small quantity(2)BatchproductionInoneyear,thesameproductsaremanufacturedrepeatedlyinbatchesFor example, the manufacturing of machine tools is characterized by batch production.The number ofthe same products in one batch is called the batch size. According to the batch size, it can be furtherclassified into:small batch---the characteristic is similarto that of single production;large batch--- thecharacteristic similar to large quantity production;medium batch --- the characteristic is betweenof single and large quantity production.(3) Large quantity productionThe quantity of each part being produced is large, and many work places often manufacture the sameproduct,carryingoutthesameoperationsoneachexampleoftheproductrepeatedlyFor example,themanufacturing of vehicles,trucks and bearings are all characterized by large quantityproductionThecharacteristics of differentproductiontypes are summarized inthefollowingtableTable 1-2 the main characteristics of different production typesType characteristicSingle productionBatch productionLarge quantity productionMade-to-fit,nointerchangeablefor mostinterchangeable for all parts, assembled withInterchangeabilityfinishedparts, a few repaired byselection and matching process when highinterchangeability,by fittersfittersprecise is requiredwithCastingmanuallyPartlydiecasting or dieDie casting or forgingwidelyused,and othemould,RawmaterialvoodenorforgetypeMedium accuracyhigh production methods also used.Highforging.metal removal methodfreely. Low accuracy,aneaccuracy and lowmetal removaland medium metal removalarge metal removalgeneralmachinepurposepurposemachineGeneraltoolsmixedwith highHighproduction,specialpurposeanoools.Arranged in groupsproductionandspecializedautomatic machine tools widely used. AlignedManufacturing equipmentaccordingtomachinetypmachine tools.Aligned byin flowlineand sizepart and operation typesStandardattachmentsusedwidely, few fixtures or jigHigh production fixtures or jigs widely usedigs or fixtures widely usedFixtures or jigsused. accuracy requirementaccuracy requirementmetbyfixture or setupfitting partly usedmet byfilingandfittingmethodmethodGeneral purpose cutting toolSpecial purpose cutting toolCuttingandinspectiorHigh speed cutting tool and inspectiorandinspection instrumentsand inspection instrumentaretoolsinstruments are usedarewidelyusedwidely usedHigh skillareOperation skill is required toLower operation skill requirement, and highoperatorsRequirementtooperatorsrequiredsome degreeoperation skill is required for the tool settersGeneralprocessrouteSprovided. For the key parts,Process routeDetailed process planning file is providedSimple process routing carddetailedprocessrouteICneeded
For example, the manufacturing of heavy-duty machines, specialized machines and new products are all done in small quantity (2) Batch production In one year, the same products are manufactured repeatedly in batches. For example, the manufacturing of machine tools is characterized by batch production. The number of the same products in one batch is called the batch size. According to the batch size , it can be further classified into : small batch -the characteristic is similar to that of single production; large batch - the characteristic similar to large quantity production ; medium batch - the characteristic is between of single and large quantity production. (3)Large quantity production The quantity of each part being produced is large, and many work places often manufacture the same product, carrying out the same operations on each example of the product repeatedly . For example, the manufacturing of vehicles, trucks and bearings are all characterized by large quantity production The characteristics of different production types are summarized in the following table. Table 1-2 the main characteristics of different production types Type characteristic Single production Batch production Large quantity production Interchangeability Made-to-fit, no interchangeability, finished by fitters interchangeable for most parts, a few repaired by fitters interchangeable for all parts, assembled with selection and matching process when high precise is required Raw material type and metal removal method Casting manually with wooden mould, or forged freely. Low accuracy, and large metal removal Partly die casting or die forging. Medium accuracy and medium metal removal Die casting or forging widely used,and other high production methods also used. High accuracy and low metal removal Manufacturing equipment General purpose machine tools. Arranged in groups according to machine type and size general purpose machine tools mixed with high production and specialized machine tools. Aligned by part and operation types High production, special purpose and automatic machine tools widely used. Aligned in flow line Fixtures or jigs Standard attachments used widely , few fixtures or jigs used. accuracy requirement met by filing and fitting method Jigs or fixtures widely used, fitting partly used High production fixtures or jigs widely used. accuracy requirement met by fixture or setup method Cutting and inspection tools General purpose cutting tool and inspection instruments are widely used Special purpose cutting tool and inspection instrument are widely used High speed cutting tool and inspection instruments are used Requirement to operators High skill operators are required Operation skill is required to some degree Lower operation skill requirement,and high operation skill is required for the tool setters Process route Simple process routing card General process route is provided. For the key parts, a detailed process route is needed Detailed process planning file is provided

