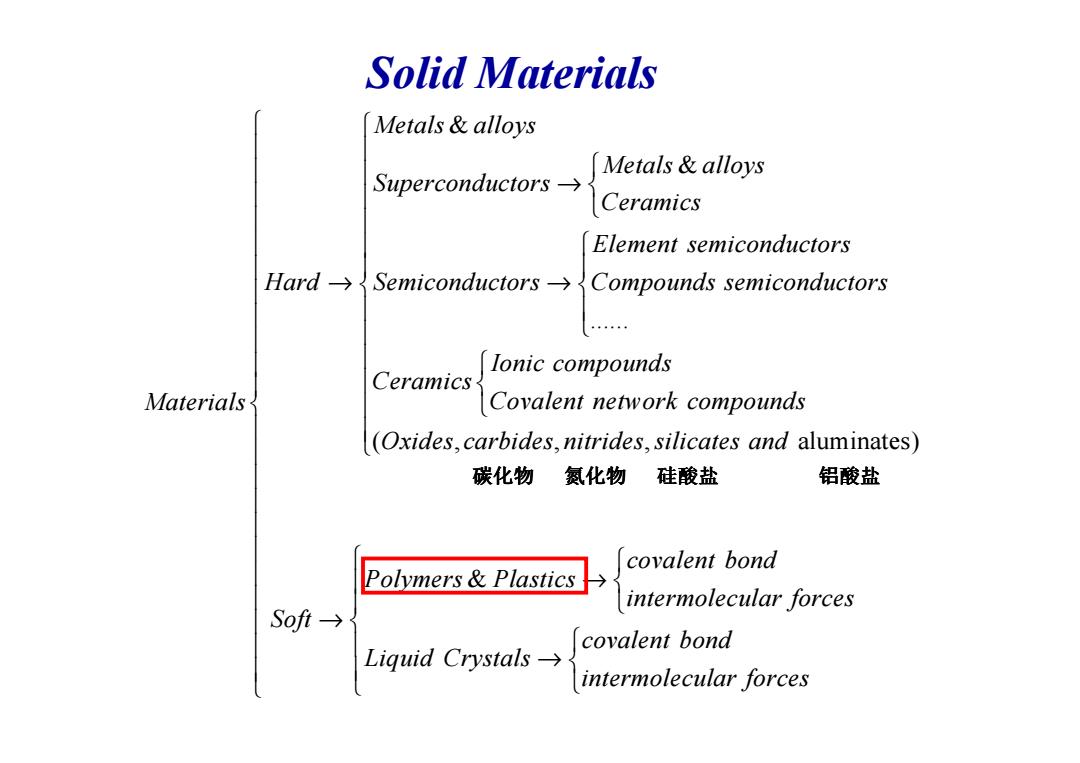
Solid Materials Metals alloys Metals alloys Superconductors→ Ceramics Element semiconductors Hard->Semiconductors->Compounds semiconductors lonic compounds Ceramics Materials Covalent network compounds (Oxides,carbides,nitrides,silicates and aluminates) 碳化物 氮化物 硅酸盐 铝酸盐 covalent bond Polymers&Plastics→ intermolecular forces Sofi→ covalent bond Liquid Crystals-→ intermolecular forces
Solid Materials & & ...... Metals alloys Metals alloys Superconductors Ceramics Element semiconductors Hard Semiconductors Compounds semiconductors Ionic compounds Ceramics → → → ( , Ceramics Materials Covalent network compounds Oxides c , , aluminates) & arbides nitrides silicates and covalent bond Polymers Plastics intermolecular forces Soft covalent bond Liquid Crystals intermolecular forces → → → 碳化物 氮化物 硅酸盐 铝酸盐
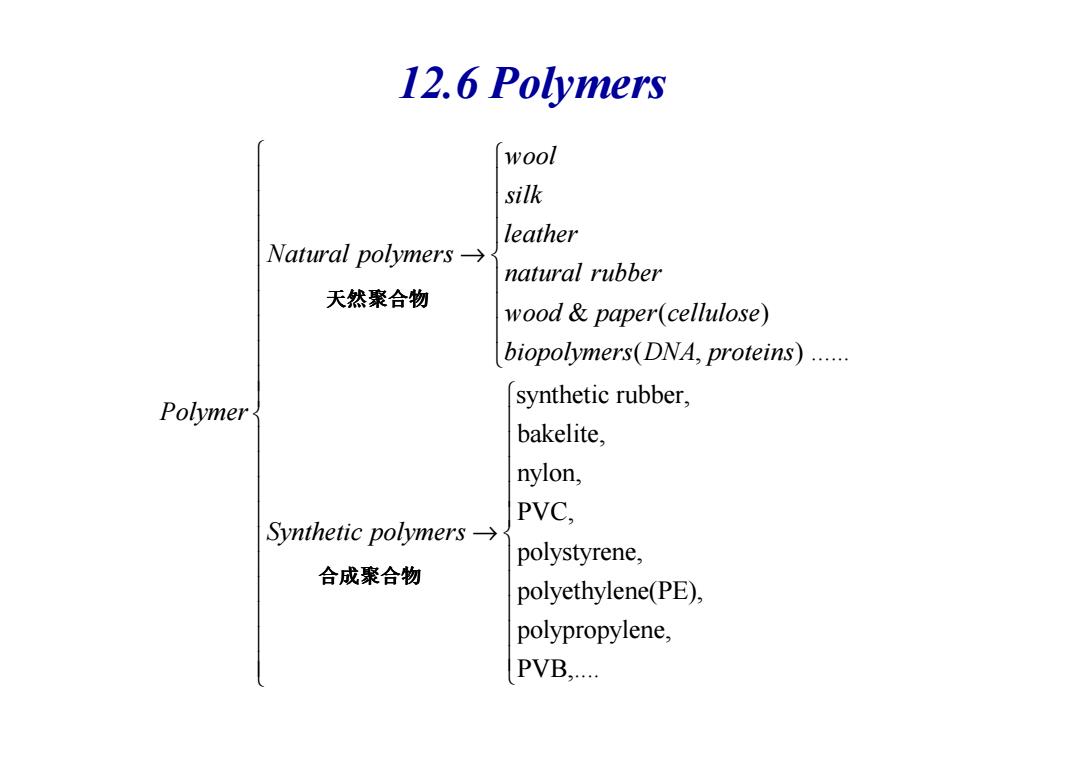
12.6 Polymers 1w00l silk leather Natural polymers→ natural rubber 天然聚合物 wood paper(cellulose) biopolymers(DNA,proteins)...... Polymer synthetic rubber, bakelite, nylon, PVC, Synthetic polymers-→ polystyrene, 合成聚合物 polyethylene(PE), polypropylene, PVB
