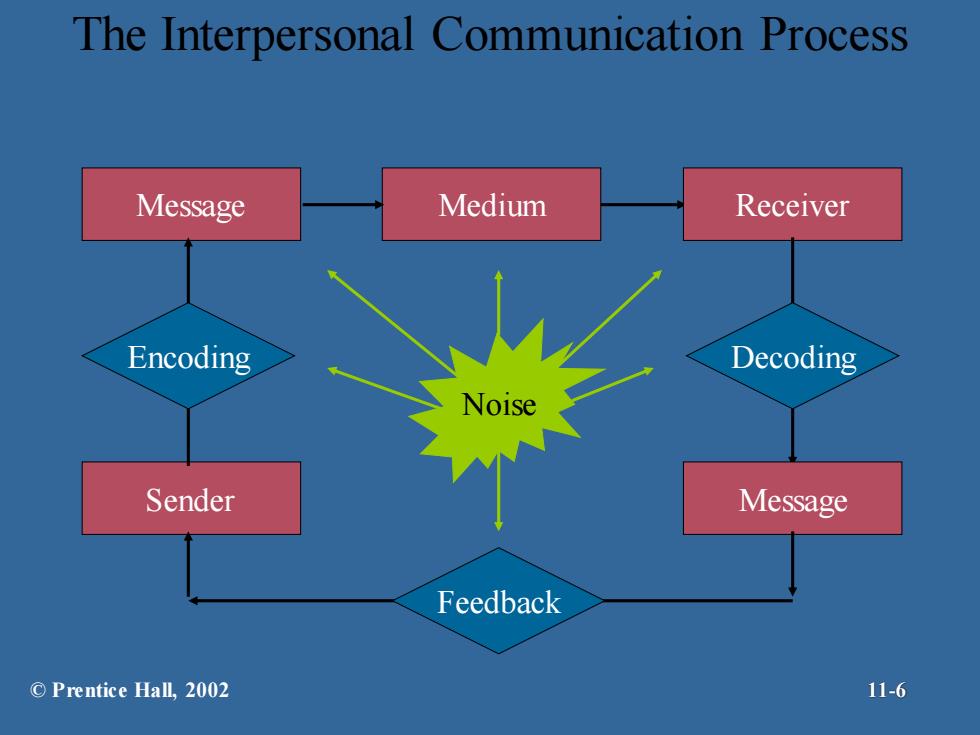
The Interpersonal Communication Process Message Medium Receiver Encoding Decoding Noise Sender Message Feedback ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-6
The Interpersonal Communication Process Sender Message Medium Receiver Encoding Noise Feedback Message Decoding © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-6

Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally -a wide variety of communication methods exist choice of a method should reflect: the needs of the sender the needs of the receiver the attributes of the message the attributes of the channel ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-7
Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally – a wide variety of communication methods exist – choice of a method should reflect: – the needs of the sender – the needs of the receiver – the attributes of the message – the attributes of the channel © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-7

