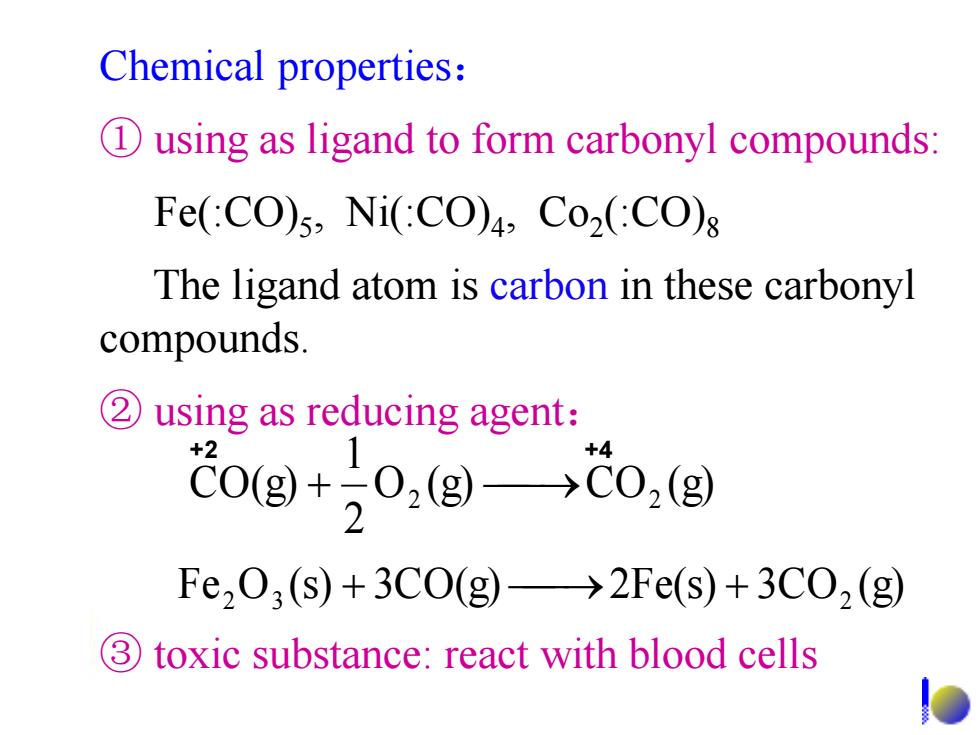
Chemical properties: D using as ligand to form carbonyl compounds: Fe(:CO)5,Ni(CO)4,Co2(:CO) The ligand atom is carbon in these carbonyl compounds. 2 using as reducing agent: C0(g+02(g)→C0,(g 2 Fe203(s)+3C0(g)→2Fe(s)+3C02(g 3) toxic substance:react with blood cells
Chemical properties: ① using as ligand to form carbonyl compounds: Fe(:CO)5 , Ni(:CO)4 , Co2 (:CO)8 The ligand atom is carbon in these carbonyl compounds. ② using as reducing agent: O (g) CO (g) 2 1 CO(g) 2 2 Fe O (s) 3CO(g) 2Fe(s) 3CO (g) 2 3 2 ③ toxic substance: react with blood cells +2 +4
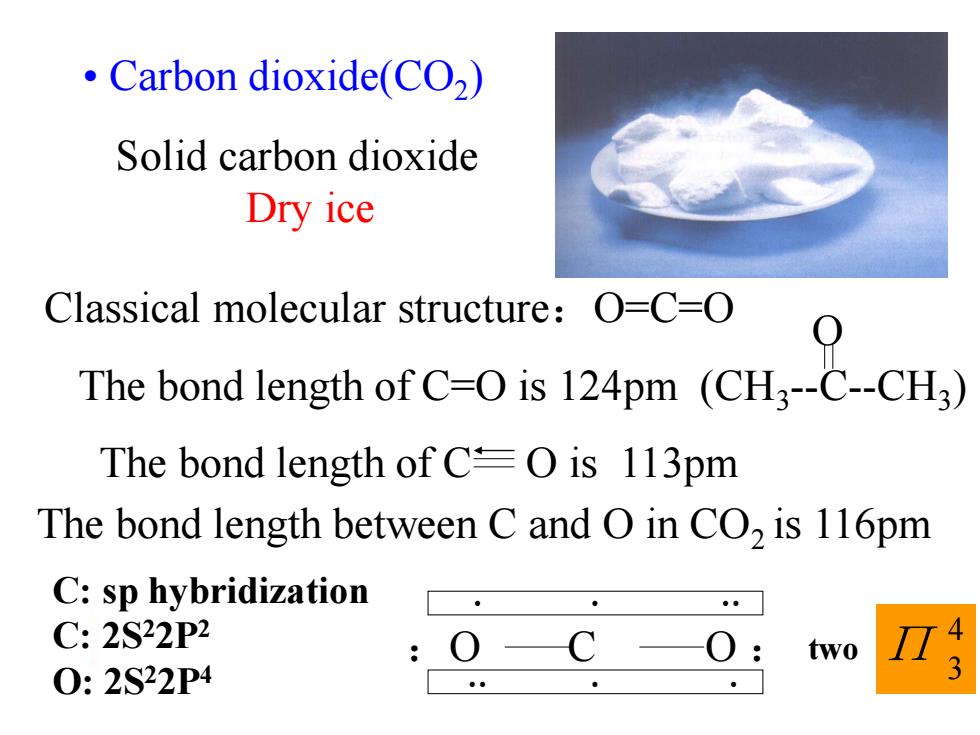
Carbon dioxide(CO2) Solid carbon dioxide Dry ice Classical molecular structure:O=C=O The bond tensth ofC-is 124m (CHCH. The bond length of C=O is 113pm The bond length between C and O in CO2 is 116pm C:sp hybridization C:2S22P2 two 0:2S22P4
