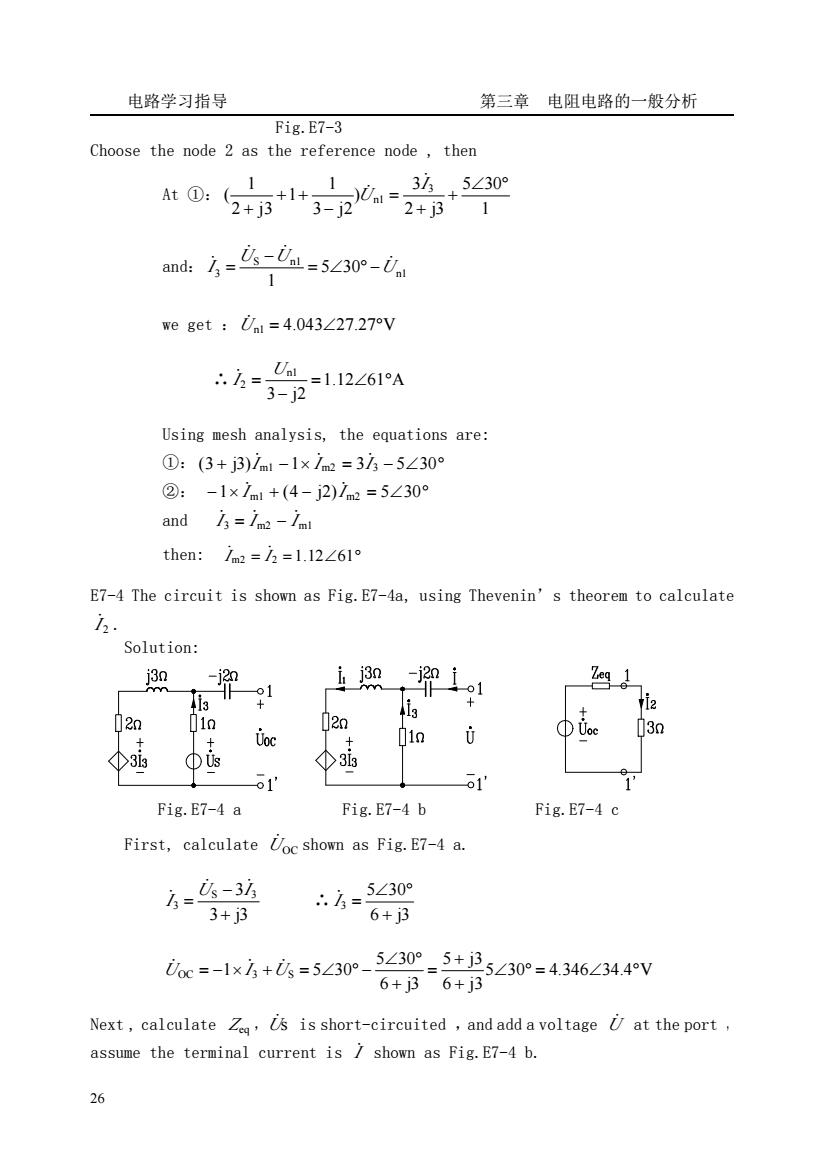
电路学习指导 第三章电阻电路的一般分析 Fig.E7-3 Choose the node 2 as the reference node,then 1 3/5∠30 At0:2+B*1+3-20=2+B+ ad方=么-么=5230m- we get Ul =4.043227.27V Using mesh analysis,the equations are: ①:(3+j3)7m1-1×1m2=33-5∠30° ②:-1x1nt+(4-j2)1nm=5∠30 and 3=/m2-/m then:im2=2=l.12∠61° E7-4 The circuit is shown as Fig.E7-4a,using Thevenin's theorem to calculate Solution: 01 Zeg 1 1 02n 20 Uoc 01n /3n 3 Φis ④3is 1 1 Fig.E7-4 a Fig.E7-4 b Fig.E7-4 c First,calculate Uoc shown as Fig.E7-4 a. 6=-3坊 3+3 6=5∠30 6+j3 ioc=-1x方+=5∠30°-5∠30°-5+i25∠30°=4346∠34.4v 6+j36+j3 Next,calculate Z,Us is short-circuited,and add a voltage U at the port assume the terminal current is shown as Fig.E7-4 b. 26
电路学习指导 第三章 电阻电路的一般分析 26 Fig.E7-3 Choose the node 2 as the reference node , then At ①: 1 5 30 2 j3 3 ) 3 j2 1 1 2 j3 1 ( 3 n1 ∠ ° + + = − + + + I U ̇ ̇ and: n1 S n1 3 5 30 1 U U U I ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ = ∠ ° − − = we get :U̇ n1 = 4.043∠27.27°V ∴ 1.12 61 A 3 j2 n1 2 = ∠ ° − = U I ̇ Using mesh analysis, the equations are: ①: (3 + j3)I m1 −1× I m2 = 3I 3 − 5∠30° ̇ ̇ ̇ ②: −1× I m1 + (4 − j2)I m2 = 5∠30° ̇ ̇ and I 3 I m2 I m1 ̇ = ̇ − ̇ then: I m2 = I 2 =1.12∠61° ̇ ̇ E7-4 The circuit is shown as Fig.E7-4a, using Thevenin’s theorem to calculate 2 I ̇ . Solution: Fig.E7-4 a Fig.E7-4 b Fig.E7-4 c First, calculate UOC ̇ shown as Fig.E7-4 a. 3 j3 S 3 3 3 + − = U I I ̇ ̇ ̇ ∴ 6 j3 5 30 3 + ∠ ° I = ̇ 5 30 4.346 34.4 V 6 j3 5 j3 6 j3 5 30 OC 1 3 S 5 30 ∠ ° = ∠ ° + + = + ∠ ° U = − × I +U = ∠ ° − ̇ ̇ ̇ Next , calculate Zeq ,Uṡ is short-circuited ,and add a voltage U̇ at the port , assume the terminal current is I ̇ shown as Fig.E7-4 b

