
上游充通大率 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Principles of Materials Processing Part Ill 全属材料热处理原理 Heat Treatment Principles of Metals Lecturer:Ke Chen 及是 2017-05-11
Principles of Materials Processing Part III - 金属材料热处理原理 Heat Treatment Principles of Metals Lecturer: Ke Chen 2017-05-11
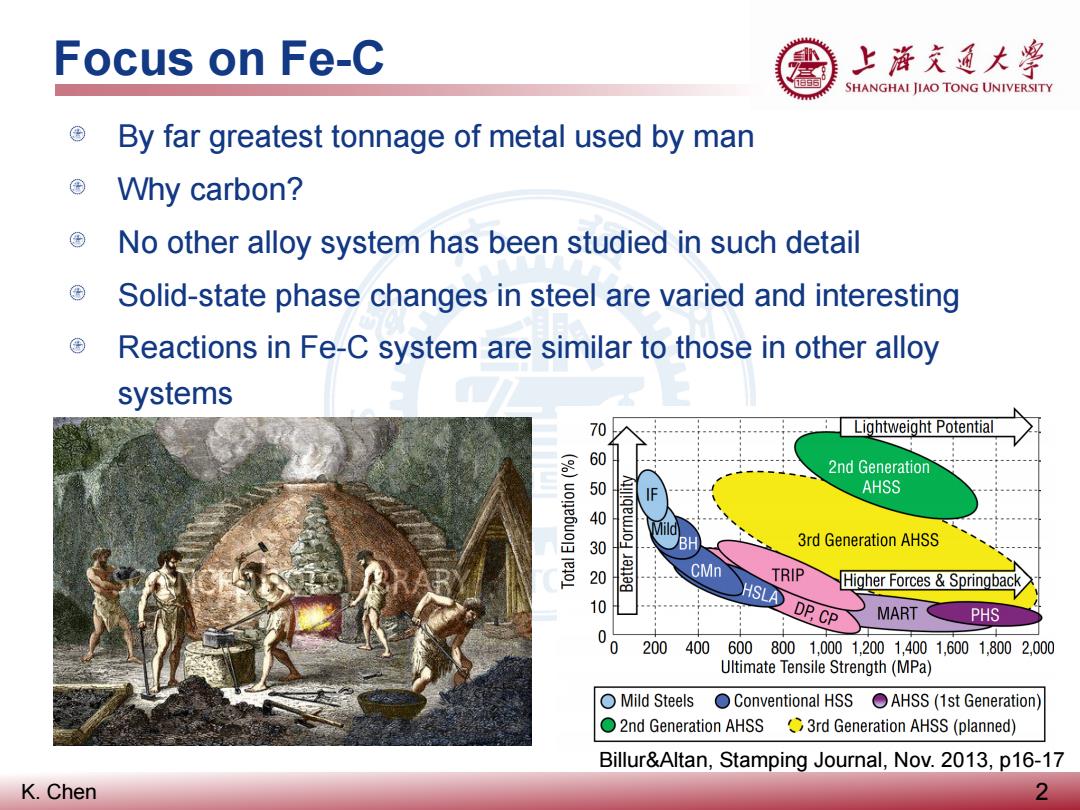
Focus on Fe-C 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY By far greatest tonnage of metal used by man Why carbon? No other alloy system has been studied in such detail Solid-state phase changes in steel are varied and interesting Reactions in Fe-C system are similar to those in other alloy systems 70 Lightweight Potential 0印 2nd Generation AHSS 3 BH 3rd Generation AHSS CMn TRIP HSLA DP.CP Higher Forces Springback 10 MART PHS 200400 6008001,0001.2001,4001,6001,8002000 Ultimate Tensile Strength(MPa) OMild Steels Conventional HSS AHSS(1st Generation) 2nd Generation AHSS3rd Generation AHSS(planned) Billur&Altan,Stamping Journal,Nov.2013,p16-17 K.Chen 2
K. Chen By far greatest tonnage of metal used by man Why carbon? No other alloy system has been studied in such detail Solid-state phase changes in steel are varied and interesting Reactions in Fe-C system are similar to those in other alloy systems Focus on Fe-C 2 Billur&Altan, Stamping Journal, Nov. 2013, p16-17

Outline for Chapter 9 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 9:Eutectoid and Reverse Eutectoid 9.1 Reverse Eutectoid Transformations 9.1.1 Intro to austenite in Fe-C system 9.1.2 Formation mechanism of austenite 9.1.3 Kinetics of austenitization 9.1.4 Austenite grain growth and its control AOTONG UNN 9.2 Eutectoid Transformations K.Chen 3
K. Chen Chapter 9: Eutectoid and Reverse Eutectoid 9.1 Reverse Eutectoid Transformations 9.1.1 Intro to austenite in Fe-C system 9.1.2 Formation mechanism of austenite 9.1.3 Kinetics of austenitization 9.1.4 Austenite grain growth and its control 9.2 Eutectoid Transformations Outline for Chapter 9 3

Glossary 上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Homogeneous/Homogeneity Spontaneous growth Inhomogeneous/Inhomogeneity v Isothermal Heterogeneous/Heterogeneity Lamella/Lamellae Eutectoid/Reverse eutectoid Lamellar/Interlamellar Ferrite/Cementite Migration Pearlite/Spheroidite Residual/Remaining Austenite/Austenitization Incubation time Normalizing Proeutectoid phase Full annealing Hypereutectoid Interstice Hypoeutectoid Octahedral/Octahedron Tetrahedral/Tetrahedron Orthorhombic Concentration gradient K.Chen 4
K. Chen Homogeneous/Homogeneity Inhomogeneous/Inhomogeneity Heterogeneous/Heterogeneity Eutectoid/Reverse eutectoid Ferrite/Cementite Pearlite/Spheroidite Austenite/Austenitization Normalizing Full annealing Interstice Octahedral/Octahedron Tetrahedral/Tetrahedron Orthorhombic Concentration gradient Spontaneous growth Isothermal Lamella/Lamellae Lamellar/Interlamellar Migration Residual/Remaining Incubation time Proeutectoid phase Hypereutectoid Hypoeutectoid Glossary 4
Intro 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Typical processes for eutectoid transformation: Normalizing(正火): Heating at least 55C above the upper critical temperature-i.e.. above Ac3 for compositions less than the eutectoid (0.76 wt%C),and above Accm for compositions greater than the eutectoid.After sufficient time has been allowed for the alloy to completely transform to austenite-the treatment is terminated by cooling in air Full Annealing(退火: 52 Heating to a temperature of about 50 C above Ac3(to form austenite) for compositions less than the eutectoid,or,for compositions in excess of the eutectoid,50 C above the A line(to form austenite and Fe3C phases);then furnace cooled (for several hours) For increased machinability and formability In both processes,austenitization occurs before eutectoid reactions a+Fe3C→Y K.Chen 5
K. Chen Typical processes for eutectoid transformation: Normalizing (正火): Heating at least 55 ºC above the upper critical temperature – i.e., above Ac3 for compositions less than the eutectoid (0.76 wt% C), and above Accm for compositions greater than the eutectoid. After sufficient time has been allowed for the alloy to completely transform to austenite – the treatment is terminated by cooling in air Full Annealing (退火): Heating to a temperature of about 50 ºC above Ac3 (to form austenite) for compositions less than the eutectoid, or, for compositions in excess of the eutectoid, 50 ºC above the A1 line (to form austenite and Fe3C phases); then furnace cooled (for several hours) For increased machinability and formability In both processes, austenitization occurs before eutectoid reactions Intro 5 α+Fe3C→γ