
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY2.Free energy changeIf G is negative number, the reaction goes spontaneouslysaid to be exergonic.If △G is positive number, the reaction does not gospontaneously, said to be endergonicIf △G is = O, the reactants are in equilibriumDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY If ΔG is negative number, the reaction goes spontaneously, said to be exergonic. If ΔG is positive number, the reaction does not go spontaneously, said to be endergonic. If ΔG is = 0, the reactants are in equilibrium. 2. Free energy change
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYATPasanenergycarrier.ATP consists of amolecule of adenosine towhich three phosphate groups are attached. Ifone phosphate is removed, adenosinediphosphate is produced; if two phosphates areremoved, adenosine monophosphate resultsDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ATP as an energy carrier • ATP consists of a molecule of adenosine to which three phosphate groups are attached. If one phosphate is removed, adenosine diphosphate is produced; if two phosphates are removed, adenosine monophosphate results
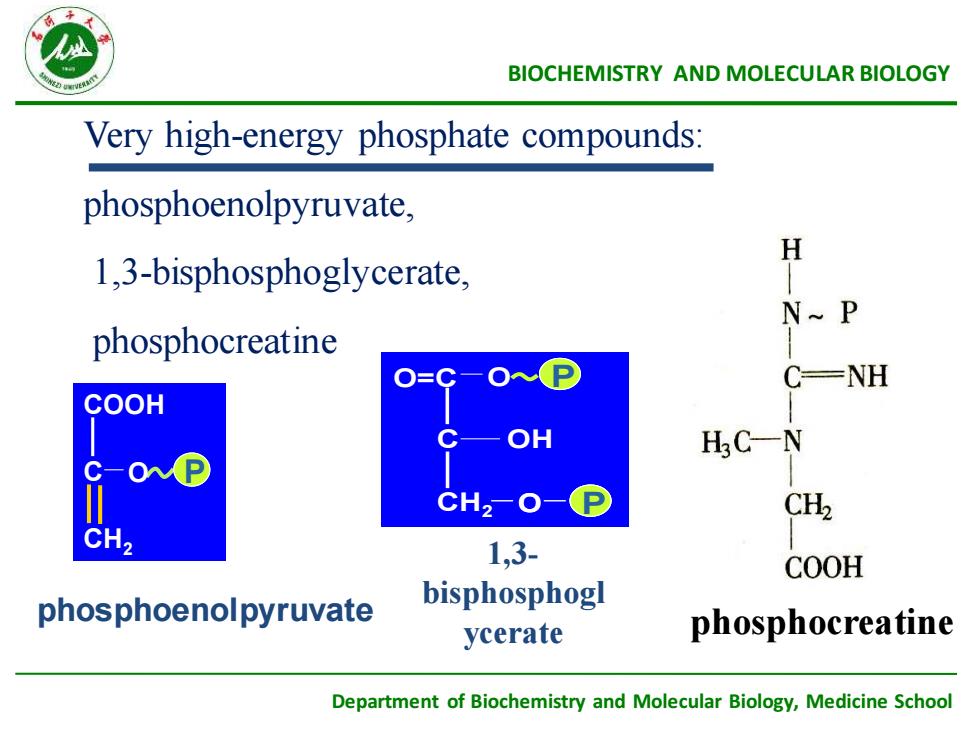
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYVery high-energy phosphate compounds:phosphoenolpyruvate,H1,3-bisphosphoglycerate,N~ PphosphocreatineCNHO=CCOOHOHHCNP0C-CH2-CH2CCH21,3-COOHbisphosphoglphosphoenolpyruvatephosphocreatineycerateDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY Very high-energy phosphate compounds: phosphoenolpyruvate, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate, phosphocreatine phosphoenolpyruvate COOH C CH2 O P 1,3- bisphosphogl ycerate O=C C OH CH2 O P O P phosphocreatine
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGYATP as an intermediate in phosphate transfer:ATP occupies an intermediate position on thebioenergetic scale of phosphate containingcompounds.Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ATP as an intermediate in phosphate transfer: ATP occupies an intermediate position on the bioenergetic scale of phosphate containing compounds
BIOCHEMISTRYANDMOLECULARBIOLOGY3.Electrontransport chainThe electron transport chain (respiratory chain):is pesent in the inner mitochondrial membrane and is thefinal common pathway by whichelectrons derived fromdifferent fuels of the body flow to oxygen.Fourcomplexcomplex INADH-CoQreductasecomplex IIsuccinate-CoQreductasecomplex IIICoQ-cytochromereductasecomplex IVcytochrome oxidaseDepartment of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,Medicine School
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Medicine School BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY The electron transport chain (respiratory chain): is pesent in the inner mitochondrial membrane and is the final common pathway by which electrons derived from different fuels of the body flow to oxygen. 3. Electron transport chain Four complex NADH-CoQ reductase complex Ⅰ succinate- CoQ reductase complex Ⅱ CoQ-cytochrome reductase complex Ⅲ cytochrome oxidase complex Ⅳ