• Carbon dioxide(CO2 ) 4 3 Π :O C O : Classical molecular structure:O=C=O O The bond length of C=O is 124pm (CH3 --C--CH3 ) The bond length of C O is 113pm The bond length between C and O in CO2 is 116pm C: sp hybridization C: 2S22P2 O: 2S22P4 Solid carbon dioxide Dry ice two
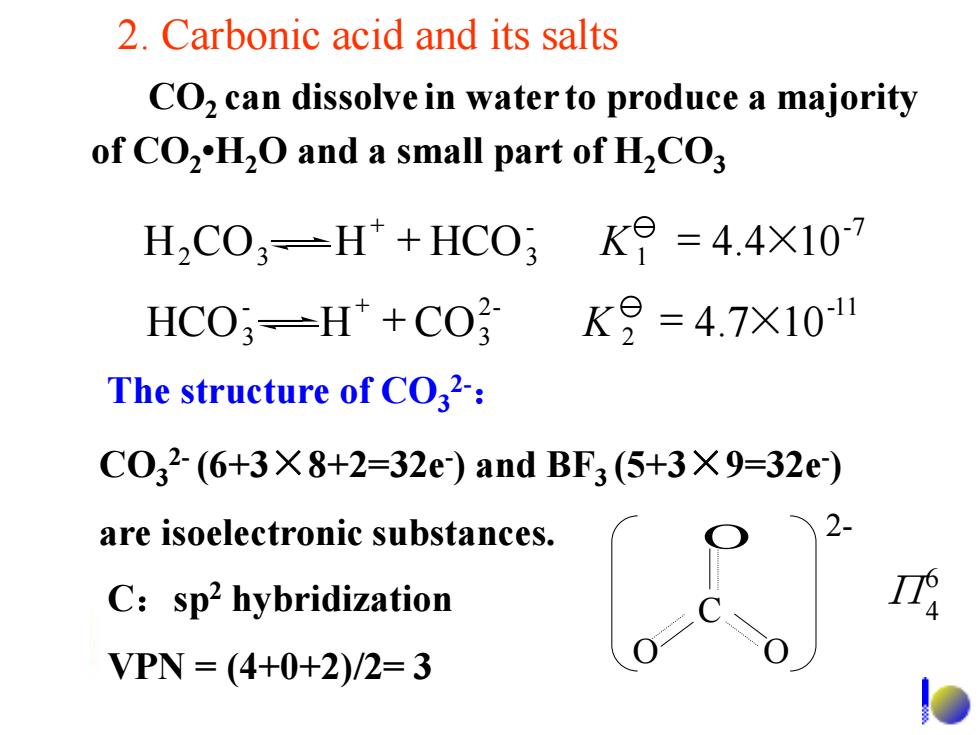
2.Carbonic acid and its salts CO,can dissolve in water to produce a majority of CO2H2O and a small part of H2CO; H2C03=H+HC03K9=4.4X107 HCO;-H*+CO K9=4.7×101 The structure of CO32-: C032(6+3X8+2=32e)and BF3(5+3×9=32e) are isoelectronic substances. C:sp2 hybridization VPN=(4+0+2)/2=3
2. Carbonic acid and its salts CO2 can dissolve in water to produce a majority of CO2 •H2O and a small part of H2CO3 The structure of CO3 2-: CO3 2- (6+3×8+2=32e- ) and BF3 (5+3×9=32e- ) are isoelectronic