
Characteristics 上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.Orientation relationships and habit planes (1)K-S (Kurdjumov-Sachs) 111,/110a (110). 110〉,1119。 (111n JIAO TONC In Fe-1.4%C steel 24 K.Chen 11
K. Chen Characteristics 11 3. Orientation relationships and habit planes (1) K-S(Kurdjumov-Sachs) {111} //{110} ' γ α 110 // 111 ' γ α In Fe-1.4%C steel 24 (110)α’
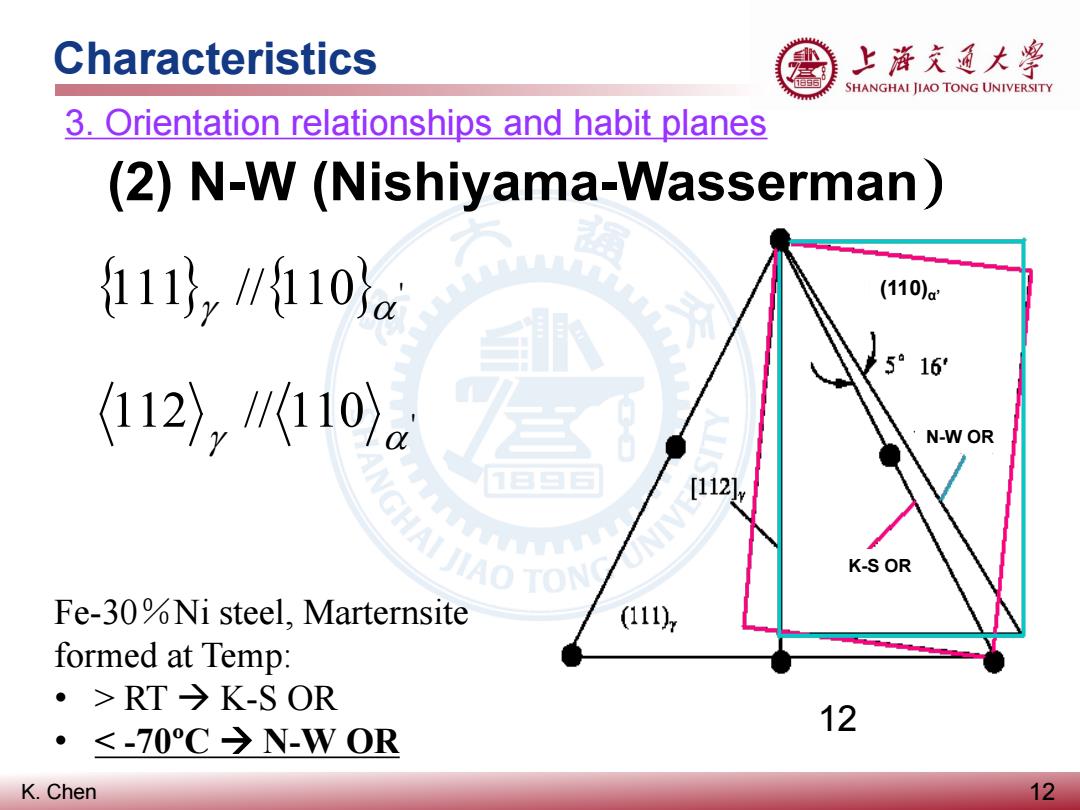
Characteristics 上浒充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.Orientation relationships and habit planes (2)N-W(Nishiyama-Wasserman) 111z/110a (110)a 5°16 112〉,110)a N-W OR [112 NIV AO TON K-S OR Fe-30%Ni steel,Marternsite (111 formed at Temp: ·>RT→K-SOR 12 <-70C→N-WOR K.Chen 12
K. Chen Characteristics 12 3. Orientation relationships and habit planes (2) N-W (Nishiyama-Wasserman) 12 {111} //{110} ' γ α 112 // 110 ' γ α Fe-30%Ni steel, Marternsite formed at Temp: • > RT K-S OR • < -70ºC N-W OR (110)α’ K-S OR N-W OR

Characteristics 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.Orientation relationships and habit planes (3)G-T (Greninger-Troiaon) 111,/110 1o difference 110),111). 2 difference Fe-0.8%C-22%Ni steel IAO TONG UNIVE K.Chen 13
K. Chen Characteristics 13 3. Orientation relationships and habit planes (3) G-T (Greninger-Troiaon) Fe-0.8%C-22%Ni steel {111} //{110} ' γ α 110 // 111 ' γ α 1o difference 2o difference
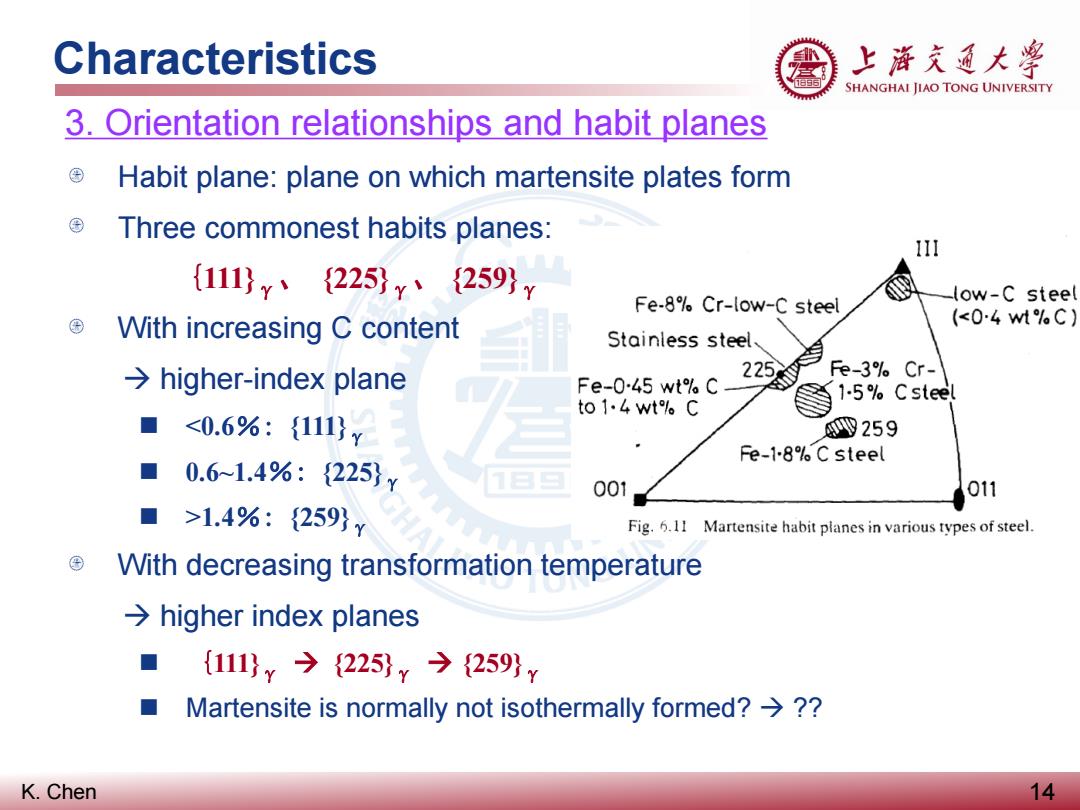
Characteristics 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 3.Orientation relationships and habit planes Habit plane:plane on which martensite plates form Three commonest habits planes: 111 {111}y、{225}y、259}y Fe-8。Cr-low-C steel -low-C steel With increasing C content (<04wM%C) Stainless steel、 →higher-.index plane Fe-0-45 wt%C_ 229 Fe-3%。Cr- to1.4wt。C 1-5%Csteel ■ <0.6%:{111}¥ 9259 Fe-18。C steel 0.61.4%:{225}y 1日三 001 011 ■ >1.4%:{259}v Fig.6.11 Martensite habit planes in various types of steel. With decreasing transformation temperature →higher index planes {111}y→{225}y今{259}y Martensite is normally not isothermally formed?→?? K.Chen 14
