
Mutation due to hydrolytic damage N Deamination C-→U H2O Hydrolysis creates apurinic deoxyribose(脱氧核醣) CH3 I N 5mC NH 2025/5/15 Deamination 5-mC->T
2025/5/15 12 Mutation due to hydrolytic damage Deamination C→U Hydrolysis creates apurinic deoxyribose (脱氧核醣) Deamination 5-mC → T

Vertebrate(脊椎动物)DNA frequently contains5'- methyl cytosine(5'-甲基胞嘧啶)in place of cytosine as a result of the action of methyl transferase 转移酶),This modified base plays a role in the transcriptional silencing The presence of U and apurinic deoxyribose in DNA resulted from hydrolytic reactions is regarded as unnatural,thus is easily be recognized and repaired. Can 5-mC->T lesion be repaired? 5-mC->T mutations are hotspots for 2ontaneous mutations in vertebrates!
2025/5/15 13 The presence of U and apurinic deoxyribose in DNA resulted from hydrolytic reactions is regarded as unnatural, thus is easily be recognized and repaired. Can 5-mC → T lesion be repaired? Vertebrate(脊椎动物)DNA frequently contains 5’- methyl cytosine (5’-甲基胞嘧啶)in place of cytosine as a result of the action of methyl transferase (甲基 转移酶). This modified base plays a role in the transcriptional silencing . 5-mC → T mutations are hotspots for spontaneous mutations in vertebrates !
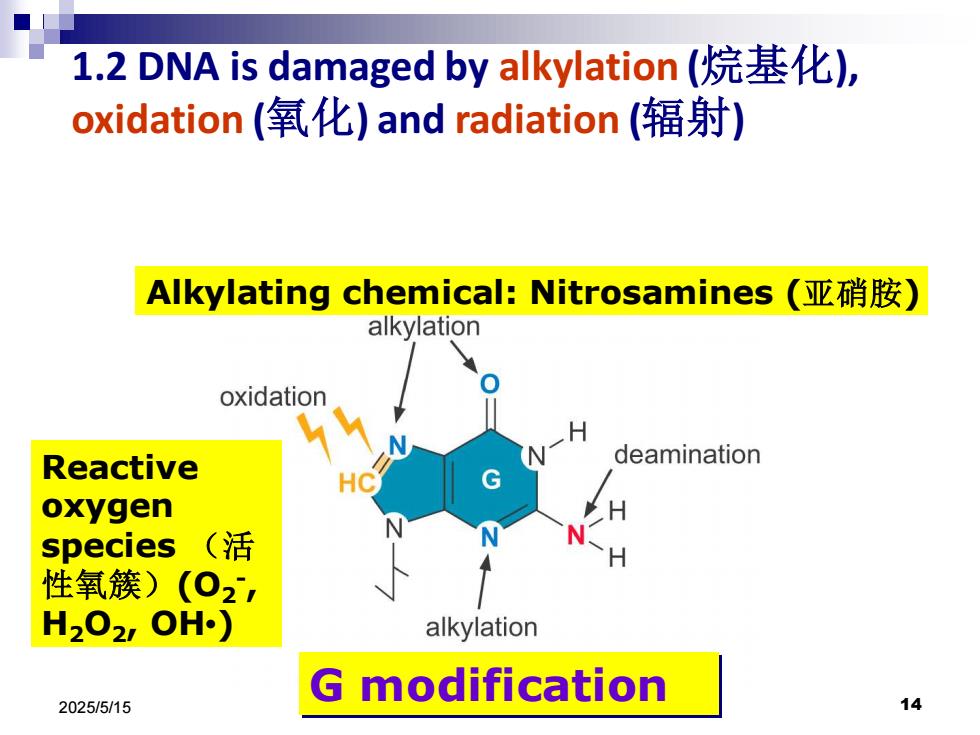
1.2 DNA is damaged by alkylation(烷基化), oxidation(氧化)and radiation(辐射) Alkylating chemical:Nitrosamines(亚硝胺) alkylation oxidation Reactive deamination G oxygen species(活 性氧簇)(O2, H202,OH) alkylation modification 2025/5/15 14
