
solution of bovine serum albumin(BSA)(see Note 4). 3.2 Microassay 1.To 1.0mL of aqueous protein solution containing 0.5-1.0 ug of protein/mL add 1 mL of SWR. 2.Incubate at 60 C for 1 h. 3.Cool,and read the absorbance at 562 nm. Notes 1.Reagents A and Bare stable indefinitely at room temperature.They may be purchased ready prepared from Pierce,Rockford,IL. 2.The sensitivity of the assay can be increased by incubating the samples longer.Altematively,if the color is becoming too dark.heating can be stopped earlier.Take care to treat standard on e the olor dovdlost ble tt I 4.Note.that like the Lowry assay.response to the BCA assay is dependent on the amino acid composition of the protein.and therefore an absolute concentration of protein cannot be determined.The BSA standard curve can only therefore be used to compare the relative protein coneentrationofsinmilarproteinsolutions. s.Some re sinterfere with the BCA assay,but nothing like asm any as with the Lowry assay (see Table 1).The presence of lipids gives excessively high absorbances with this assay. Variations produced by buffers with sulfhydryl agents and detergents have been deseribed. 6.Since the method relies on the use of Cu,the presence of chelating agents such as EDTA will of course severely interfere with the method.However.it may be possible to overcome such mains high to the assay (see Table 1).In each case it is of course necesary to run an appropriate control sample to allow for any residual color development.A modification of the assay has been deseribed that overcomes lipid interference when measuring lipoprotein protein content. Table 1 Effect of Selected Potential Interfering Compounds" BCA assay (pg BSA found) Lowry assay (ug BSA found) Sample (50 gg BSA) Water blank Interference blank Water blank Interference blank in the following corrected 0.00 420 43 0.IN NaOH 49.00 50.60 5060 0.2%Sodium azide 51.10 50.90 4920 49.00 002%Sodium azide 51.10 51.00 49.50 49.60 1.0 M Sodium由Lorid 51.30 51.10 50.20 50.10 100 mM EDTA(4 Na 50 mM EDTA (4 Na 20 29.40 10 mM EDTA (4 Na) 48.80 49.10 33.60 12.70 50 mM EDTA (4 Na).pH 11.25 31.50 32.80 T2.30 5.00
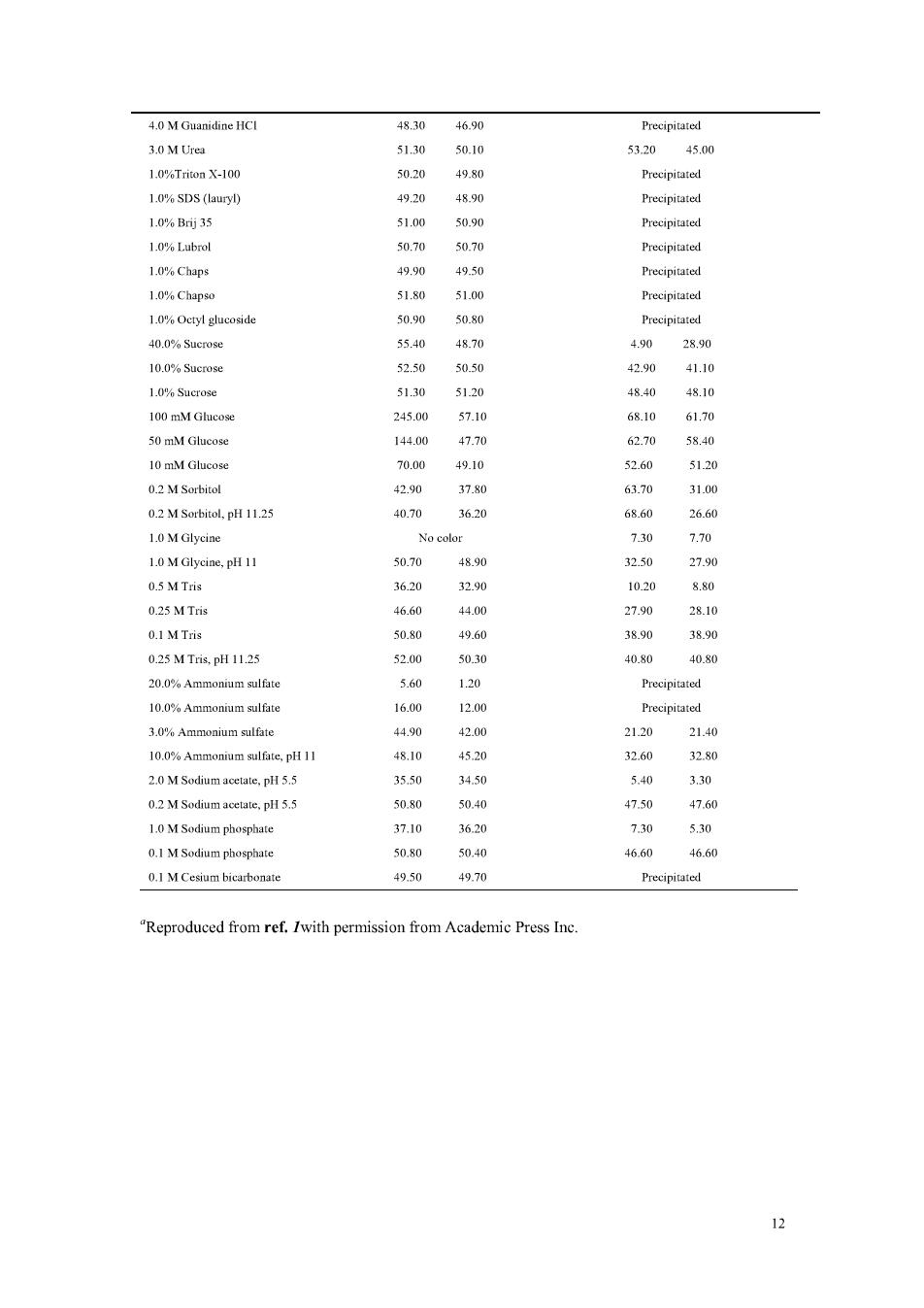
4.0 M Guanidine HCI 48.30 46.90 Precipitated 5320 45 1.0%Triton X-100 1.0%SDS (lauryl) 4920 Precipitated 1.0%B35 51.00 50.90 Precipitated 1.0%Lubrol 50.70 50.70 1.0%Chaps 49.50 1.0%Chap 50.90 50.80 40.0%Sucrose 5540 0 28.90 10.0%Sucrose 52.50 50.50 42.90 41.10 51.30 4840 4810 2450 68.10 50 mM Glucose 140 10 mM Glueose 70.00 49.10 0.2 M Sorbitol 4290 3780 6汤 31.0 0.2 M Sorbitol.pH 11.25 40.70 3630 26.60 1.MGlyciae 2.70 1.0 MGlyciae,p 0.5 M Tris 3620 3290 0.25 MTris 4660 27.9 28.10 01 M Tris 508 49.60 3890 3890 0.25MT,pH1125 520 50.30 40.80 40.s0 3.0%Ammonium sulfate 4490 420 2120 2140 10.0%Ammonium sulfate.pH 11 48.10 4520 2.0 M Sodium acetate.pH 5.5 3550 3450 5.40 3.30 02M Sodum 5080 1.0 M Sodium phosphate 3620 730 550 0.1 M Sodium phosphate 50.80 50.40 46. .6 0.I M Cesium bicarbonate 49.50 49.70 Reproduced from ref.Iwith permission from Academic Press Inc