1.2The function and design method of process planningfileThetermprocessroute(工艺规程)istheprocessplanningfileinwhichtheprocessandoperationmethod are specified.In another word, the aligned sequence of each operation, the part dimensions,tolerance and technical requirement, technical equipment and measures, cutting parameters, standardproductiontime,andlevelsofoperatorsskillareall included intheprocessplanningfile4-2-1 Theformatof process sheetIn 1982, the pre-mechanical industry ministry issued the ministry standard to regulate the format ofprocess sheet (referred to JB/Z1 187.3-82). Operation sheets vary greatly as to details:Nameofpartandtype:Name and No. of part ;Raw material ;Name ofoperation;Nameof plantBefore products are manufactured,technical and production preparation can be made beforehandaccording to the demands of process planning sheet.Accordingtotheprocessplanningsheet,thekinds,typeandnumberofmachinetools,theproductionareaneeded,theplanarrangementof equipment,thenumber,typeand classof operators requiredcan albe decided. Then, the planning of factory preparation, enlarging or rebuilding will be decided accordingly.1.2.2Thefunctionof process planning sheetThefunction of theprocess planning sheet is as follows:(1)The main technique for givingregulations to guide the production(2)Thebasisoforganizationandmanagement(3) The main information to guide the building, enlarging or rebuilding ofa mechanical factory1.2.3 Design procedures of process planning(1) Design procedures of process planningFirstly, the function, importance and working condition ofthe part should be clarified.If the design details are considered unreasonable or wrong during inspection, suggestions to modifythe design can be proposed.(2)Determination of production type according to production expectationTheexpectednumberofpartscanbecalculatedaccordingtothefollowingformula,Np=N·n(1+ a) (1+β)Where,Npthe expected number of parts in one year;N-theexpected numberofproducts inoneyear;n-thenumberofpartsinoneproduct;a -percent of spare parts;βpercent of scrap parts;tablel-6 can be used as a reference to guide the classification of production typeOutput number in oneyeartypeLightMedium sizeLarge and heavysingleBelow5Below 10Below100small5~1010~200100~500batchmedium100~300200~500500~5000300~1000500~50005000~50000arge
1.2 The function and design method of process planning file The term process route(工艺规程) is the process planning file in which the process and operation method are specified. In another word, the aligned sequence of each operation, the part dimensions, tolerance and technical requirement, technical equipment and measures, cutting parameters, standard production time, and levels of operators’skill are all included in the process planning file. 4·2·1 The format of process sheet In 1982, the pre-mechanical industry ministry issued the ministry standard to regulate the format of process sheet (referred to JB/Z1 187.3-82). Operation sheets vary greatly as to details: Name of part and type ; Name and No. of part ; Raw material ; Name of operation ; Name of plant . Before products are manufactured,technical and production preparation can be made beforehand according to the demands of process planning sheet. According to the process planning sheet, the kinds, type and number of machine tools, the production area needed , the plan arrangement of equipment, the number, type and class of operators required can all be decided. Then, the planning of factory preparation, enlarging or rebuilding will be decided accordingly. 1.2.2 The function of process planning sheet The function of the process planning sheet is as follows : (1)The main technique for giving regulations to guide the production (2) The basis of organization and management (3) The main information to guide the building, enlarging or rebuilding of a mechanical factory 1.2.3 Design procedures of process planning (1)Design procedures of process planning Firstly, the function, importance and working condition of the part should be clarified. If the design details are considered unreasonable or wrong during inspection, suggestions to modify the design can be proposed. (2) Determination of production type according to production expectation The expected number of parts can be calculated according to the following formula, Np=N·n(1+α) ·(1+β) Where, Np—the expected number of parts in one year; N —the expected number of products in one year; n —the number of parts in one product ; α—percent of spare parts; β—percent of scrap parts; table1—6 can be used as a reference to guide the classification of production type Output number in one year type Large and heavy Medium size Light single Below 5 Below 10 Below 100 small 5~10 10~200 100~500 batch medium 100~300 200~500 500~5000 large 300~1000 500~5000 5000~50000

