
8.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale 8.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water 8.2.2 The pH scale
§ 8.2 Ionization equilibrium of water and the pH scale 8.2.2 The pH scale 8.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water
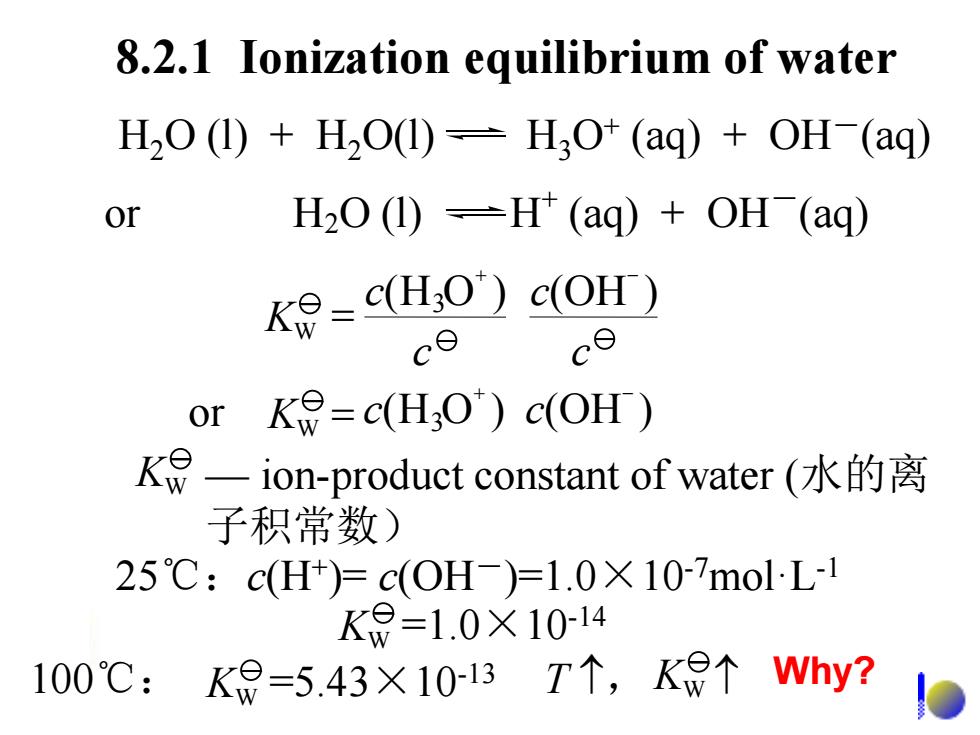
8.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water H2O (1)+HO(1)=H3O+(aq)+OH (aq) or H2O(1)-H(aq)+OH (ag) Ke=c(HO)c(OH) ce or K=c(H;O)c(OH) K9一ion-product constant of water(水的离 子积常数) 25℃:c(H+)=c(0H-)=1.0×107molL1 K8=1.0×10-14 100℃:kg=5.43×10-1B7个,Ke个why?D
8.2.1 Ionization equilibrium of water H2O (l) + H2O(l) H3O+ (aq) + OH-(aq) or H2O (l) H + (aq) + OH-(aq) — ion-product constant of water (水的离 子积常数) KW 25℃:c(H+ )= c(OH-)=1.0×10-7mol·L-1 100℃: =1.0×10 K -14 W =5.43×10 K -13 W T , KW (H O ) (OH ) 3 + - or K = c c W (H O ) (OH ) 3 + - = c c c c KW Why?
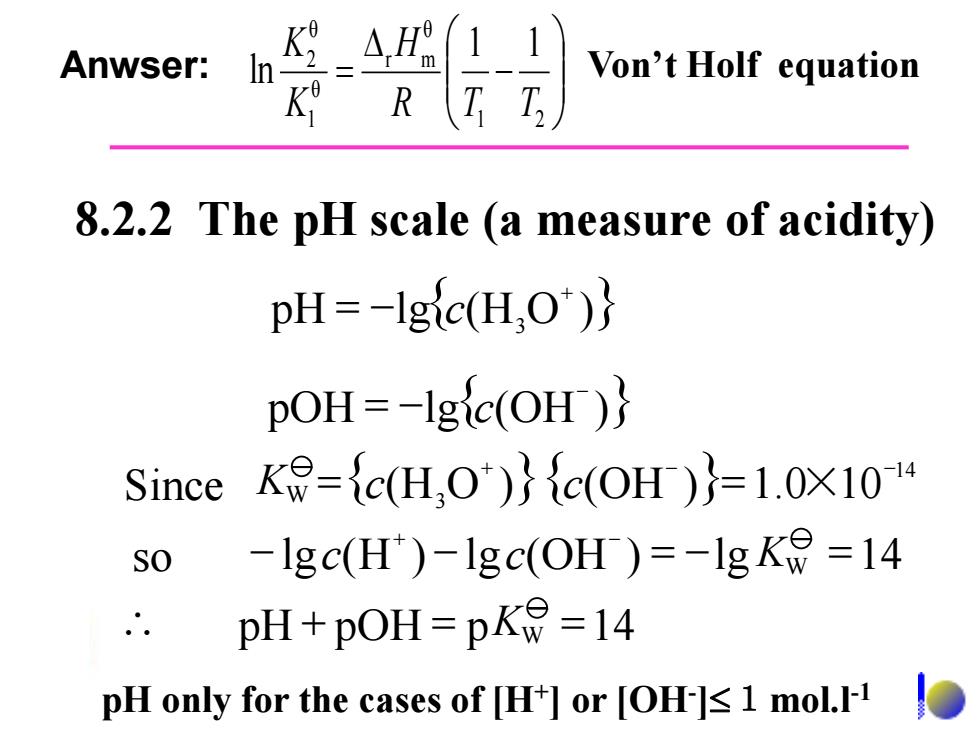
11 Anwser: Von't Holf equation K R T D 8.2.2 The pH scale (a measure of acidity) pH=-Igic(H.O")} pOH=-1gic(OH)} Since K=c(H,O')c(OH )=1.0X101 SO -Igc(H)-Igc(OH )=-1gK=14 pH+pOH=p=14 pH only for the cases of [H+]or [OH 1 mol.I-1
pOH = -lg{ (OH )} - c pH lg{ (H O )} 3 = - + c 8.2.2 The pH scale (a measure of acidity) { (H O )}{ (OH )} 1.0 10 14 = 3 = × + - - Since KW c c - lg (H ) - lg (OH ) = -lg =14 + - so c c KW \ pH + pOH = p KW =14 - \ = 1 2 θ r m θ 1 θ 2 1 1 ln R T T H K K Anwser: Von’t Holf equation pH only for the cases of [H+ ] or [OH- ]1mol.l-1

Q?Calculate the pH of a solution of 1.0X108mol.dm-3 HCIH2O。 Answer: pH=-g0x08=8
Q? Calculate the pH of a solution of 1.0×10-8mol.dm-3 HCl/H2O。 Answer: pH=-lg1.0x10-8 = 8

8.3 Equilibrium of ionization for weak acids and bases 8.3.1 Equilibrium of ionization for monoprotic acids and bases 8.3.2 Equilibrium of ionization for polyprotic acids -8.3.3 Acid-base equilibrium in salt(!?) solution
§ 8.3 Equilibrium of ionization for weak acids and bases 8.3.3 Acid-base equilibrium in salt(!?) solution 8.3.2 Equilibrium of ionization for polyprotic acids 8.3.1 Equilibrium of ionization for monoprotic acids and bases