
Maillard Reaction 9Non-enzymatic browning 9Complex set of reactions between amines, usually from proteins, and carbonyl compounds, generally sugars. 9The consequences: – formation of many products, most of which have some impact on the flavor and appearance of the cooked food
Maillard Reaction 9Non-enzymatic browning 9Complex set of reactions between amines, usually from proteins, and carbonyl compounds, generally sugars. 9The consequences: – formation of many products, most of which have some impact on the flavor and appearance of the cooked food
Effects of Maillard Reaction 9 Desirable: – Color - bread crust, syrup, meat Flavor - coffee, cocoa, meats Antioxidants 9 Undesirable – Color - changes in color during storage Flavor - changes during processing and storage Nutritional loss - essential amino acids, Vitamins (vit c), palatability and digestibility Toxicity/mutagenicity
Effects of Maillard Reaction 9 Desirable: – Color - bread crust, syrup, meat Flavor - coffee, cocoa, meats Antioxidants 9 Undesirable – Color - changes in color during storage Flavor - changes during processing and storage Nutritional loss - essential amino acids, Vitamins (vit c), palatability and digestibility Toxicity/mutagenicity

Steps 9Condensation - amine/carbonyl 9Rearrangement - enolization 9Fragmentation 9Strecker degradation 9Polymerization - brown color
Steps 9Condensation - amine/carbonyl 9Rearrangement - enolization 9Fragmentation 9Strecker degradation 9Polymerization - brown color

Initial Step 9 Reaction between a reducing sugar and a primary amino acid. 9 Loss of water from this molecule produces an imine that is able to cyclise, resulting in the formation of an N glycoside (a sugar attached to an NR2 group)
Initial Step 9 Reaction between a reducing sugar and a primary amino acid. 9 Loss of water from this molecule produces an imine that is able to cyclise, resulting in the formation of an N glycoside (a sugar attached to an NR2 group)
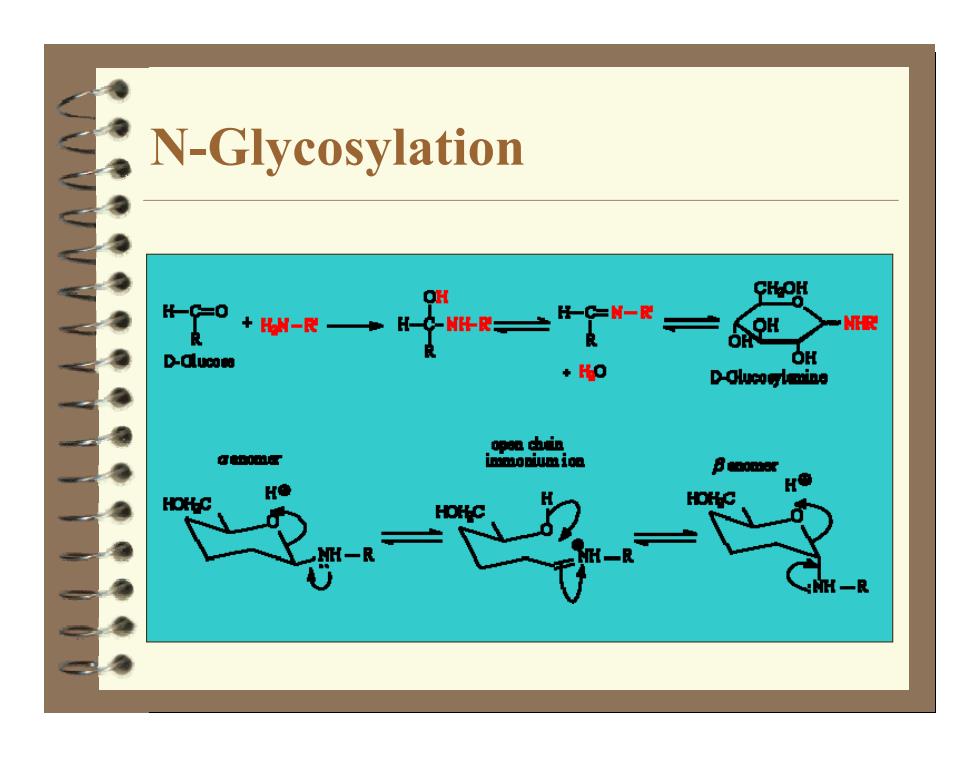
N-Glycosylation
N-Glycosylation