
第七章:密度泛函理论方法 Chapter 7 DFT
第七章:密度泛函理论方法 1 Chapter 7 DFT
Why DFT Density Functional Theory (DFT) DFT is an alternative approach to the theory of electronic structure; electron density plays a central role in DFT. Why a new theory? HF method scales as N4 (N -of basis functions) Cl methods scale as N6-N10 MPn methods scale as >N5 CC methods scale as >N6 >Correlated methods are not feasible for medium and large sized molecules!
Why DFT Density Functional Theory (DFT) DFT is an alternative approach to the theory of electronic structure; electron density plays a central role in DFT. Why a new theory? HF method scales as N4 (N - # of basis functions) CI methods scale as N6-N10 MPn methods scale as >N5 CC methods scale as >N6 Correlated methods are not feasible for medium and large sized molecules!
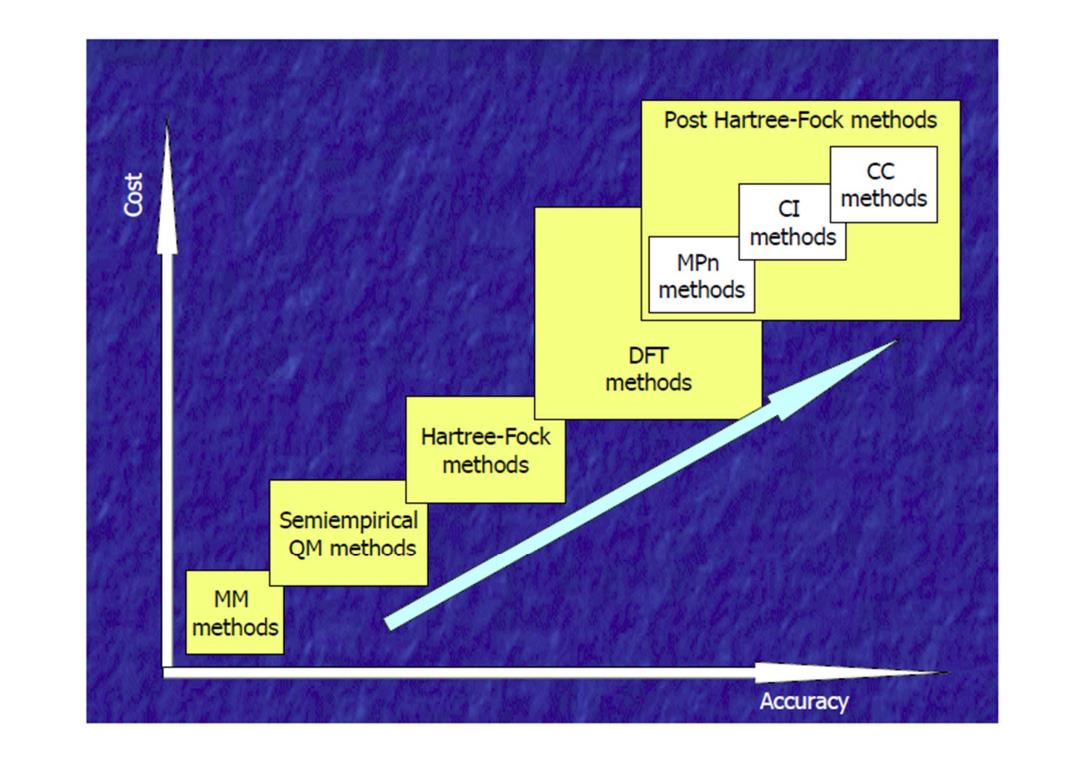
Post Hartree-Fock methods CC 1500 cI methods methods MPn methods DFT methods Hartree-Fock methods Semiempirical QM methods MM methods Accuracy
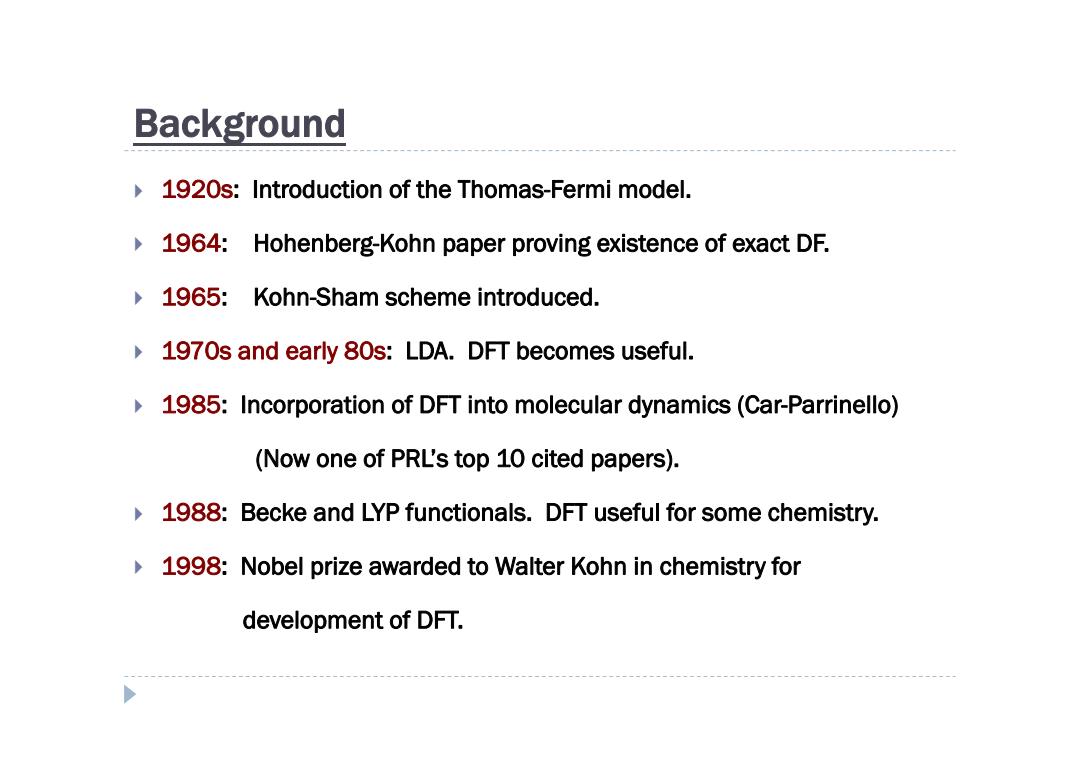
Background 1920s:Introduction of the Thomas-Fermi model. 1964:Hohenberg-Kohn paper proving existence of exact DF. 1965:Kohn-Sham scheme introduced. 1970s and early 80s:LDA.DFT becomes useful. 