
Chapter 19 OPERATIONS DROB BI NS ACOULTER AND VALUE CHAIN MANAGEMENT ©Prentice Hall,2002 19-1
Chapter 19 OPERATIONS AND VALUE CHAIN MANAGEMENT © Prentice Hall, 2002 19-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: -Describe the role of the transformation process in operations management Explain why operations management is important to all types of organizations Define value chain management Discuss the goal of value chain management Explain the organizational and managerial requirements for value chain management ©Prentice Hall,2002 19-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Describe the role of the transformation process in operations management – Explain why operations management is important to all types of organizations – Define value chain management – Discuss the goal of value chain management – Explain the organizational and managerial requirements for value chain management © Prentice Hall, 2002 19-2

Learning Objectives (cont. You should learn to: Describe the benefits of and obstacles to value chain management Discuss technology's role in operations management Describe how quality affects operations management Explain ISO 9000 and Six Sigma ©Prentice Hall,2002 19-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Describe the benefits of and obstacles to value chain management – Discuss technology’s role in operations management – Describe how quality affects operations management – Explain ISO 9000 and Six Sigma © Prentice Hall, 2002 19-3

What Is Operations Management? Operations Management the design,operation,and control of the transformation process that converts such resources as labor and raw materials into goods and services that are sold to customers every organization has an operations system that creates value by transforming inputs into outputs every unit in an organization also has an operations system ©Prentice Hall,2002 19-4
What Is Operations Management? Operations Management – the design, operation, and control of the transformation process that converts such resources as labor and raw materials into goods and services that are sold to customers – every organization has an operations system that creates value by transforming inputs into outputs • every unit in an organization also has an operations system © Prentice Hall, 2002 19-4
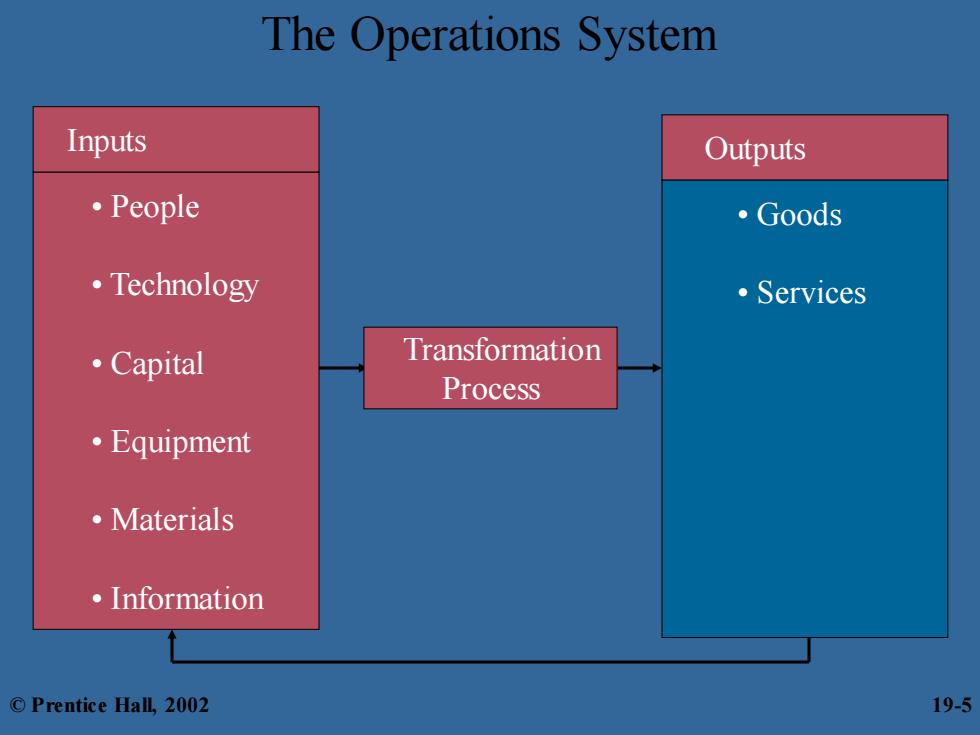
The Operations System Inputs Outputs ·People ·Goods ·Technology ·Services 。Capital Transformation Process ·Equipment ·Materials ·Information ©Prentice Hall,2002 19-5
The Operations System • People • Technology • Capital • Equipment • Materials • Information Inputs Outputs • Goods • Services Transformation Process © Prentice Hall, 2002 19-5