
Contents of Today S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Review previous Second law Functions F and G Property relation Property relation derived from U,H.F,and G etc. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation I Contents of Today Review previous Second law Functions F and G Property relation Property relation derived from U, H, F, and G etc
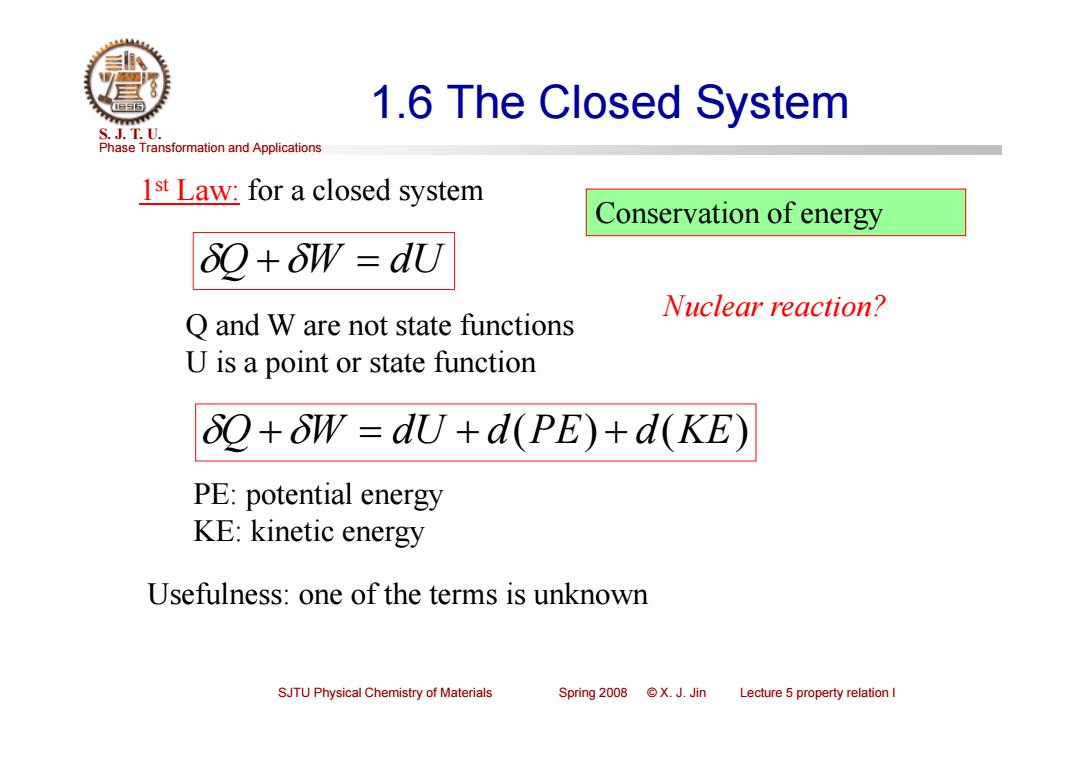
1.6 The Closed System S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications 1st Law:for a closed system Conservation of energy 6Q+δW=dU Nuclear reaction? Q and W are not state functions U is a point or state function 2+δW=dU+d(PE)+d(KE) PE:potential energy KE:kinetic energy Usefulness:one of the terms is unknown SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation I 1.6 The Closed System 1st Law: for a closed system Q W dU Q and W are not state functions U is a point or state function Q W dU d(PE) d(KE) PE: potential energy KE: kinetic energy Usefulness: one of the terms is unknown Conservation of energy Nuclear reaction?