K. Chen Characteristics 14 3. Orientation relationships and habit planes Habit plane: plane on which martensite plates form Three commonest habits planes: {111}γ、 {225}γ、 {259}γ With increasing C content higher-index plane <0.6%: {111}γ 0.6~1.4%: {225}γ >1.4%: {259}γ With decreasing transformation temperature higher index planes {111}γ {225}γ {259}γ Martensite is normally not isothermally formed? ??

Characteristics 上游充道大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 4.Transformation in a temperature range M:martensite start temperature,below which austenite> martensite transformation occurs M:martensite finish temperature,corresponding to the temperature below which further cooling does not increase the amount of martensite In practice the M may not correspond to 100%martensite,and some retained austenite can be left even below M(the untransformed austenite is termed as remaining austenite) There is no incubation time for martensite transformation,the rate of which is close to the speed of sound in the solid. Transformation fraction is a function of temperature,unrelated to isothermal holding time K.Chen 15
K. Chen Characteristics 15 4. Transformation in a temperature range Ms: martensite start temperature, below which austenite martensite transformation occurs Mf : martensite finish temperature, corresponding to the temperature below which further cooling does not increase the amount of martensite In practice the Mf may not correspond to 100% martensite, and some retained austenite can be left even below Mf (the untransformed austenite is termed as remaining austenite) There is no incubation time for martensite transformation, the rate of which is close to the speed of sound in the solid. Transformation fraction is a function of temperature, unrelated to isothermal holding time