1985:Incorporation of DFT into molecular dynamics(Car-Parrinello) (Now one of PRL's top 10 cited papers). 1988:Becke and LYP functionals.DFT useful for some chemistry. 1998:Nobel prize awarded to Walter Kohn in chemistry for development of DFT
Background 1920s: Introduction of the Thomas-Fermi model. 1964: Hohenberg-Kohn paper proving existence of exact DF. 1965: Kohn-Sham scheme introduced. 1970s and early 80s: LDA. DFT becomes useful. 1985: Incorporation of DFT into molecular dynamics (Car-Parrinello) (Now one of PRL’s top 10 cited papers). 1988: Becke and LYP functionals. DFT useful for some chemistry. 1998: Nobel prize awarded to Walter Kohn in chemistry for development of DFT

Basic Theory:The electron density is the essential Probability of finding electron 1 in dx1,electron 2 in dx2,...electron N in dxN: |Ψ(x1,x2,…,xw)l2dx1dx2.dxw Integrating over the space and spin coordinates of electron 2,3,...,N and the spin coordinate of electron 1 one obtaines the probability of finding electron 1 in volume element dr whilst the other electrons are anywhere: (-∫axz.w)Pdsa.dwan Multiplying by N one obtaines the probability of finding any electron in dr1: v(-∫lw,x,xw)Ids.dxzdxx)ah=p)an The quantity p(r1)is the electron density: v-6 .)ds,dx…dw
Basic Theory: The electron density is the essential