
Heisenberg's Uncertainty Principle De Broglie's Matter Wave h h △x·m△)≥ = 4π mv A model:precisely describes the energy of the electron while describing its location not precisely,but in terms of probability! Macroscopic objects h △x·m△)≥ h二 4元 mv Microscopic objects Matter at the subatomic level
Macroscopic objects Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle & De Broglie’s Matter Wave 4 h x m υ π ∆ ⋅ ∆ ≥ mv h λ = A model: precisely describes the energy of the electron while describing its location not precisely, but in terms of probability! Macroscopic objects , ; ------------------------- 4 v Microscopic objects x h m h m υ π λ ∆ ∆ ⋅ ≥ = → Matter at the subatomic level
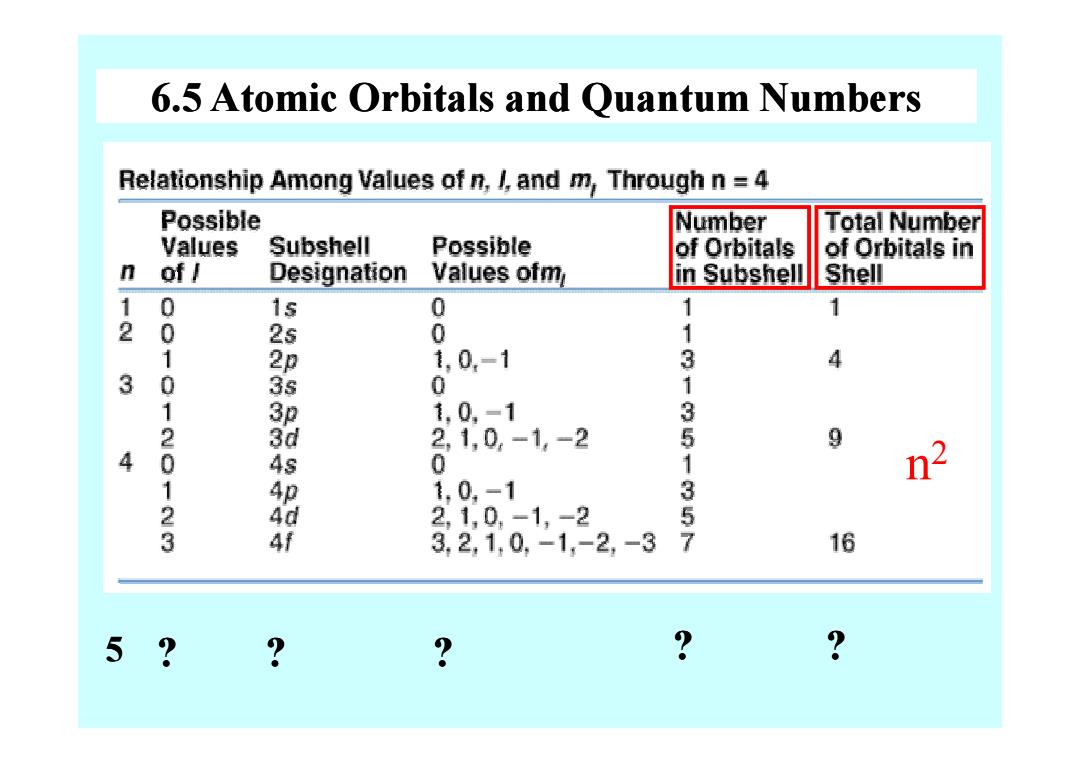
6.5 Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers Relationship Among Values of n,/and m,Through n =4 Possible Number Total Number Values Subshell Possible of Orbitals of Orbitals in n of/ Designation Values ofm in Subshell Shell 0 1s 2 0 25 00 1 1 1 1 1,0,-1 3 4 3 0 0 1 服 1,0,-1 3 20 2,1,0,-1,-2 9 4 4s 1 n 1 1,0,-1 23 21,0-1, -2 3 2,1,0,-1,-2,-3 357 16 5 ? ? ?
6.5 Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers n 2 5 ? ? ? ? ?
