Differential Heb Learning >Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCMs) >Adaptive Causal Inference >Klopfs Drive Reinforcement Model >Concomitant Variation as Statistical Covariance >Pulse-Coded DifferentialHebbian Learning 2006.10.30
2006.10.30 Differential Heb Learning ➢ Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCMs) ➢ Adaptive Causal Inference ➢ Klopf’s Drive Reinforcement Model ➢ Concomitant Variation as Statistical Covariance ➢ Pulse-Coded Differential Hebbian Learning
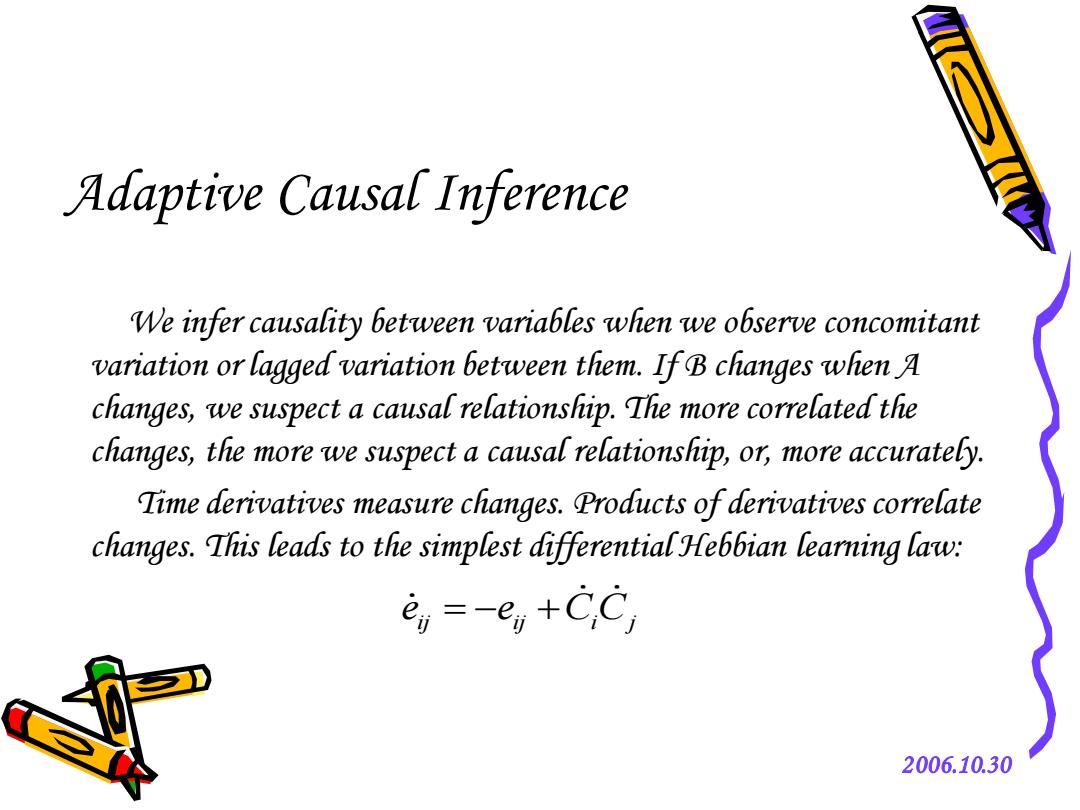
Adaptive Causal Inference We infer causality between variables when we observe concomitant variation or lagged variation between them.If B changes when A changes,we suspect a causal relationship.The more correlated the changes,the more we suspect a causal relationship,or,more accurately. Time derivatives measure changes.Products of derivatives correlate changes.This leads to the simplest differential Hebbian learning law: e,=-e,+CC, 2006.10.30
2006.10.30 Adaptive Causal Inference We infer causality between variables when we observe concomitant variation or lagged variation between them. If B changes when A changes, we suspect a causal relationship. The more correlated the changes, the more we suspect a causal relationship, or, more accurately. Time derivatives measure changes. Products of derivatives correlate changes. This leads to the simplest differential Hebbian learning law: ij ij i j e e C C = − +
