
3.6晶格振动的实验观测 三種装 非弹性X-射线散射 三.Raman散射和Brilouin散射 四.远红外和红外吸收光谱 五.非弹性中子散射 参考:黄昆书3.6节,Kittel8版4.5节 P.Bruesch Phonons:Theory and Experiments I,Ⅱ,Ⅲ 其中第2卷是测量方法
3.6 晶格振动的实验观测 参考:黄昆 书 3.6 节, Kittel 8 版 4.5 节 P.Bruesch Phonons: Theory and Experiments Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ 其中第2卷是测量方法。 一 . 一般描述 二. 非弹性X-射线散射 三. Raman 散射和Brilouin 散射 四. 远红外和红外吸收光谱 五. 非弹性中子散射
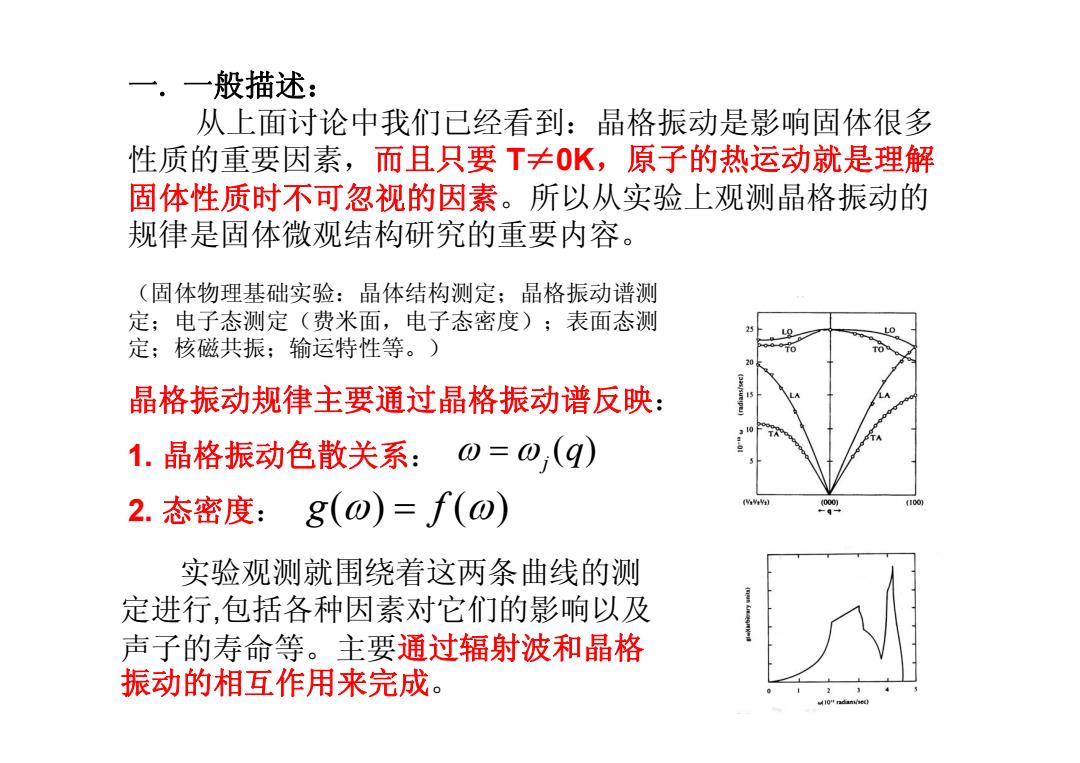
一.一般描述: 从上面讨论中我们已经看到:晶格振动是影响固体很多 性质的重要因素,而且只要T≠0K,原子的热运动就是理解 固体性质时不可忽视的因素。所以从实验上观测晶格振动的 规律是固体微观结构研究的重要内容。 (固体物理基础实验:晶体结构测定;晶格振动谱测 定;电子态测定(费米面,电子态密度);表面态测 9 LO 定;核磁共振:输运特性等。) 9T0 晶格振动规律主要通过晶格振动谱反映: 1.晶格振动色散关系:0=0,((q) 2.态密度:8(0)=f(0) 实验观测就围绕着这两条曲线的测 定进行,包括各种因素对它们的影响以及 声子的寿命等。主要通过辐射波和晶格 振动的相互作用来完成
一. 一般描述: 从上面讨论中我们已经看到:晶格振动是影响固体很多 性质的重要因素,而且只要 T≠0K,原子的热运动就是理解 固体性质时不可忽视的因素。所以从实验上观测晶格振动的 规律是固体微观结构研究的重要内容。 晶格振动规律主要通过晶格振动谱反映: 1. 晶格振动色散关系: 2. 态密度: ( ) j ω = ω q g f () () ω = ω 实验观测就围绕着这两条曲线的测 定进行,包括各种因素对它们的影响以及 声子的寿命等。主要通过辐射波和晶格 振动的相互作用来完成。 (固体物理基础实验:晶体结构测定;晶格振动谱测 定;电子态测定(费米面,电子态密度);表面态测 定;核磁共振;输运特性等。)

