
Outline Introduction Processing maps Elements of plastic theory Plastic deformation mechanism Recovery recrystallization
Outline Processing maps Plastic deformation mechanism Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization Introduction
上清充通大学 SHEAMGRAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Introduction of dislocation Introduction Elastic properties of dislocation Processing maps Dislocation and plastic deformation Plastic deformation by slip Elements of plastic theory Initial plastic deformation Plastic deformation mechanism ○) Flow stress and work hardening Recovery recrystallization Deformation by twinning Deformation for polycrystals Deformation texture
Introduction Elements of plastic theory Recovery & recrystallization 1 1 Plastic deformation mechanism Introduction of dislocation Elastic properties of dislocation Dislocation and plastic deformation Plastic deformation by slip Initial plastic deformation Flow stress and work hardening Deformation by twinning Deformation for polycrystals Deformation texture 1 1 Processing maps 1

Reference books 上清充通大¥ SHANCBHAI JUAO TONO UNTVEEETTY Mechanical Metallurgy* George E Dieter McGraw-Hill Book Company,London(1988) Introduction to Dislocations (further reading) D.Hull and D.J.Bacon Pergamon Press,Oxford(1984) Theory of Dislocations (advanced reading) J.P.Hirth and J.Lothe McGraw-Hill,New York (1968) Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 4
Reference books Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 4 • Mechanical Metallurgy * George E Dieter McGraw‐Hill Book Company, London (1988) • Introduction to Dislocations (further reading) D. Hull and D.J. Bacon Pergamon Press, Oxford (1984) • Theory of Dislocations (advanced reading) J. P. Hirth and J. Lothe McGraw-Hill, New York (1968)