电路学习指导 第三章电阻电路的一般分析 0=-j2i-3 {(2+j3)1+313+1=0(2) 4=1+3 (3) 50方=-2+) 6+3 insert it to equation (1).we get:2+ 6+j3 6+j3 s乙-号-3-1754-48阳 according Fig.E7-4 c, Uoc h=3+Z -=1.12∠61A E7-5 The circuit is shown as Fig.E7-5,using three meters to measure the parameters Rand L of the inductor coil,where V=50V,A=IA,W=30W /=50HZ.Determine:)the values of R L:(2)the complex power absorbed by the coil. Solution: The reading of the voltmeter and ammeter boths are the effective values,The reading of the powermeter is the average power absorbed by the coil (1)According to P=U/cos Fig.E7-5 p_30=0.6 We get cos50 =cos市0.6=53.13° Z=|A∠D=R+joL 月-n .R+joL=50∠53.13°=(30+j40)2 40 R=302,oL=402,∠=314=127mH 27
电路学习指导 第三章 电阻电路的一般分析 27 ⎪ ⎩ ⎪ ⎨ ⎧ = + + + + = = − − (3) (2 j3) 3 0 (2) j2 (1) 1 3 1 3 3 3 I I I I I I U I I ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ so I I ̇ ̇ 6 j3 (2 j3) 3 + − + = insert it to equation (1), we get :U I I I ̇ ̇ ̇ ̇ 6 j3 8 j9 6 j3 2 j3 j2 + − = + + = − + thus = ∠ − °Ω + − = = 1.795 74.93 6 j3 8 j9 eq I U Z ̇ ̇ according Fig.E7-4 c , 1.12 61 A 3 eq OC 2 = ∠ ° + = Z U I ̇ ̇ E7-5 The circuit is shown as Fig.E7-5, using three meters to measure the parameters R and L of the inductor coil ,where V = 50V , A =1A , W = 30W , f = 50HZ .Determine:(1)the values of R、 L;(2)the complex power S absorbed by the coil. Solution: The reading of the voltmeter and ammeter both are the effective values , The reading of the powermeter is the average power absorbed by the coil (1) According to P =UI cosΦ Fig.E7-5 We get 0.6 50 30 cos = = = UI P Φ = cos 0.6 = 53.13° -1 Φ Φ Z = Z ∠Φ= R + jωL = = 50Ω I U Z ∴ R + jωL = 50∠53.13° = (30 + j40)Ω R = 30Ω , ωL = 40Ω , 127mH 314 40 L = =