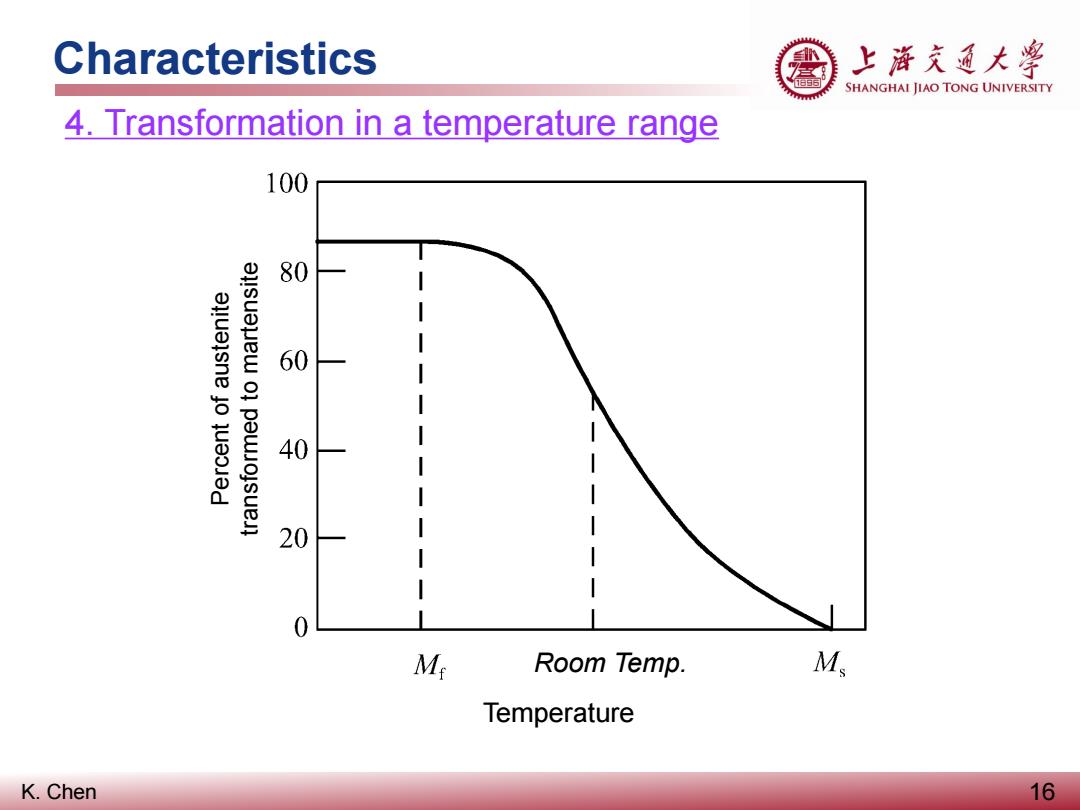
Characteristics 上游充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 4.Transformation in a temperature range 100 80 60 40 20 0 M Room Temp. M Temperature K.Chen 16
K. Chen Characteristics 16 4. Transformation in a temperature range Percent of austenite transformed to martensite Temperature Room Temp
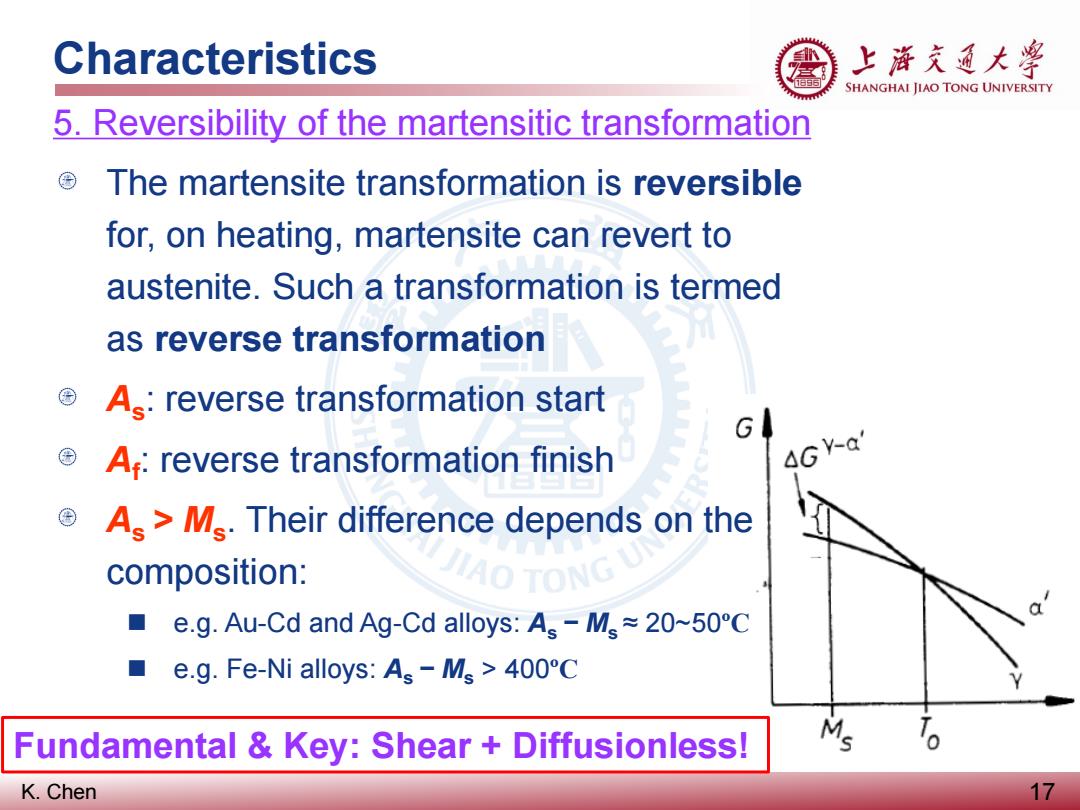
Characteristics 上浒充通大兽 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 5.Reversibility of the martensitic transformation The martensite transformation is reversible for,on heating,martensite can revert to austenite.Such a transformation is termed as reverse transformation A:reverse transformation start G A:reverse transformation finish 4GY-a As>M.Their difference depends on the composition: AO TONG ■ e.g.Au-Cd and Ag-Cd alloys:As-M~20~50C e.g.Fe-Ni alloys:As-Ms>400C Fundamental Key:Shear Diffusionless! M K.Chen 17
K. Chen Characteristics 17 5. Reversibility of the martensitic transformation The martensite transformation is reversible for, on heating, martensite can revert to austenite. Such a transformation is termed as reverse transformation As: reverse transformation start Af : reverse transformation finish As > Ms. Their difference depends on the composition: e.g. Au-Cd and Ag-Cd alloys: As − Ms ≈ 20~50ºC e.g. Fe-Ni alloys: As − Ms > 400ºC Fundamental & Key: Shear + Diffusionless!