Large quantityBeyond1000Beyond5000Beyond50000To classify theproduction type, both the expected number and the volume, weight of the part shouldbetaken into account(3)Determination of rawmaterial typeThe determination of raw material is related with the part geometrical shape, dimensions, mechanicalperformanceofmaterial and production type,current production conditions oftheworkshop.Casting:includes cast steel, cast iron, cast alloy etc.The shape of the casts can vary from complicationtosimplicity,anddimensionscanbeverylargeForging: has better mechanical performance than castings, however. many intricate and cored shapespossible in casting cannot be forged.Profiled bar: The shape of cross section can be round, rectangular or other different shapes. Bars areoftenmachined into shafts,dishes orround shells with engine lathe,turret lathe,orautomatic or semiautomaticlathe,and thedimensions canvaryfrom smalltomediumsize.but itsthicknessis limited withina range.Welding:for complicated and large parts canbewelded from profiled bar orforged parts,but thewelded partperformsbadlyin somerespectsEngineering plastic:used widely in mechanical manufacturing in recent years. Its shape can vary fromsimple to complicated, and the dimension accuracy is high, but mechanical performance is weak.In large batch or largequantityproduction,highlyprecise and efficientmanufacturingmethods for rawmaterial areoften used, suchasdie casting,precisecasting,dieforging,cold punching,andpowdermetallurgy.All thesemethodsmaketherawmaterial shapeclosetothatof thefinal designpart.Therefore,thelabor required in metal removal can be greatly reduced,sometimes even no metal removal is needed.Not only can the material be saved, but also the mechanical manufacturing cost can be reducedInsingle or small batch production, sand casting with wooden mould or free deformed forging areoften used. Therefore, the accuracy is low, the cost is high, the acceptance ratio is low, and the laborengaged in metal removal is large.(4)ProcessrouteplanningIt includes selection of mounting surface and machining method, classification of process phases,sequencing the operations,determining thedegreeof operation distribution,arrangementof hot working orinspection and other auxiliary operations(5)selection ofmachinetools,technical equipment (including cutting tools,fixtures and inspectiontools) and auxiliary tools for each operation.(6)selectionofmetalremoval,operationdimensionsandtolerancesforeachoperation(7)Selectionofmetal cuttingparameters and standardoperationtimes(8) technical economical analysis(9)formtheprocessfile1.3selectionofpositioningreference(datum)positioning reference is used to define the position of other points, lines or surfaces of the part arecalled thepositioning referencedatum.1.3.1ClassificationofpositioningreferencePositioningreference canbe classified into twocategories according to application purpose.1.3.1.1 Design referenceThe points, lines or surfaces that are used by designers to determine the dimensions or relativepositionsof otherpoints,lines or surfaces are calledthedesignreference.Forexample,inFigl-3a
Large quantity Beyond 1000 Beyond 5000 Beyond 50000 To classify the production type, both the expected number and the volume, weight of the part should be taken into account (3)Determination of raw material type The determination of raw material is related with the part geometrical shape, dimensions, mechanical performance of material and production type, current production conditions of the workshop. Casting:includes cast steel, cast iron, cast alloy etc. The shape of the casts can vary from complication to simplicity, and dimensions can be very large. Forging:has better mechanical performance than castings, however. many intricate and cored shapes possible in casting cannot be forged. Profiled bar:The shape of cross section can be round, rectangular or other different shapes. Bars are often machined into shafts, dishes or round shells with engine lathe, turret lathe, or automatic or semi automatic lathe, and the dimensions can vary from small to medium size. but its thickness is limited within a range. Welding:for complicated and large parts can be welded from profiled bar or forged parts,but the welded part performs badly in some respects. Engineering plastic:used widely in mechanical manufacturing in recent years. Its shape can vary from simple to complicated, and the dimension accuracy is high, but mechanical performance is weak. In large batch or large quantity production, highly precise and efficient manufacturing methods for raw material are often used, such as die casting, precise casting, die forging, cold punching ,and powder metallurgy. All these methods make the raw material shape close to that of the final design part. Therefore, the labor required in metal removal can be greatly reduced , sometimes even no metal removal is needed. Not only can the material be saved, but also the mechanical manufacturing cost can be reduced. In single or small batch production, sand casting with wooden mould or free deformed forging are often used. Therefore, the accuracy is low, the cost is high, the acceptance ratio is low, and the labor engaged in metal removal is large. (4) Process route planning It includes selection of mounting surface and machining method, classification of process phases, sequencing the operations, determining the degree of operation distribution, arrangement of hot working or inspection and other auxiliary operations . (5)selection of machine tools, technical equipment (including cutting tools, fixtures and inspection tools) and auxiliary tools for each operation. (6)selection of metal removal, operation dimensions and tolerances for each operation (7)Selection of metal cutting parameters and standard operation times 。 (8)technical economical analysis (9)form the process file 1.3 selection of positioning reference(datum) positioning reference is used to define the position of other points, lines or surfaces of the part are called the positioning reference datum. 1.3.l Classification of positioning reference Positioning reference can be classified into two categories according to application purpose. 1.3.1.1 Design reference The points, lines or surfaces that are used by designers to determine the dimensions or relative positions of other points, lines or surfaces are called the design reference. For example, in Fig1—3a