
6.4 Particle-Wave Duality Is light a wave or a particle? Light's wave characteristics-- electromagnetic radiation Light's particle characteristics- based on Einstein's interpretation of the photoelectric effect. E=h.v Particle-wave duality: “photons' It's both a wave and a particle!
6.4 Particle 6.4 Particle-Wave Duality Wave Duality • Light’s wave characteristics -- electromagnetic radiation • Light’s particle characteristics– based on Einstein’s interpretation of the photoelectric effect. Particle Particle-wave duality wave duality : “photons” It’s both a wave and a particle! E = ⋅ h ν
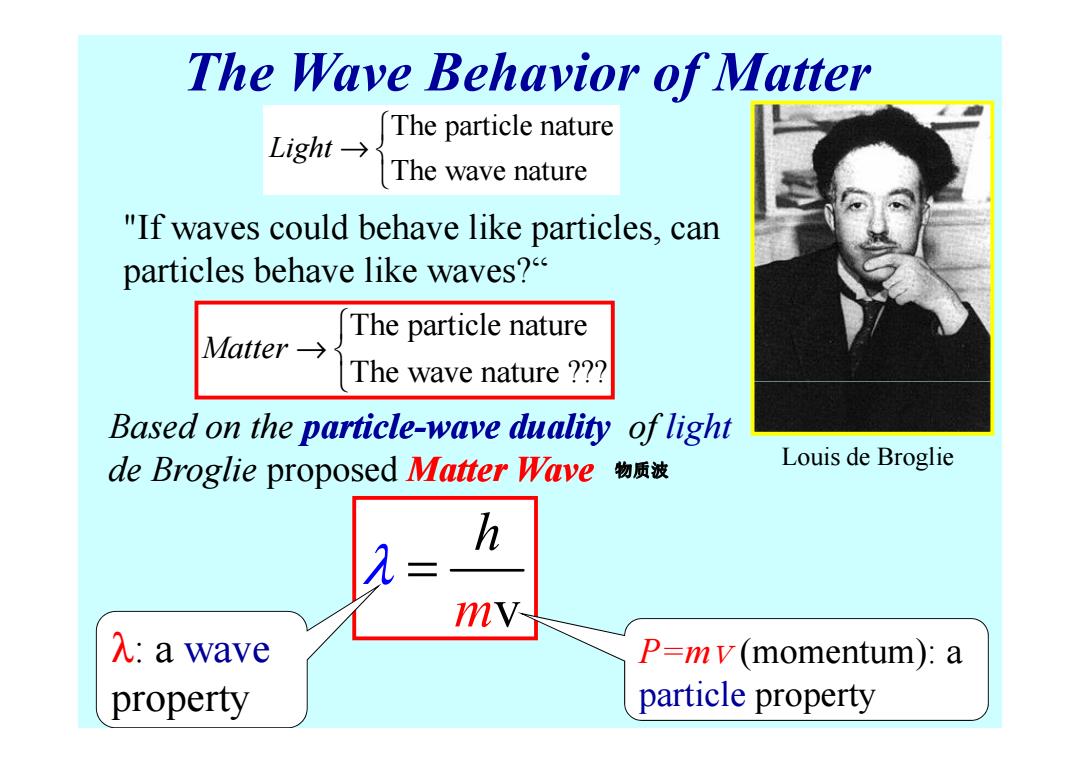
The Wave Behavior of Matter The particle nature Light→ The wave nature "If waves could behave like particles,can particles behave like waves? The particle nature Aatter→s The wave nature ?? Based on the particle-wave duality of light de Broglie proposed Matter Wave物质被 Louis de Broglie h mV- λ:a wave P=mv(momentum):a property particle property