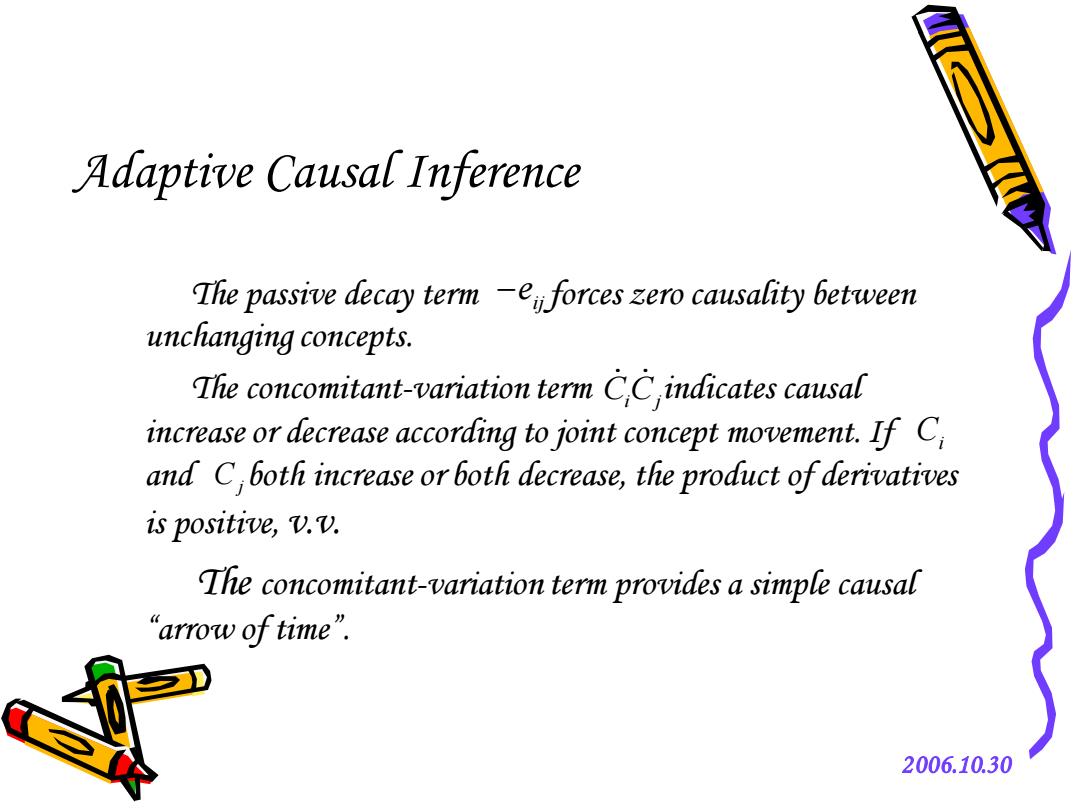
Adaptive Causal Inference The passive decay term-eforces zero causality between unchanging concepts. The concomitant-variation term CCindicates causal increase or decrease according to joint concept movement.If C and C both increase or both decrease,the product of derivatives is positive,V.V. The concomitant-variation term provides a simple causal 'arrow of time". 2006.10.30
2006.10.30 Adaptive Causal Inference The passive decay term forces zero causality between unchanging concepts. The concomitant-variation term indicates causal increase or decrease according to joint concept movement. If and both increase or both decrease, the product of derivatives is positive, v.v. The concomitant-variation term provides a simple causal “arrow of time”. ij −e CCi j Ci Cj
Differential Heb Learning >Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCMs) >Adaptive Causal Inference >Klopfs Drive Reinforcement Model >Concomitant Variation as Statistical Covariance >Pulse-Coded DifferentialHebbian Learning 2006.10.30
2006.10.30 Differential Heb Learning ➢ Fuzzy Cognitive Maps (FCMs) ➢ Adaptive Causal Inference ➢ Klopf’s Drive Reinforcement Model ➢ Concomitant Variation as Statistical Covariance ➢ Pulse-Coded Differential Hebbian Learning