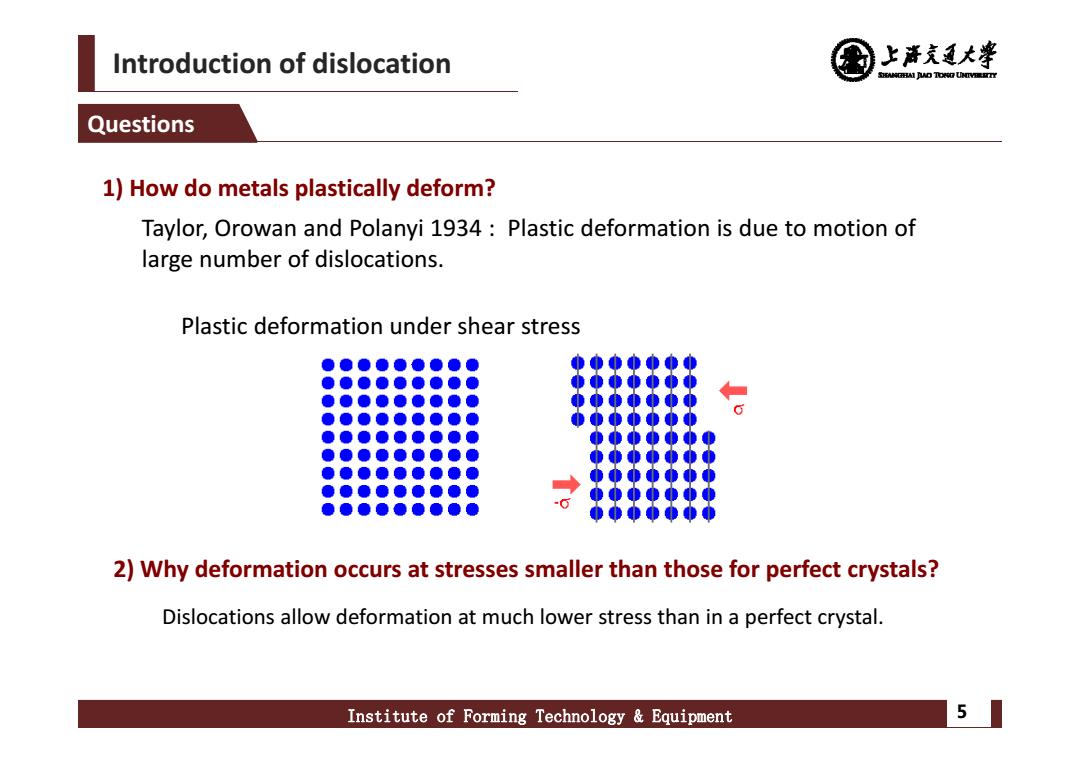
Introduction of dislocation 上产克大睾 SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Questions 1)How do metals plastically deform? Taylor,Orowan and Polanyi 1934:Plastic deformation is due to motion of large number of dislocations. Plastic deformation under shear stress ●●●●●●●●● 000ǜ00 ● 0o000●0 2)Why deformation occurs at stresses smaller than those for perfect crystals? Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 5
Introduction of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 5 Questions 1) How do metals plastically deform? Taylor, Orowan and Polanyi 1934 : Plastic deformation is due to motion of large number of dislocations. Plastic deformation under shear stress 2) Why deformation occurs at stresses smaller than those for perfect crystals? Dislocations allow deformation at much lower stress than in a perfect crystal
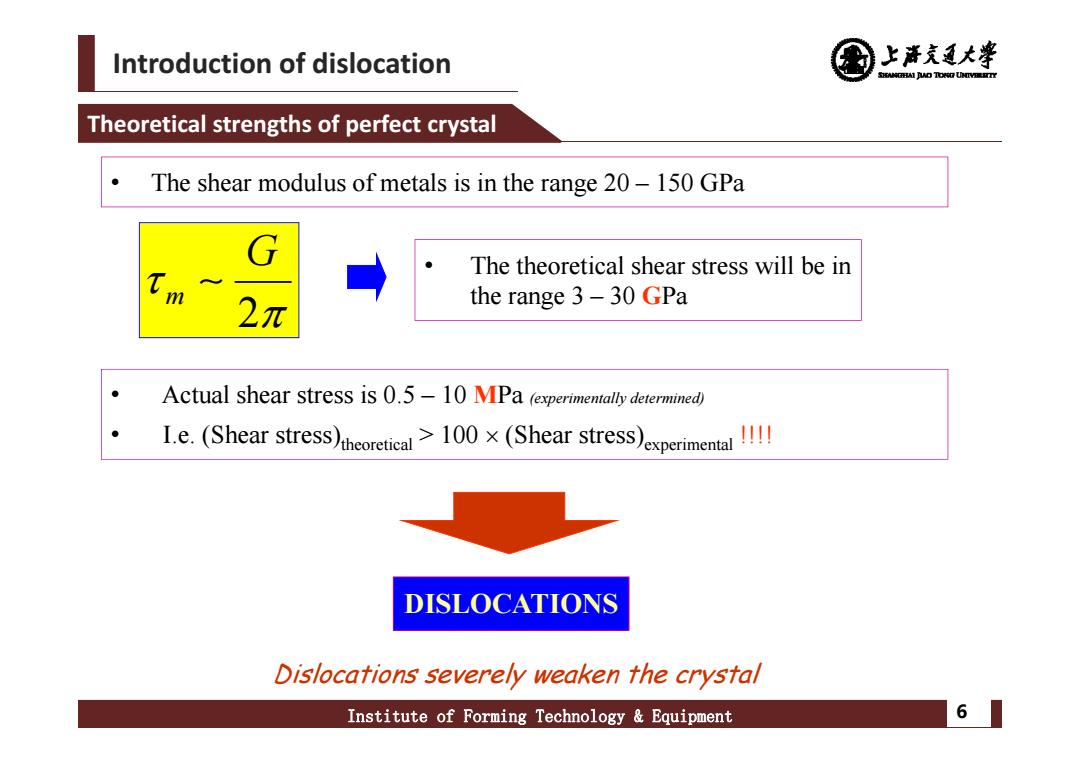
Introduction of dislocation 上清充通大学 SANCEAI JUO TO阳UY Theoretical strengths of perfect crystal The shear modulus of metals is in the range 20-150 GPa G The theoretical shear stress will be in 2元 the range 3-30 GPa Actual shear stress is 0.5-10 MPa (experimentally determined) I.e.(Shear stress)theoretical>100x(Shear stress)experimental DISLOCATIONS Dislocations severely weaken the crystal Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 61
Introduction of dislocation Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 6 Theoretical strengths of perfect crystal 2 m G • The shear modulus of metals is in the range 20 – 150 GPa DISLOCATIONS • Actual shear stress is 0.5 – 10 MPa (experimentally determined) • I.e. (Shear stress)theoretical > 100 (Shear stress)experimental !!!! Dislocations severely weaken the crystal • The theoretical shear stress will be in the range 3 – 30 GPa