The Wave Behavior of Matter The particle nature The wave nature Light → The particle nature The wave nature ??? Matter → "If waves could behave like particles, can particles behave like waves?“ Based on the particle particle-wave duality wave duality of light de Broglie proposed Matter Wave The wave nature ??? m v h λ = P=m v (momentum): a particle property λ: a wave property Louis de Broglie 物质波
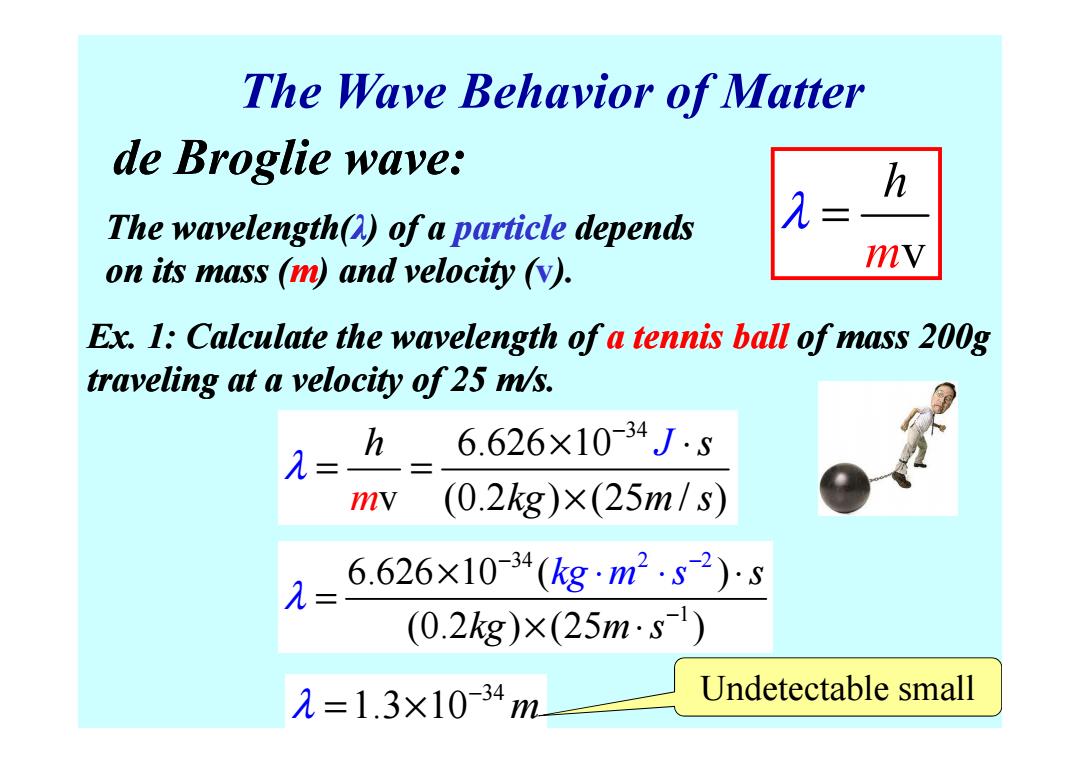
The Wave Behavior of Matter de Broglie wave: h The wavelength(A)of a particle depends on its mass (m)and velocity (v). mV Ex.1:Calculate the wavelength of a tennis ball of mass 200g traveling at a velocity of 25 m/s. h 6.626×10-34Js = mv (0.2kg)×(25m/s) 6.626×10-34(kg·m2.s2)s (0.2kg)×(25m·s) 元=1.3×10-34m Undetectable small
The Wave Behavior of Matter Ex. 1: Calculate the wavelength of a tennis ball of mass 200g traveling at a velocity of 25 m/s. m v h λ = de Broglie wave: The wavelength(λ) of a particle depends on its mass (m) and velocity (v). traveling at a velocity of 25 m/s. 34 6.626 10 v (0.2 ) (25 / ) h s J m kg m s λ − × ⋅ = = × 1 34 2 2 6.626 10 ( ) (0.2 ) (25 ) s kg m s kg m s λ − − − × ⋅ = × ⋅ ⋅ ⋅ 34 λ 1.3 10 m − = × Undetectable small
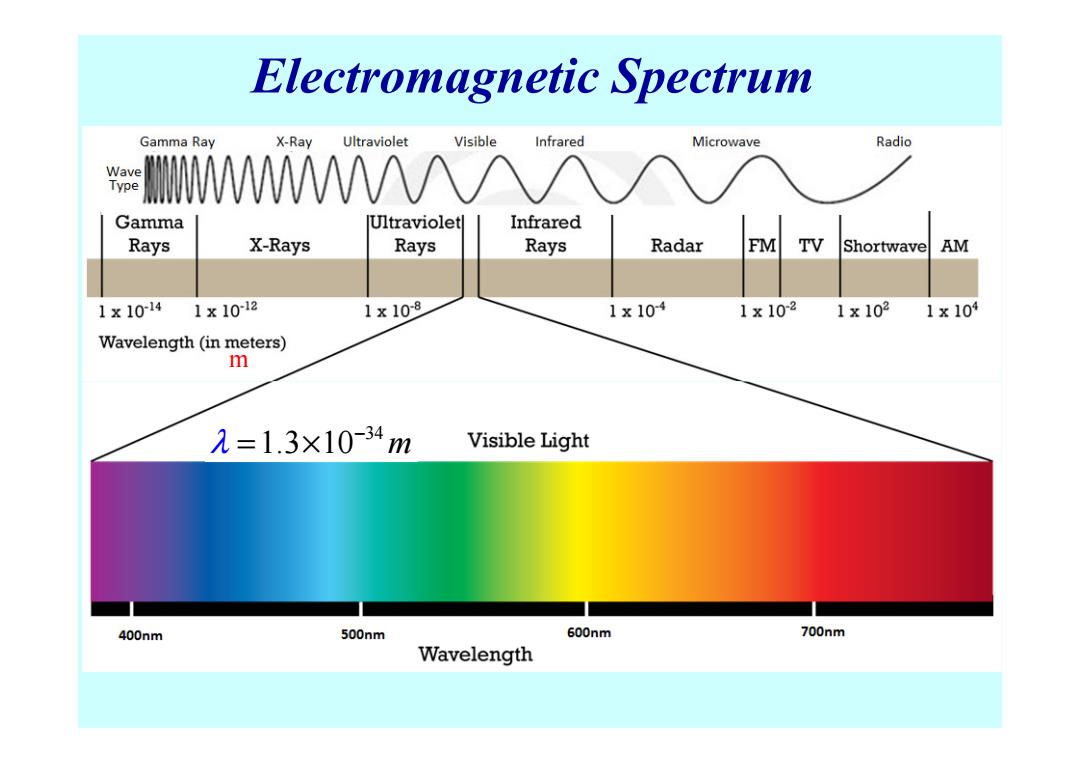