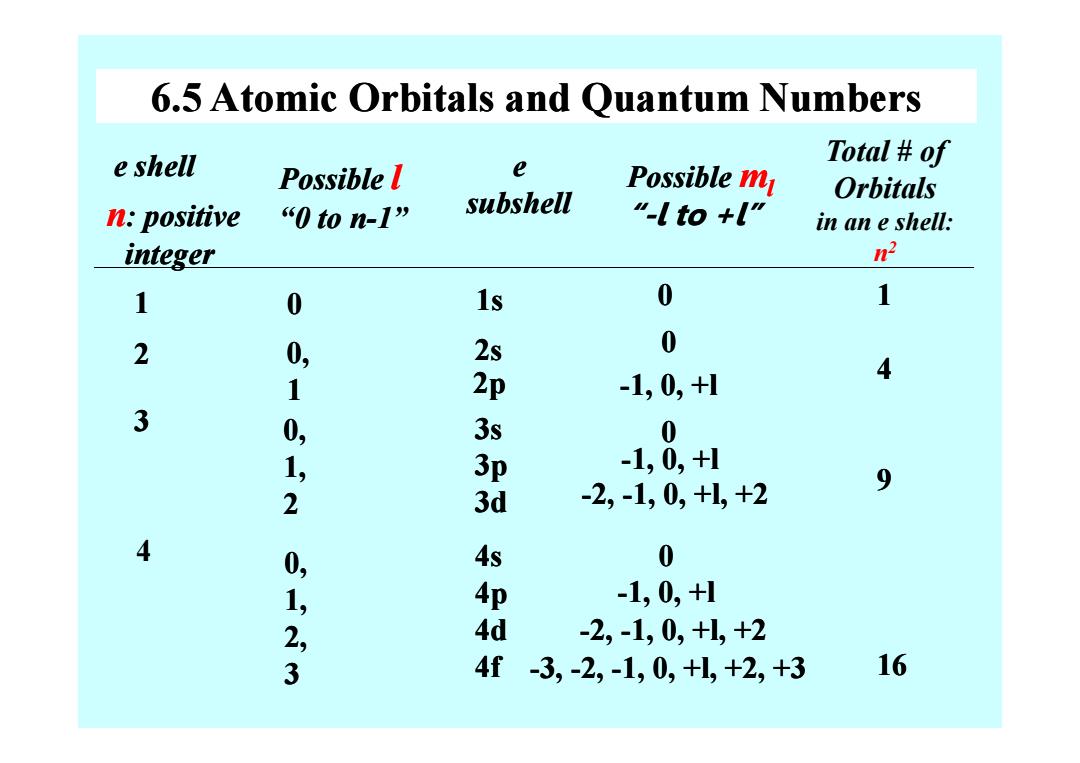
6.5 Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers e shell Total of Possible l e Possible m Orbitals n:positive “0ton-l” subshell "-l to +l" in an e shell: integer n2 1 0 1s 0 1 2 0, 2s 0 4 1 2p -1,0,+1 3 0, 3s 0 1, 3p -1,0,+1 -2,-1,0,+l,+2 9 2 3d 4 0, 4s 0 1, 4p -1,0,+1 23 4d -2,-1,0,+1,+2 4f-3,-2,-1,0,+L,+2,+3 16
6.5 Atomic Orbitals and Quantum Numbers e shell 12 e subshell Possible l “0 to n “0 to n-1” 0 0, 1 n: positive integer 1s 2s 2p Possible ml “-l to +l” l to +l” 00 -1, 0, +l Total # of Orbitals in an e shell: n 2 14 3 4 1 0, 1, 2 0, 1, 2, 3 2p 3s 3p 3d 4s 4p 4d 4f -1, 0, +l 0 -1, 0, +l 1, 0, +l -2, -1, 0, +l, +2 1, 0, +l, +2 0 -1, 0, +l 1, 0, +l -2, -1, 0, +l, +2 1, 0, +l, +2 -3, -2, -1, 0, +l, +2, +3 1, 0, +l, +2, +3 49 16
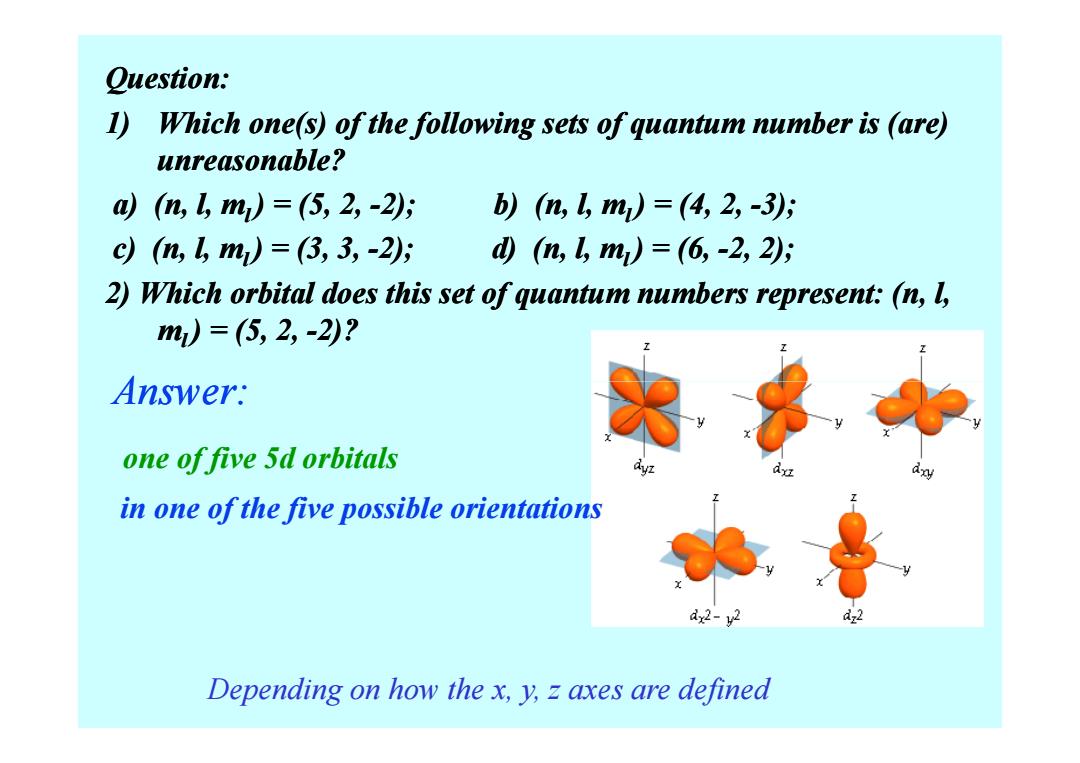
Question: 1)Which one(s)of the following sets of quantum number is (are) unreasonable? 则(n,4m)=(5,2,-2; b)(m,m)=(4,2,-35 cn,↓m)=(3,3,-25 d(n,gm)=(6,-2,2; 2)Which orbital does this set of quantum numbers represent:(n,l, m)=(5,2,-2)? Answer: one of five 5d orbitals in one ofthe five possible orientations dx2-y2 Depending on how the x,y,z axes are defined
