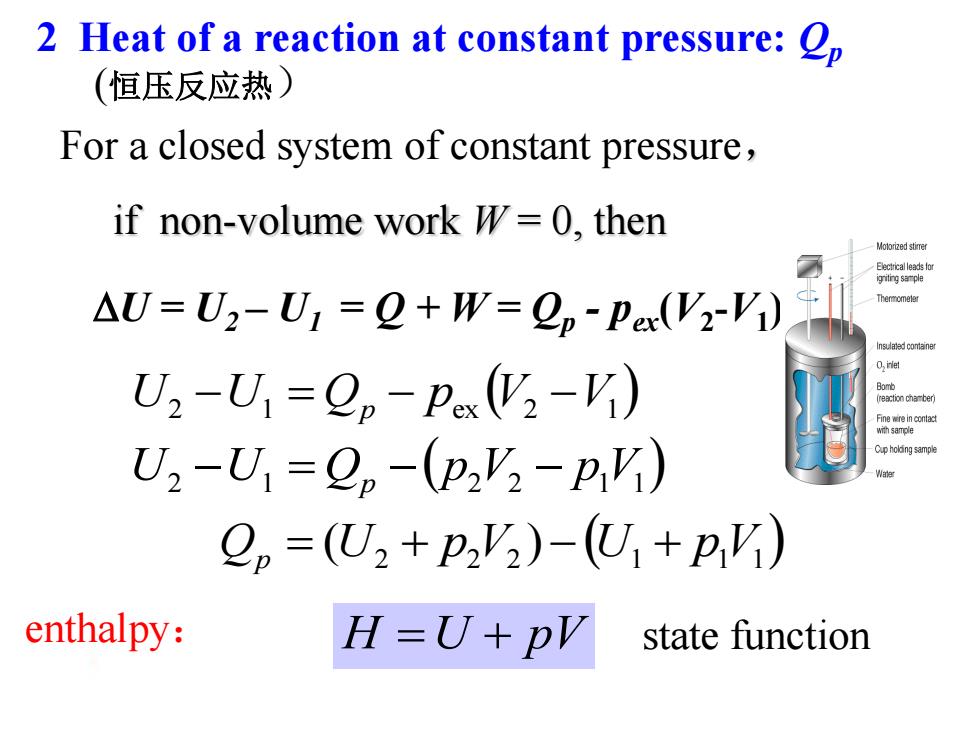
2 Heat of a reaction at constant pressure:p (恒压反应热) For a closed system of constant pressure, if non-volume work W=0,then Moio应ed stime Ecc达o AU=U2-U:=2+W=ep-Pex(V2-V1) nsadconisne U2-U1=Op-px(2-) eaction chamber Fine wire in contac with samole U2-U1=2,-(p2'2-pY) Cupholing sample 2p=(U2+P2'2)-(U+pY) enthalpy: H=U+pV state function
enthalpy: H U pV state function 2 2 2 1 1 1 Qp (U p V ) U pV U2 U1 Qp p2 V2 p1 V1 U2 U1 Qp pex V2 V1 U = U2 – U1 = Q + W = Qp - pex(V2 -V1 ) 2 Heat of a reaction at constant pressure: Qp For a closed system of constant pressure, if non-volume work W = 0, then (恒压反应热)

Q。=(U2+P'2)-(U,+pV) enthalpy: H=U+PV state function enthalpy change:A.H=H2-H p=△H Heat of a reaction at constant pressure is equal to the enthalpy change endothermic reactions AH-0; Prescript: exothermic reactions AH<0
enthalpy: enthalpy change: Qp = r H H U pV state function 2 2 2 1 1 1 Qp (U p V ) U pV endothermic reactions ΔH>0; exothermic reactions ΔH<0 Heat of a reaction at constant pressure is equal to the enthalpy change Prescript: r H = H2 –H1

3.Stoichiometric equation and the extent of a reaction (计量化学反应和反应进度) stoichiometric equation: aA+bB-→yY+zZ→0=-aA-bB+yY+z☑ 0=∑eB B B-stoichiometric number of substance B VA=-a,VB=-b,Vy=y,V7=Z extent of reaction(5,Zeta发音):反应进展的程度 s- △nB_B(5)-nB(0) the unit ofξis mol VB VB
3. Stoichiometric equation and the extent of a reaction B— stoichiometric number of substance B stoichiometric equation: νA= -a, νB= -b, νY= y, νZ= z B B B B B ( ) (0) n n n extent of reaction (ξ, Zeta发音):反应进展的程度 the unit of ξ is mol B 0 B B A B Y Z a b y z 0 aA bB yY zZ (计量化学反应和反应进度)

N2(g)+3H2(g)→2NH,g) 5 to:nB/mol 3.0 10.0 0 0 1:ng/mol 2.0 7.0 2.0 5 2:ng/mol 1.5 5.5 3.0 52 s △n,(N2)_(2.0-3.0)mo vN2) =1.0mol -1 △n,(H2))_(7.0-10.0)mol v(H2) =1.0mol -3 51= △n,(NH3)_(2.0-0)mol =1.0mol vNH2) 2 52=1.5mol
N g 3H g 2NH g 2 2 3 t0 : nB /mol 3.0 10.0 0 0 t1 : nB /mol 2.0 7.0 2.0 t2 : nB /mol 1.5 5.5 3.0 1 2 1.0mol 1 (2.0 3.0)mol N N 2 1 2 1 n 1.5mol 2 1.0mol 2 (2.0 0)mol NH NH 3 1 3 1 n 1.0mol 3 (7.0 10.0)mol H H 2 1 2 1 n

N,g)+H,g)→NH,g) t=0 3.0 10.0 0 (mol) t= 2.0 7.0 2.0 (mol) △n=(2.0-3.0)mol =2.0mol V(N2) -1/2 The extent of a reaction g must match the corresponding stoichiometric equation
The extent of a reaction ξ must match the corresponding stoichiometric equation. H g NH g 2 3 N g 2 1 2 2 3 2.0mol 1/ 2 (2.0 3.0)mol 2 2 N ' N 1 n 1 t t 2.0 7.0 2.0 (mol) t 0 3.0 10.0 0 (mol)