Evaluating Communication Methods FFeedback-how quickly can the receiver respond to the message? Complexity capacity-can the method effectively process complex messages? Breadth potential-how many different messages can be transmitted using this method? Confdentialliy-can communicators be reasonably sure their messages are received only by those intended? EEncoding ease-can sender easily and quickly use this channel? Decodingease-can receiver easily and quickly decode messages? Time-space constraint-do senders and receivers need to communicate at the same time and in the same space? Cost-how much does it cost to use this method? Interpersonal warth-how well does this method convey interpersonal warmth? Formality-does this method have the needed amount of formality? Scanabiity-does this method allow the message to be easily browsed or scanned for relevant information? Time of consumption-does sender or receiver exercise the most control over when the message is dealt with? ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-8
Evaluating Communication Methods Feedback - how quickly can the receiver respond to the message? Complexity capacity - can the method effectively process complex messages? Breadth potential- how many different messages can be transmitted using this method? Confidentiality - can communicators be reasonably sure their messages are received only by those intended? Encoding ease - can sender easily and quickly use this channel? Decoding ease - can receiver easily and quickly decode messages? Time-space constraint- do senders and receivers need to communicate at the same time and in the same space? Cost- how much does it cost to use this method? Interpersonal warmth - how well does this method convey interpersonal warmth? Formality - does this method have the needed amount of formality? Scanability - does this method allow the message to be easily browsed or scanned for relevant information? Time of consumption - does sender or receiver exercise the most control over when the message is dealt with? © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-8
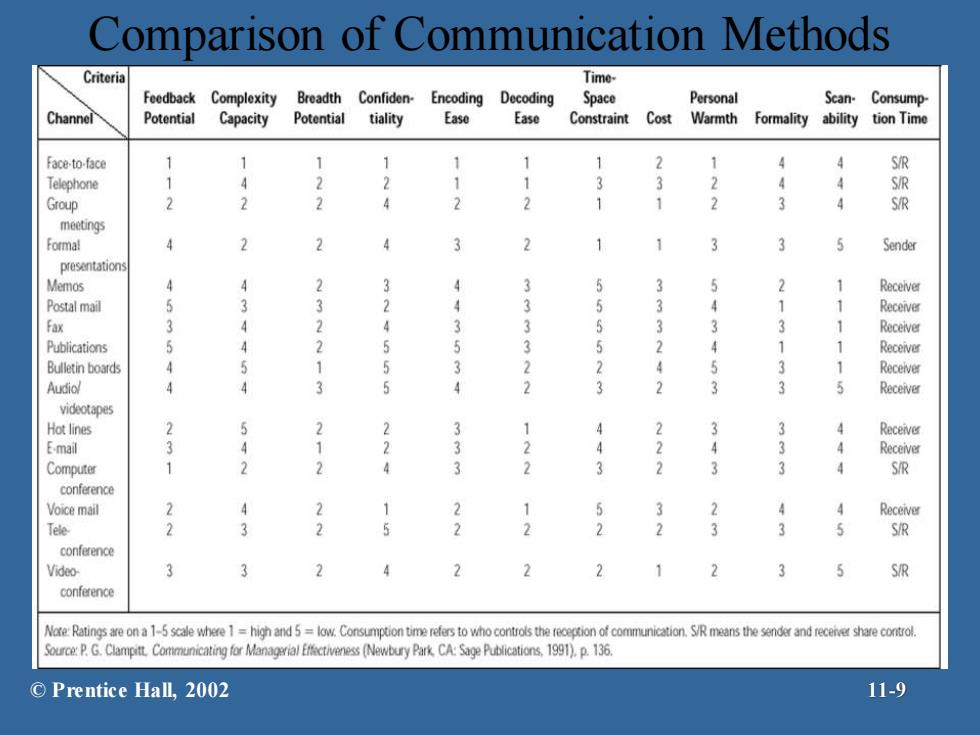
Comparison of Communication Methods Criteria Time- Feedback Complexity Breadth Confiden-Encoding Decoding Space Personal Scan-Consump Channel Potential Capacity Potential tiality Ease Ease Constraint Cost Warmth Formality ability tion Time Face-to-face 1 1 S/R Telephone 1 2 4 4 S/R Group 2 2 2 3 4 S/R meetings Formal 4 2 3 5 Sender presentations Memos 4 2 1 Receiver Postal mail 5 1 Receiver Fax 3 3 Receiver Publications 5 1 1 Receiver Bulletin boards 4 3 1 Receiver Audiol 4 Receiver videotapes Hot lines 2 Receiver Email 3 3 4 Receiver Computer 1 3 4 S/R conference Voice mail 2 2 4 Receiver Tele 2 3 2 3 3 S/R conference Video 3 2 2 2 3 S/R conference Nore:Ratings are on a 1-5 scale where 1=high and 5=low.Consumption time refers to who controls the reception of communication.S/R means the sender and recenve share control. PG.Clampitt Communcatngfor Mangrial Ecivness (Newbury Park CA:Sae Publications 1991).p.136. ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-9
Comparison of Communication Methods © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-9

Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont. Methods of Communicating Interpersonally (cont.) nonverbal communication -communication without words ·types -body language-gestures,facial expressions,and other body movements that convey meaning verbal intonation emphasis someone gives to words or phrases that conveys meaning every oral communication is accompanied by a nonverbal message nonverbal component usually carries the greatest impact ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-10
Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally (cont.) – nonverbal communication - communication without words • types – body language - gestures, facial expressions, and other body movements that convey meaning – verbal intonation - emphasis someone gives to words or phrases that conveys meaning • every oral communication is accompanied by a nonverbal message • nonverbal component usually carries the greatest impact © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-10