Table 1.1.Experimental methods used to study phonons Method Abbreviations Measurement of Main Informations Far-infrared and FIR the intensity of transmitted Infrared dielectric properties infrared spectroscopy IR or reflected light of insulators and semiconductors; 研究声子的 as a function of frequency optical phonons ato Raman spectroscopy the intensity of scattered light as Optical phonons at g0 a function of frequency Polaritons 实验方法 Brillouin spectroscopy as for Raman spectroscopy Acoustic modes at small wave vectors g Diffuse X-ray scattering the intensity of scattered X-rays Limited information about phonon as a function of momentum transfer dispersion Inelastic neutron INS the intensity of scattered neutrons Phonon dispersions,density of scattering as a function of energy and stales momentum transfer Ultrasonic methods US the velocity and attenuation of Sound velocities ultrasonic pulses phonon-phonon interactions Inelastic electron IETS current-voltage characteristics of Vibrational properties of thin tunneling spectroscopy metal-insulator-metal tunneling films and adsorbates junctions Point contact PCS current-voltage characteristics of Electron-phonon interaction in spectroscopy point contacts between two metals metals and alloys Electron energy loss EELS the intensity of backscattered elec- Optical surface phonons spectroscopy trons as a function of energy transfer Inelastic molecular IMBS the intensity of backscattered mole- Dispersion of acoustic surface beam spectroscopy cules as a function of energy and phonons momentum transfer Attenuated total ATR the intensity of light totally reflec- Vibrational properties of insula reflection ted within an ATR crystal in direct tors and semiconductors contact with the sample as a function of frequency Frustrated total FTR the intensity of light totally reflec- 见Phonons p7 Dispersion of optical surface refection ted within a prism which is separated phonons from the sample by a small air gap,as a function of frequency Infrared reflection IRAS the intensity of multiply reflected Vibrational properties of thin absorption spectroscopy light between two metal plates covered films and adsorbates with the thin flm as a function of frequency
研究声子的 实验方法 见Phonons p7

其中最重要、最普遍的方法是: Far-Infrared and (FIR) 电磁波 Infrared Spectroscope (IR) 远红外和红外光谱 Raman Spectroscope (R) 喇曼光谱 Brilouin Spectroscope (B) 布里渊散射谱 Diffuse X-Ray Scattering X射线漫散射 Inelastic neutron Scattering (INS) 非弹性中子散射 Ultrasonic methods (US) 超声技术 Inelastic electron tunnelling Spectroscope (IETS) 非弹性电子隧道谱
Far- Infrared and (FIR) Infrared Spectroscope (IR) 远红外和红外光谱 Raman Spectroscope (R) 喇曼光谱 Brilouin Spectroscope (B) 布里渊散射谱 Diffuse X-Ray Scattering X 射线漫散射 Inelastic neutron Scattering (INS) 非弹性中子散射 Ultrasonic methods (US) 超声技术 Inelastic electron tunnelling Spectroscope (IETS) 非弹性电子隧道谱 其中最重要、最普遍的方法是: 电磁波

几种辐射波的能量关系如下: 电磁波: &hkc hs C是光速,Ω是圆频率。 电子或中子: 方2k2 中子质量是电子质量的 2m 1836倍 声波: 0=V,9 辐射波照射晶体后,由于和晶格振动发生了能量交换, 吸收或者激发出一个声子而改变能量和方向。测出辐射波的 能量和方向的变化量,即可确定出一个声子的能量和波矢。 衣=k0+q 2=2±w(q) 这种过程也可能由几个声子同时参与,但多数情形和一 个声子发生相互作用的几率要大的多,称为一级过程
几种辐射波的能量关系如下: 2 2 2 kc k m ε ε = = Ω = = = = 电磁波: 电子或中子: c 是光速, 是圆频率。 中子质量是电子质量的 1836 倍 s 声波: ω = v q 辐射波照射晶体后,由于和晶格振动发生了能量交换, 吸收或者激发出一个声子而改变能量和方向。测出辐射波的 能量和方向的变化量,即可确定出一个声子的能量和波矢。 Ω 0 0 ( ) kk q ω q = + Ω=Ω ± GG G 这种过程也可能由几个声子同时参与,但多数情形和一 个声子发生相互作用的几率要大的多,称为一级过程