Question: 1) Which one(s) of the following sets of quantum number is ( Which one(s) of the following sets of quantum number is (are) unreasonable? a) (n, l, ml ) = (5, 2, ) = (5, 2, -2); b) (n, l, m 2); b) (n, l, ml ) = (4, 2, ) = (4, 2, -3); c) (n, l, ml ) = (3, 3, ) = (3, 3, -2); d) (n, l, m 2); d) (n, l, ml ) = (6, ) = (6, -2, 2); 2) Which orbital does this set of quantum numbers represent: (n, l, ml ) = (5, 2, ) = (5, 2, -2)? Answer: Depending on how the x, y, z axes are defined one of five 5d orbitals in one of the five possible orientations
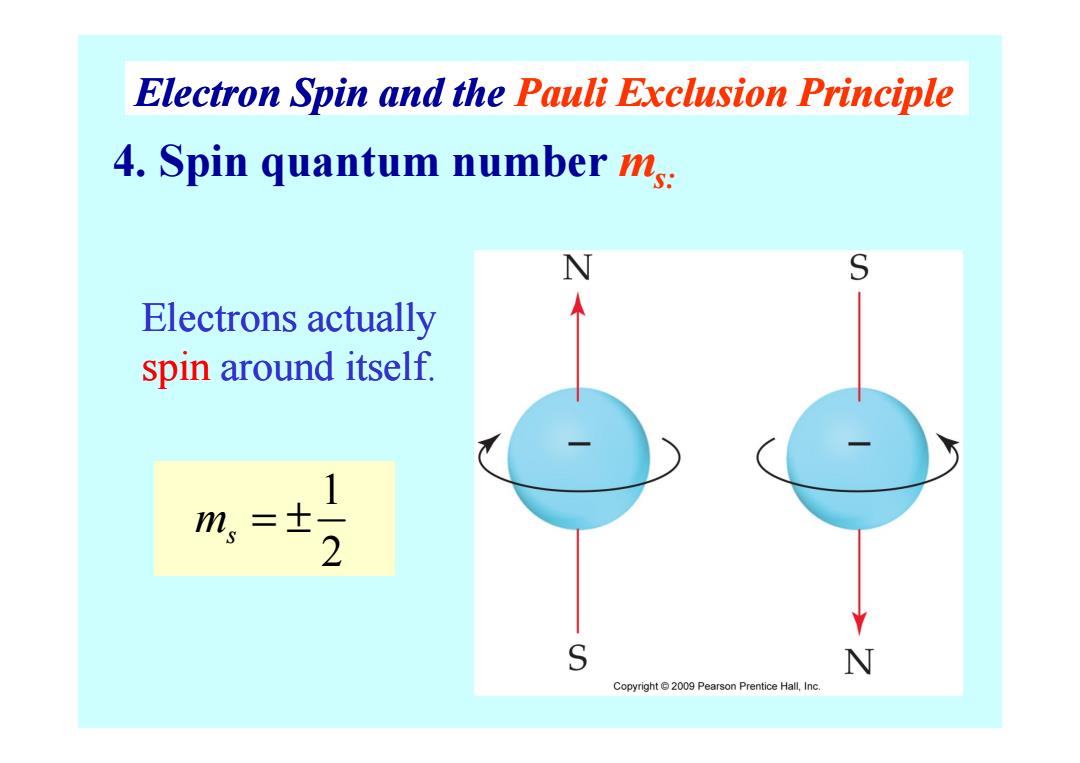
Electron Spin and the Pauli Exclusion Principle 4.Spin quantum number ms: N S Electrons actually spin around itself. 1 m,=士 2 S N Copyright2009 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
4. Spin quantum number ms: Electrons actually spin around itself. Electron Spin and the Pauli Exclusion Principle 1 2 m s = ± spin around itself