substances. C:sp2 hybridization VPN = (4+0+2)/2= 3 C O O O 2- 6 Π4 -7 1 - H2CO3 H HCO3 = 4.4×10 K -11 2 2- 3 - HCO3 H CO = 4.7×10 K
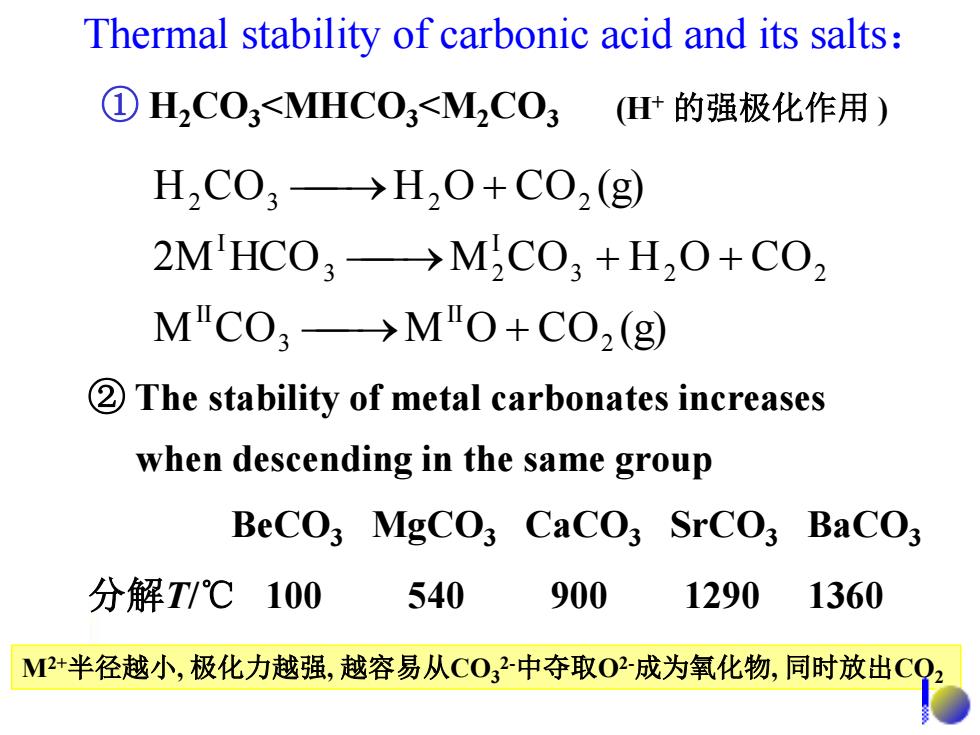
Thermal stability of carbonic acid and its salts: ①H2C03<MHC03<M2C03 H+的强极化作用) H2C03→H20+C02(g) 2M'HC03→M2C03+H20+C02 M"C03→M"O+C0O2(g) 2The stability of metal carbonates increases when descending in the same group BeCO;MgCO3 CaCO3 SrCO3 BaCO; 分解T/℃100 540 900 1290 1360 M2+半径越小,极化力越强,越容易从C032中夺取02成为氧化物,同时放出C
Thermal stability of carbonic acid and its salts: ① H2CO3<MHCO3<M2CO3 M C O M O C O (g) 2M HCO M C O H O C O H C O H O C O (g) 2 II 3 II 3 2 2 I 3 2 I 2 3 2 2 ② The stability of metal carbonates increases when descending in the same group BeCO3 MgCO3 CaCO3 SrCO3 BaCO3 分解T/℃ 100 540 900 1290 1360 M2+半径越小, 极化力越强, 越容易从CO3 2-中夺取O2-成为氧化物, 同时放出CO2 (H+ 的强极化作用 )