Electromagnetic Spectrum Gamma Ray X-Ray Ultraviolet Visible Infrared Microwave Radio Wave Type WWAA/ Gamma Ultraviolet Infrared Rays X-Rays Rays Rays Radar FM V Shortwave AM 1x1014 1×1012 1x10-8 1x104 1×102 1×102 1x104 Wavelength(in meters) m 元=1.3×10-34m Visible Light 400nm 500nm 600nm 700nm Wavelength
Electromagnetic Spectrum m 34 λ 1.3 10 m − = ×
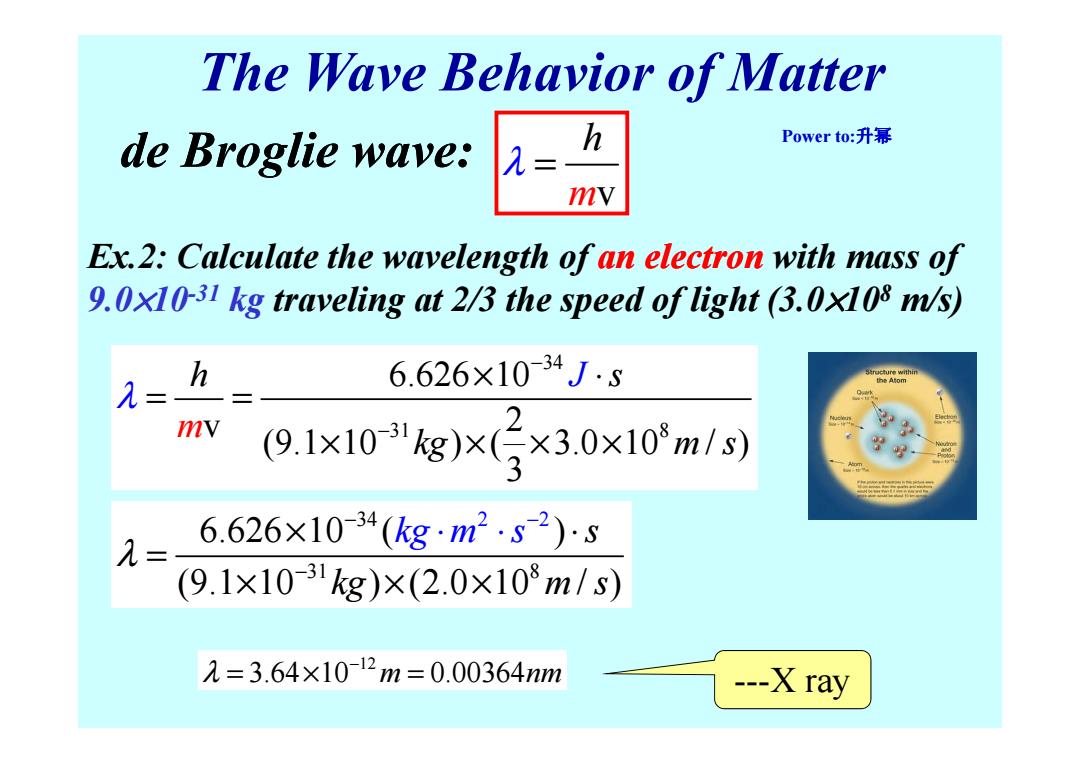
The Wave Behavior of Matter de Broglie wave: h Power to:升幂 = mv Ex.2:Calculate the wavelength of an electron with mass of 9.0x10-31 kg traveling at 2/3 the speed of light (3.0x108 m/s) h 6.626×10-34J5 λ= mv (9.1x10kg)x3×3.0×10m/s) 6.626×10-34(kgm2.82)s (9.1×1031kg)×(2.0×108m/s) 2=3.64×10-12m=0.00364m ---X ray
The Wave Behavior of Matter Ex.2: Calculate the wavelength of an electron with mass of 9.0×10-31 kg traveling at 2/3 the speed of light (3.0×10 8 m/s) m v h de Broglie wave: λ = 34 h s 6.626 10 J λ − × ⋅ = = Power to:升幂 31 8 6.626 10 v 2 (9.1 10 ) ( 3.0 10 / ) 3 h s kg J m m s λ − × ⋅ = = × × × × 34 3 2 2 1 8 6.626 10 ( ) (9.1 10 ) (2.0 10 / ) s kg m m s s kg λ − − − × ⋅ = × × × ⋅ ⋅ 12 λ 3.64 10 0.00364 m nm − = × = ---X ray