12.6 Polymers & ( ) ( , ) ...... synthetic rubber, wool silk leather Natural polymers natural rubber wood paper cellulose biopolymers DNA proteins → 天然聚合物 synthetic rubber, bakelite, nylon, PVC, polystyrene, polyethylene(PE Polymer Synthetic polymers → ), polypropylene, PVB,.... 合成聚合物
Soft materials:Polymers and Plastics Polymers are substances containing a large number of structural units joined by the same type of linkage. These substances often form into a chain-like structure Polymers already have a range of applications that far exceeds that of any other class of material available to human being. tp://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/polymers/ware.html
Soft materials: Polymers and Plastics Polymers are substances containing a large number of structural units joined by the same type of linkage. These substances often form into a chain-like structure. Polymers already have a range of applications that far exceeds that of any other class of material available to human being. http://matse1.matse.illinois.edu/polymers/ware.html
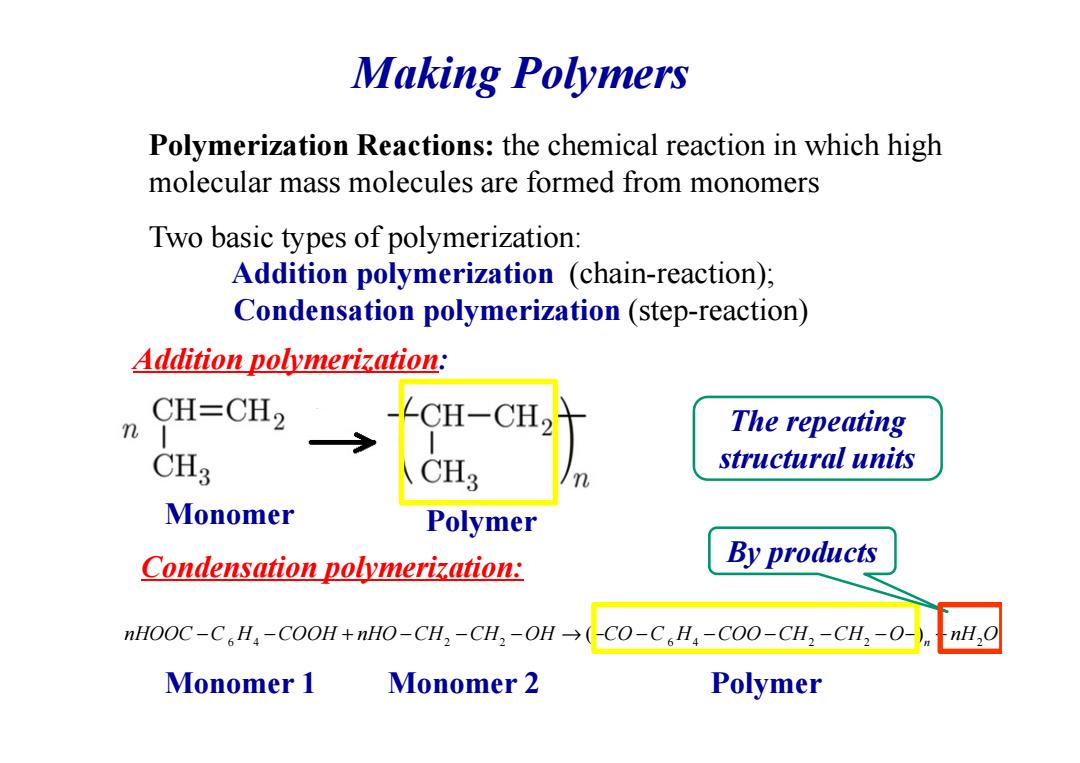
Making Polymers Polymerization Reactions:the chemical reaction in which high molecular mass molecules are formed from monomers Two basic types of polymerization: Addition polymerization (chain-reaction); Condensation