Experiment 2 Purification of Y-globins from Human Serum Purpose 1.To master the principle and method of salting ou method in protein 2.To learn the principle and method of gel filtration in the extraction and purification of biological macromolecules. Principle The globins in human serum are classified into albumin,a-globins.B-globins and Y-globins.which can be separated by ammonium sulfate step-precipitation method depending on the difference of solubility.Pure Y-globins are collected afier removing salts from the fractions by gel filtration. Methods Step 1,Salting out (1).Add 1.0 ml serum into a centrifugal tube.and add 1.0 ml phosphate buffer saline (PB).Mix adequately.Then.add ml ammonium sulfate drop by drop,shaking the mixture constantly during the adding of ammonium sulfate After calming down at room temperature for 10-20 minutes.spin down the precipitation by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 10 min.Pour the supernatant into a clean tube (labeled A.which are mainly albumins).take the precipitation to(2). (2),Dissolve the precipitation in 1.0 ml PBS adequately in the centrifugal tube add 0.5 ml saturated ammonium sulfate drop by drop,remember keeping shaking the mixture.After calming down at room temperature for 10-20 minutes.spin down the precipitation by centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 10 min.Pour the supernatant into a clean tube (labeled B.which are mainly a-and B-globins),the precipitation are primary purif fied -globins with salt.To get purer Y-globins,this step (2)can b repeated for 1-2 times. Step 2,Desalting (1)Colm packing.Fix the glass com(mn) shelf,keep it vertical and the bottom switch on.Stir up the Sephadex G-25 beads gently and pour about 10 ml into the column rapidly.When the column is filled,turn the bottom switch off.Knock the column gently by finger.Then turn the bottom switch on and let the liquid drop down slowly,about 8-10 drops per minute.When the

surface of the liquid is cqual to the surfacc of the beads.turn the bottom switch tion:the (Preparation of Sephadex G-25 is listed at the end of this protocol) (2)Desalting.The y-globins precipitation in the centrifugal tube is dissolved in nto dissolve it thoroughly.Use the burette to remove the Y-globinsonto the co crefully,do not disturb the beads and ther turn the bottom switch on.Let the buffer drop down slowly (8-10 drops per min) When all the y-globins are loaded into the column,add 1.0 ml PBS onto the beads carefully following the inside wall of the column.When most PBS is loaded into the (3)Collection.After the sample is loaded into the column,begin to collect the flow through.1.0 ml for each tube and total 12 tubes are collected. (4)Checking the collected fractions.Take one drop of sar mple fr rom each of the drop reaction board respectively Add on rop trichlorine acetate to each well.Record the phenomenon,label a+'sign for precipitation and a-'sign for clear.Conserve one tube of sample that has heaviest precipitation,which will be used in next experiment. (5)Recycle the Sephadex G-25 beads Reagents 1.human scrum phosphate buffer saline(PBS):0.