
上游充通大率 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Principles of Materials Processing Part Ill 全属材料热处理原理 Heat Treatment Principles of Metals Lecturer:Ke Chen 2017-06-02
Principles of Materials Processing Part III - 金属材料热处理原理 Heat Treatment Principles of Metals Lecturer: Ke Chen 2017-06-02

Outline for Chapter 11 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Chapter 11:Precipitation transformations 11.1 Precipitation and Aging 11.1.1 Introduction 11.1.2 Continuous Precipitation 11.1.3 Discontinuous Precipitation 11.2 Tempering of Ferrous Martensite AIJIAO TONG UNI K.Chen 2
K. Chen Chapter 11: Precipitation transformations 11.1 Precipitation and Aging 11.1.1 Introduction 11.1.2 Continuous Precipitation 11.1.3 Discontinuous Precipitation 11.2 Tempering of Ferrous Martensite Outline for Chapter 11 2
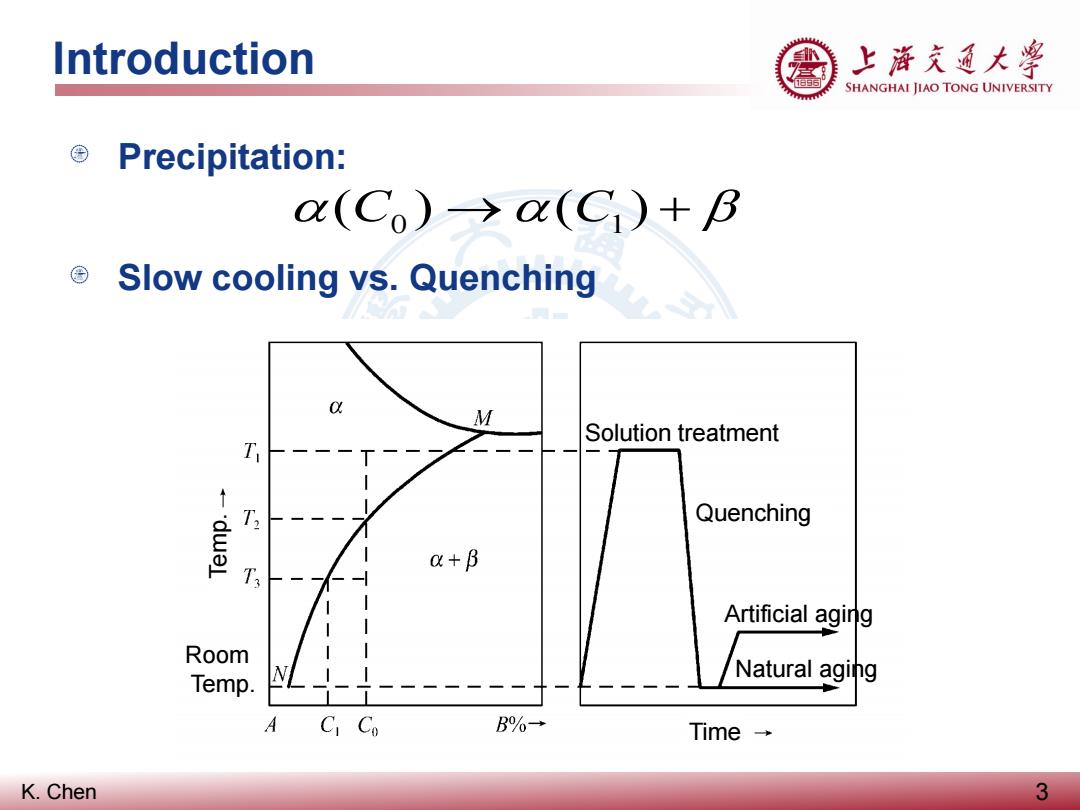
Introduction 上游充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ©Precipitation: (Co)→o(C1)+B © Slow cooling vs.Quenching M Solution treatment T Quenching a+B T Artificial aging Room Temp. L Natural aging A CI Co B%→ Time→ K.Chen 3
K. Chen Precipitation: Slow cooling vs. Quenching Introduction 3 α(C0 ) →α(C1) + β Solution treatment Quenching Artificial aging Natural aging Time Room Temp. Temp

Introduction 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Ageing(时效): ■ When a precipitation hardening alloy is quenched after solution treatment,its alloying elements will be trapped in solution,resulting in a soft metal. ■ Aging a“solutionized”(固溶处理)metal will allow the alloying elements to diffuse through the microstructure and form intermetallic particles. Natural aging(自然时效):aging at room temperature Artificial aging(人工时效):aging at elevated temperature K.Chen 4
K. Chen Ageing (时效): When a precipitation hardening alloy is quenched after solution treatment, its alloying elements will be trapped in solution, resulting in a soft metal. Aging a “solutionized” (固溶处理) metal will allow the alloying elements to diffuse through the microstructure and form intermetallic particles. Natural aging (自然时效): aging at room temperature Artificial aging (人工时效): aging at elevated temperature Introduction 4
Introduction 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY ©→Precipitation hardening(沉淀强/硬化)or ageing hardening(时效强/硬化) Continuous precipitation vs.Discontinuous precipitation ■ Continuous (precipitation (or general precipitation): it occurs generally throughout the matrix on dislocations or grain boundaries,etc.and the composition of matrix surrounding the precipitates decreases continuously with time Discontinuous(不连续)precipitation(or cellular precipitation,胞状脱溶):the composition of the matriⅸ changes discontinuously as the cell front passes K.Chen 5
K. Chen Precipitation hardening (沉淀强/硬化) or ageing hardening (时效强/硬化) Continuous precipitation vs. Discontinuous precipitation Continuous (连续) precipitation (or general precipitation): it occurs generally throughout the matrix on dislocations or grain boundaries, etc. and the composition of matrix surrounding the precipitates decreases continuously with time Discontinuous (不连续) precipitation (or cellular precipitation, 胞状脱溶): the composition of the matrix changes discontinuously as the cell front passes Introduction 5