2025/5/15 14 1.2 DNA is damaged by alkylation (烷基化), oxidation (氧化) and radiation (辐射) G modification Alkylating chemical: Nitrosamines (亚硝胺) Reactive oxygen species (活 性氧簇)(O2 - , H2O2, OH•)
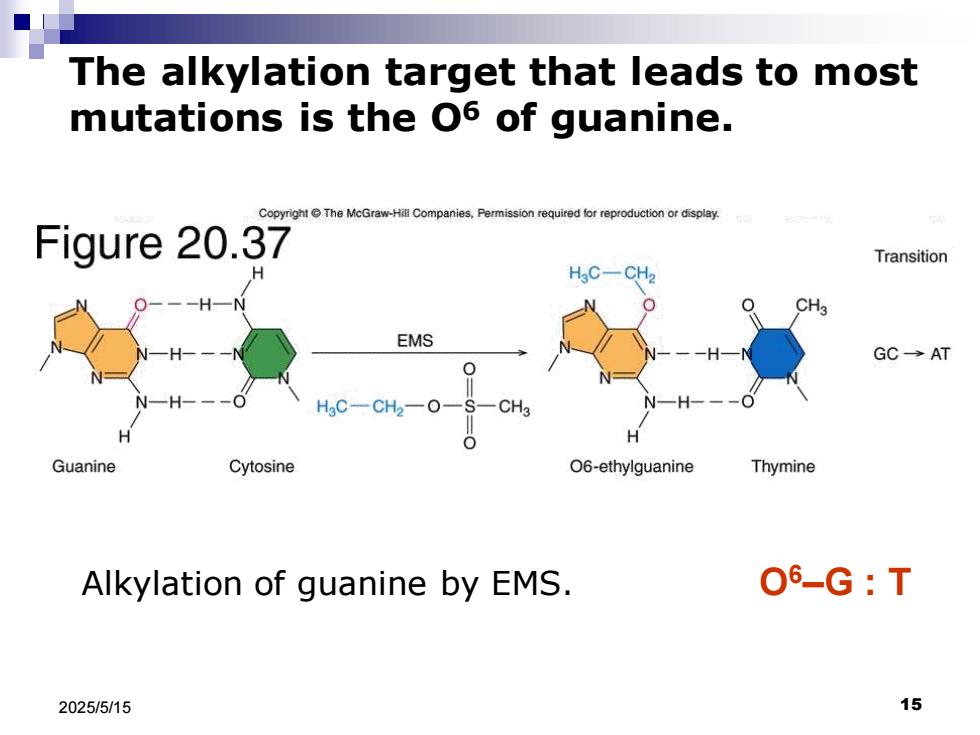
The alkylation target that leads to most mutations is the O6 of guanine. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies ission required for reproductionor display Figure 20.37 Transition H3C一CH CH EMS GC→AT -CH -0 CH Guanine Cytosine 06-ethylguanine Thymine Alkylation of guanine by EMS. O6-G:T 2025/5/15 15
2025/5/15 15 Alkylation of guanine by EMS. O6–G : T The alkylation target that leads to most mutations is the O6 of guanine
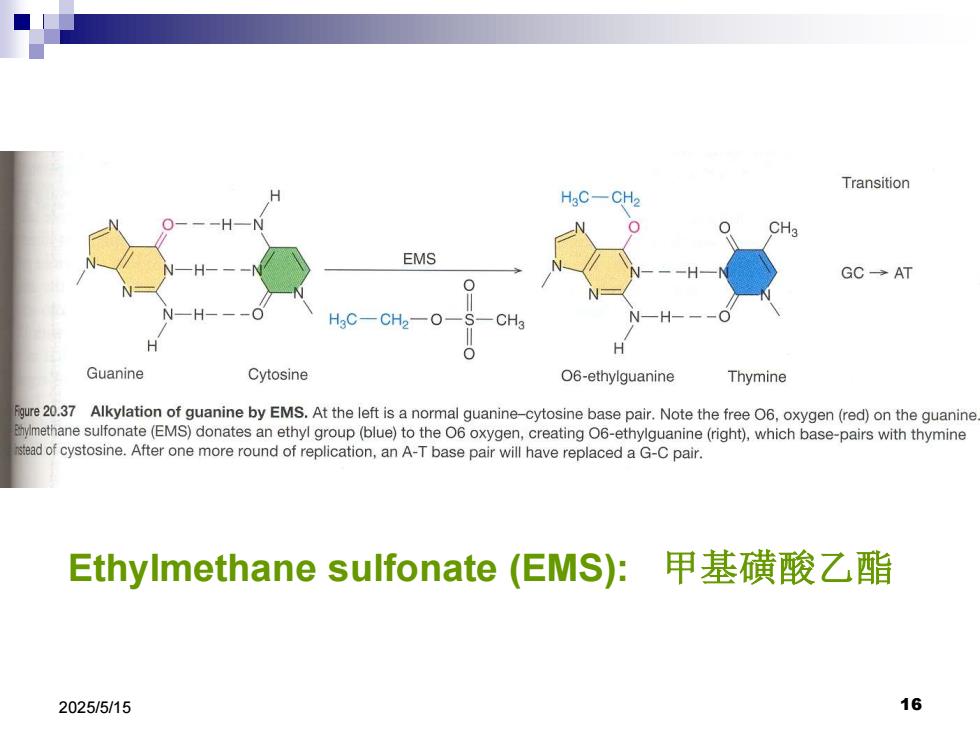
Transition HgC-CH2 CH3 EMS GC→AT HC-CH2一O Guanine Cytosine O6-ethylguanine Thymine Fgure 20.37 Alkylation of guanine by EMS.At the left is a normal guanine-cytosine base pair.Note the free O6,oxygen(red)on the guanine Ehylmethane sulfonate(EMS)donates an ethyl group(blue)to the O6 oxygen,creating O6-ethylguanine(right),which base-pairs with thymine stead of cystosine.After one more round of replication,an A-T base pair will have replaced a G-C pair. Ethylmethane sulfonate(EMS:甲基磺酸乙酯 2025/5/15 16
2025/5/15 16 Ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS): 甲基磺酸乙酯