
Chapter 6 DECISION MAKING: DROB BI NS ACOULTER THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER'S JOB ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-1
Chapter 6 DECISION MAKING: THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER’S JOB © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: -Outline the steps in the decision-making process Explain why decision making is so pervasive in organizations Describe the rational decision maker Contrast the perfectly rational and boundedly rational approaches to decision making Explain the role that intuition plays in the decision-making process ©Prentice Hal,2002 6-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Outline the steps in the decision-making process – Explain why decision making is so pervasive in organizations – Describe the rational decision maker – Contrast the perfectly rational and boundedly rational approaches to decision making – Explain the role that intuition plays in the decision-making process © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-2

Learning Objectives (cont. You should learn to: Identify the two types of decision problems and the two types of decisions that are used to solve them Differentiate the decision conditions of certainty. risk,and uncertainty Describe the different decision-making styles ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Identify the two types of decision problems and the two types of decisions that are used to solve them – Differentiate the decision conditions of certainty, risk, and uncertainty – Describe the different decision-making styles © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-3

Decision Making Decisions choices from two or more alternatives all organizational members make decisions Decision-Making Process a comprehensive,8-step process Step I-Identifying a Problem problem-discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs -must be such that it exerts pressure to act manager is unlikely to characterize a situation as a problem unless s/he has resources necessary to act ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-4
Decisions – choices from two or more alternatives – all organizational members make decisions Decision-Making Process – a comprehensive, 8-step process – Step 1 - Identifying a Problem • problem - discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs –must be such that it exerts pressure to act –manager is unlikely to characterize a situation as a problem unless s/he has resources necessary to act Decision Making © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-4
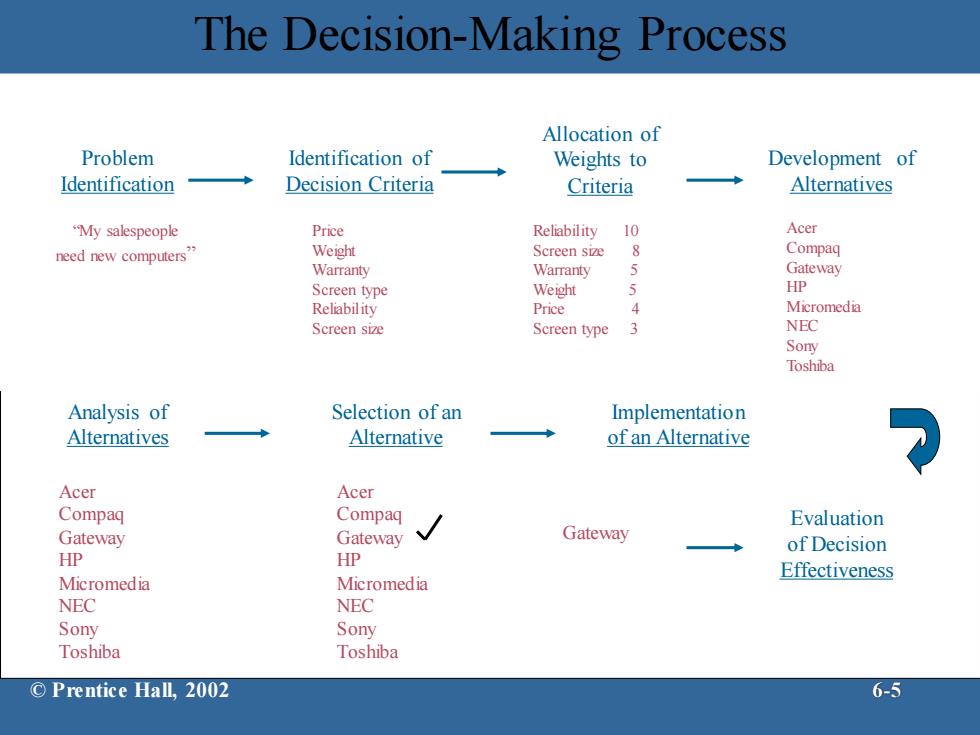
The Decision-Making Process Allocation of Problem Identification of Weights to Development of Identification Decision Criteria Criteria Alternatives "My salespeople Price Reliability 10 Acer need new computers” Weight Screen size 8 Compaq Warranty Warranty 5 Gateway Screen type Weight 5 HP Reliability Price 4 Micromedia Screen size Screen type 3 NEC Sony Toshiba Analysis of Selection of an Implementation Alternatives Alternative of an Alternative Acer Acer Compaq Compaq Evaluation Gateway Gateway Gateway of Decision HP HP Micromedia Micromedia Effectiveness NEC NEC Sony Sony Toshiba Toshiba ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-5
The Decision-Making Process Problem Identification “My salespeople need new computers” Identification of Decision Criteria Price Weight Warranty Screen type Reliability Screen size Allocation of Weights to Criteria Reliability 10 Screen size 8 Warranty 5 Weight 5 Price 4 Screen type 3 Development of Alternatives Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba Implementation of an Alternative Gateway Evaluation of Decision Effectiveness Analysis of Alternatives Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba Selection of an Alternative Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-5