polymerization (step-reaction) Addition polymerization: CH=CH2 CH-CH2 The repeating CH3 CH3 structural units Monomer Polymer Condensation polymerization: By products nHOOC-C H:-COOH+nHO-CH,-CH,-OH(-CO-C.H,-C00-CH,-CH:-0-) nH,O Monomer 1 Monomer 2 Polymer
Making Polymers Polymerization Reactions: the chemical reaction in which high molecular mass molecules are formed from monomers Addition polymerization : Two basic types of polymerization: Addition polymerization (chain-reaction); Condensation polymerization (step-reaction) 6 4 2 2 6 4 2 2 2 ( ) n nHOOC C H COOH nHO CH CH OH CO C H COO CH CH O nH O − − + − − − → − − − − − − − + The repeating structural units Condensation polymerization: Monomer Polymer Monomer 1 Monomer 2 Polymer By products
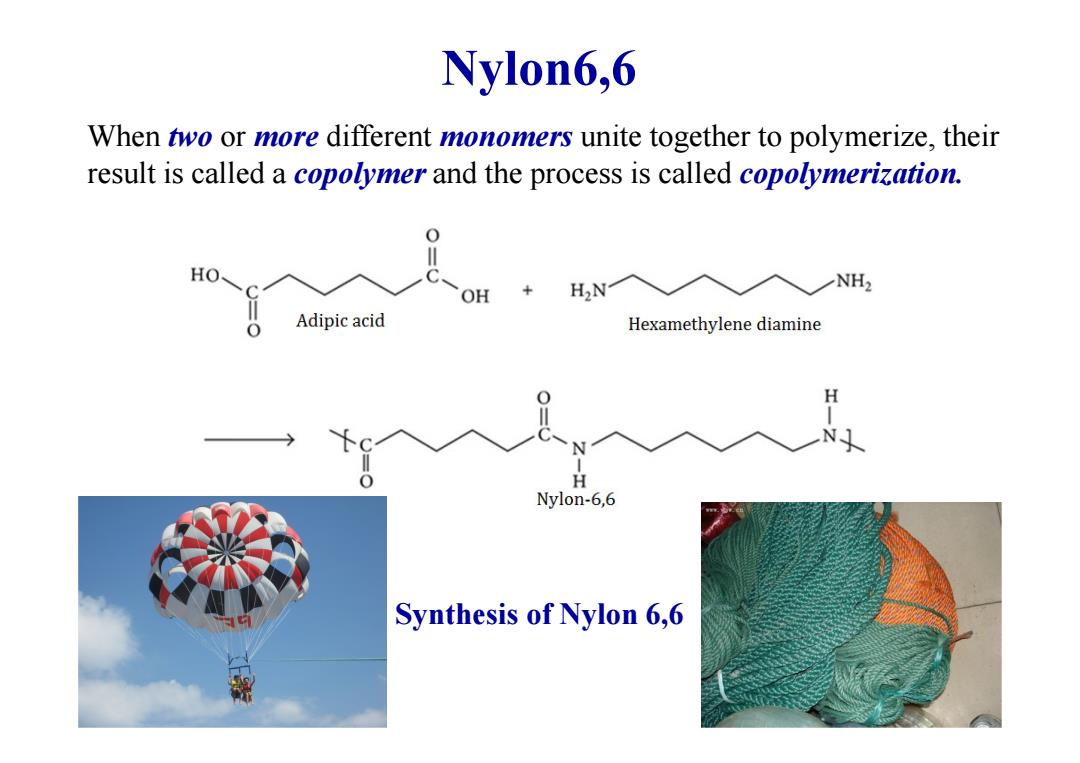
Nylon6,6 When two or more different monomers unite together to polymerize,their result is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerization. 0 HO、 NH2 OH ,+H2N Adipic acid Hexamethylene diamine H N H Nylon-6,6 Synthesis of Nylon 6,6
Nylon6,6 When two or more different monomers unite together to polymerize, their result is called a copolymer and the process is called copolymerization. Synthesis of Nylon 6,6