Thermodynamics h 上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.Thermodynamic conditions © Driving force:AG-=Ga-G ©Ms<To→△GY+a,<0 as driving force 4G Y-a M K.Chen 18
K. Chen Thermodynamics 18 1. Thermodynamic conditions Driving force: △Gγ→α′ =Gα′ -Gγ Ms < T0 △Gγ→α′ <0 as driving force
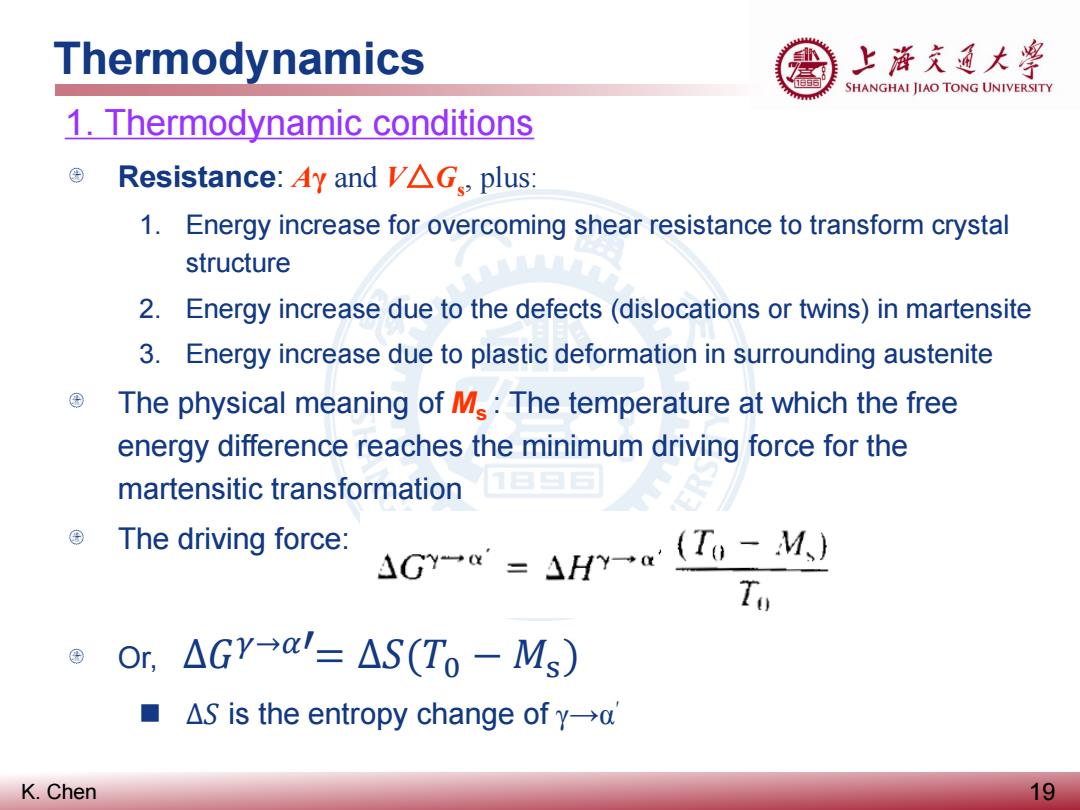
Thermodynamics 上游充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.Thermodynamic conditions ©Resistance:Ay and V△Gs,plus: 1.Energy increase for overcoming shear resistance to transform crystal structure 2.Energy increase due to the defects(dislocations or twins)in martensite 3.Energy increase due to plastic deformation in surrounding austenite The physical meaning of M:The temperature at which the free energy difference reaches the minimum driving force for the martensitic transformation The driving force: AGY-=H-a (To-M.) To © Or,△GY-a'=△S(T0-Ms) ■AS is the entropy change of y-→a K.Chen 19
K. Chen Thermodynamics 19 1. Thermodynamic conditions Resistance: Aγ and V△Gs , plus: 1. Energy increase for overcoming shear resistance to transform crystal structure 2. Energy increase due to the defects (dislocations or twins) in martensite 3. Energy increase due to plastic deformation in surrounding austenite The physical meaning of Ms : The temperature at which the free energy difference reaches the minimum driving force for the martensitic transformation The driving force: Or, ∆𝐺𝐺𝛾𝛾→𝛼𝛼′ = ∆𝑆𝑆(𝑇𝑇0 − 𝑀𝑀s) ∆𝑆𝑆 is the entropy change of γ→α′

Thermodynamics 上浒充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 1.Thermodynamic conditions 4G Y-a The difference btw.M.and A decreases with the plastic deformation. Austenite is plastically deformed at T's higher than M.>Induce martensite transformation>increase M,to Ma Martensite is plastically deformed at T's 0'-Y lower than A.>Induce reverse transformation>Decrease A,to Ad A M:Deformation-induced martensite transformation start temperature (upper Y→0' limit is To) A:Deformation-induced austenite Ms transformation start temperature (lower M limit is To) Content of alloying element K.Chen 20
K. Chen Content of alloying element Temperature Thermodynamics 20 1. Thermodynamic conditions The difference btw. Ms and As decreases with the plastic deformation. Austenite is plastically deformed at T’s higher than Ms Induce martensite transformation increase Ms to Md Martensite is plastically deformed at T’s lower than As Induce reverse transformation Decrease As to Ad Md: Deformation-induced martensite transformation start temperature (upper limit is T0) Ad: Deformation-induced austenite transformation start temperature (lower limit is T0) Md Ad