%NaCl in 0.01 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) 0.01 M pH 7.phosphate buffer is made by 20folds dilution of the mixture of7.0m 0.2 M NaHPO and 28.0 ml 0.2 M NaH,POa. 3.pH 7.2 saturated ammonium sulfide:adjust the pH of saturated ammonium sulfide to 7.2 using ammonia. 4.prepa tion of Sephadex G-25:1g Sephadex G-25 powder is treated in boiling in 10 ml PBS

Experiment 3 Cellulose Acetate Membrane Electrophoresis of Serum Protein Purpose: Master the principle method and application of acetate membrane electrophoresis to separate the various protein fractions in serum. Principle: Electrophoresis an important technique for the oteins based on the migratio of charged proteins in an electric ield,is especially useful as an analytical method.Under different pH conditions.the amount of net charges that a protein molecule carried is different.When pH is higher than the pl (isoelectric piont). the protein molecule carries net negative charges and will move to anode,whereas pH to cathode .The speed of the movement depe nds mainly on number of charges,molec ar weigh cular shape. molecules that have more charges and lower molecular weight move faster than others. Cellulose acetate membrane elctrophoresis,which was first developed by Kohn in1956, ses cellul acetate film a he supporting me This te chniqu several advantages:time-save procedure,less sample needed (can less than 10 microlitres).high resolution and clear results.The cellulose acetate membrane is more convenient for conservation and quantitive analysis than agarose gel electrophoresis, starch gel electrophoresis and SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. Serum proteins are grossly separated into albumin and globulins.Albumin is the protein of highest concentration in the serum (plasma is serum plus fibrinogen). Albumin is a carrier of many small molecules but is also of prime importance in maintaining the osmotic pressure of the blood(that is keeping the fluid from leaking out into the tissues).Globulins are roughly divided into alpha-1,alpha-2.beta,and a globulin These can be separated and quantitated in laboratory by electrophoresis and densitometry. Use cellulose acetate film as the supporting medium and separate SERUM PROTEIN by electrophoresis in electric field.The blood serum is placed on specially treated cellulose etate film and e a electric field.Bec ause the pH of with different speeds.The various proteins migrate (move on the film)to form bands that indicate the relative proportion of each protein fraction.After electrophoresis, immerse cellulose acetate film into the dye solution.Then every bands of serum 15