
Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING ROB B I N S COULTER GROUPS AND TEAMS ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-1
Chapter 15 UNDERSTANDING GROUPS AND TEAMS © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: Differentiate between formal and informal groups Describe the five stages of group development -Identify how roles and norms influence an employee's behavior -Describe the key components in the group behavior model Identify the advantages and disadvantages of group decision making ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Differentiate between formal and informal groups – Describe the five stages of group development – Identify how roles and norms influence an employee’s behavior – Describe the key components in the group behavior model – Identify the advantages and disadvantages of group decision making © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-2

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: -Explain the increased popularity of teams in organizations -Describe the four most common types of teams in organizations -List the characteristics of effective teams Identify how managers can build trust ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Explain the increased popularity of teams in organizations – Describe the four most common types of teams in organizations – List the characteristics of effective teams – Identify how managers can build trust © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-3

Understanding Group Behavior Group two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve particular goals foragroups-established by the organization -have designated work assignments and specific tasks different types exist informal groups-occur naturally in the workplace in response to the need for social contact ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-4
Understanding Group Behavior Group – two or more interacting and interdependent individuals who come together to achieve particular goals • formal groups - established by the organization –have designated work assignments and specific tasks –different types exist • informal groups- occur naturally in the workplace in response to the need for social contact © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-4
Examples of Formal Groups mmado These re the basic,rar groups determined byfomuthy reltiornshipsanddeoictedontheorgenizationalchat.Theytypicalyincludeamanagrandthose susprtttohimh. m These n tothrth dandsills fnis fromvaious wrkareas inmthirainoblm.fiatmas incudehmmbers have benndchos. S Theseare ssntially independnto that,inthir rain takemanagemniis snai and performance evaluaions. Task forces.These are tmporary goupracomplish aii task.One th task is mle,thisisan ©Prentice Hall,2002 15-5
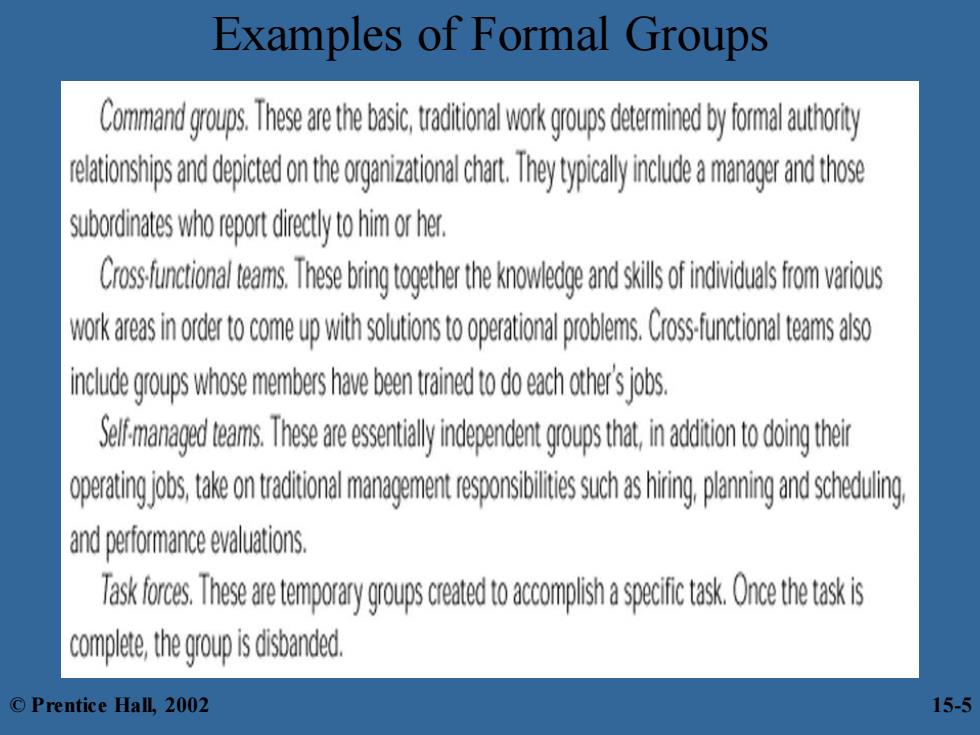
Examples of Formal Groups © Prentice Hall, 2002 15-5