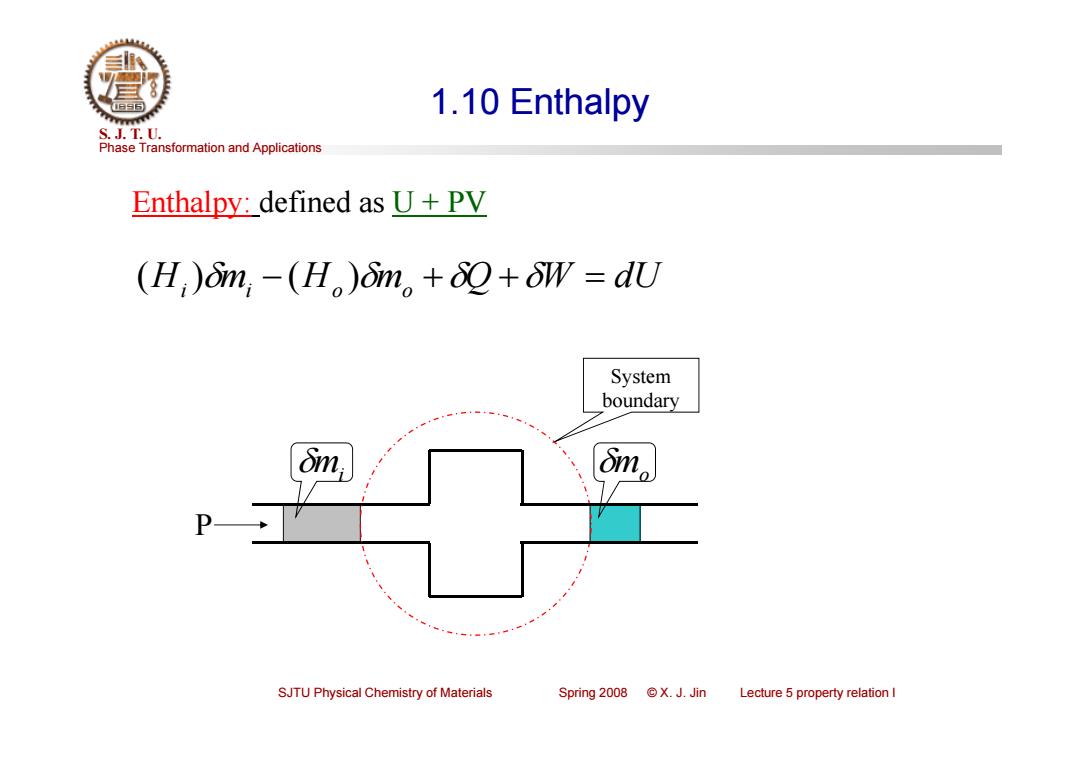
1.10 Enthalpy S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Enthalpy:defined as U+PV (H;)6im,-(H。)n。+2+oW=dU System boundary SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring2008©X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation I 1.10 Enthalpy (Hi)mi (Ho )mo Q W dU Enthalpy: defined as U + PV System boundary P mi mo
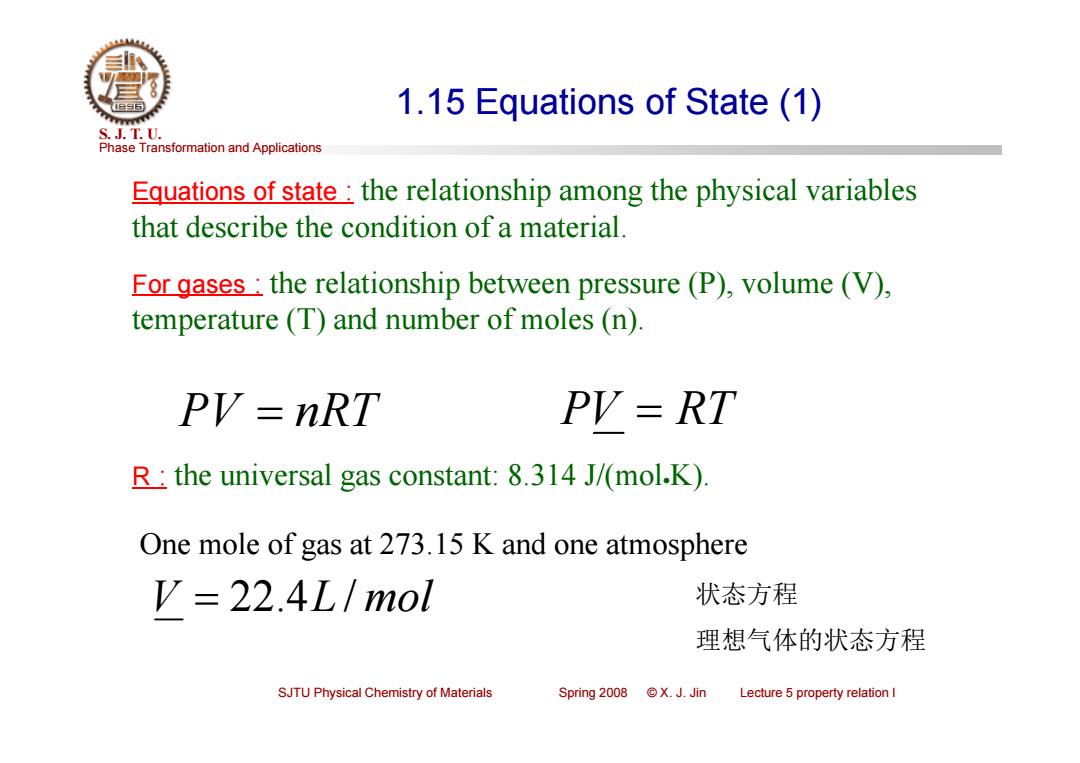
1.15 Equations of State (1) S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications Equations of state:the relationship among the physical variables that describe the condition of a material. For gases:the relationship between pressure(P),volume (V), temperature (T)and number of moles (n). PV=nRT PV=RT R:the universal gas constant:8.314 J/(mol.K) One mole of gas at 273.15 K and one atmosphere V=22.4L/mol 状态方程 理想气体的状态方程 SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation I 1.15 Equations of State (1) Equations of state : the relationship among the physical variables that describe the condition of a material. For gases : the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T) and number of moles (n). PV nRT PV RT R : the universal gas constant: 8.314 J/(molK). V 22.4L / mol One mole of gas at 273.15 K and one atmosphere 状态方程 理想气体的状态方程
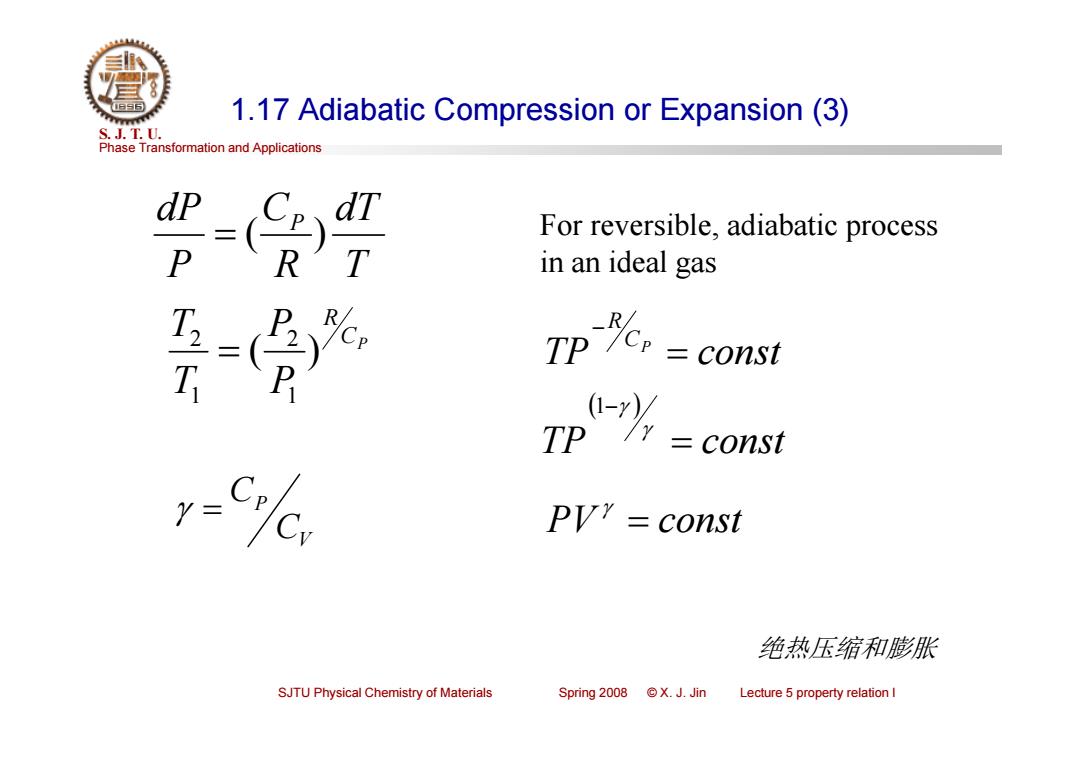
1.17 Adiabatic Compression or Expansion(3) S.J.T.0. Phase Transformation and Applications dl For reversible,adiabatic process in an ideal gas T 7p% T const const PV?=const 绝热压缩和膨胀 SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 X.J.Jin Lecture 5 property relation I
Phase Transformation and Applications S. J. T. U. SJTU Physical Chemistry of Materials Spring 2008 © X. J. Jin Lecture 5 property relation I 1.17 Adiabatic Compression or Expansion (3) T dT R C P dP P ( ) CP R P P T T ( ) 1 2 1 2 For reversible, adiabatic process in an ideal gas TP const CP R TP const 1 PV const V P C C 绝热压缩和膨胀