Chemical Kinetics
Chemical Kinetics
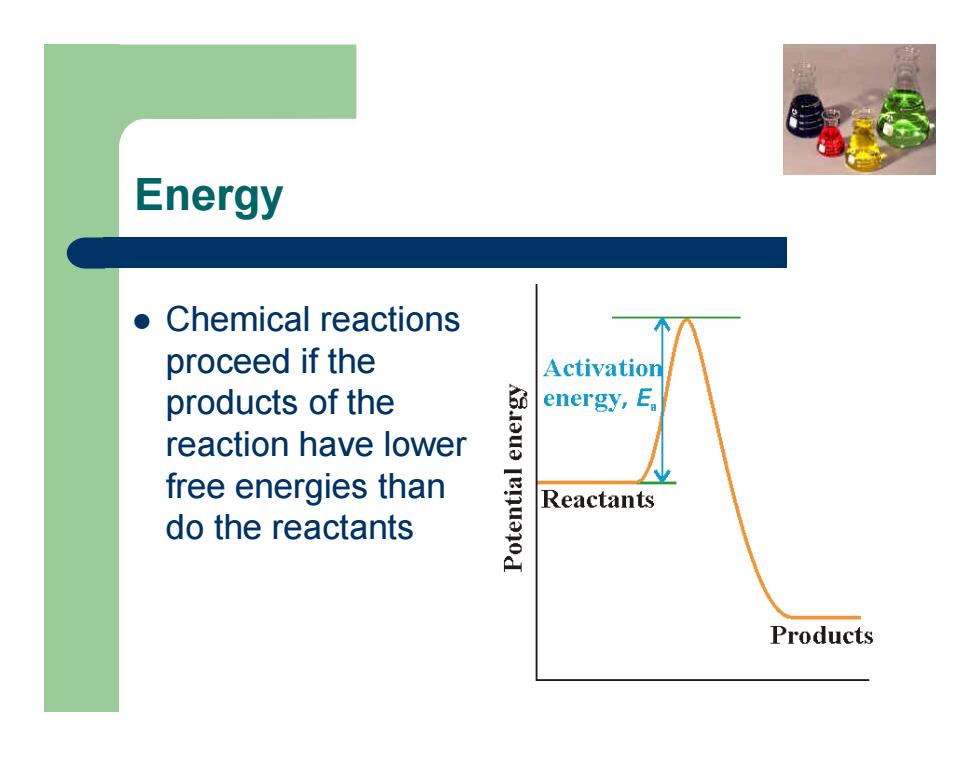
Energy z Chemical reactions proceed if the products of the reaction have lower free energies than do the reactants
Energy z Chemical reactions proceed if the products of the reaction have lower free energies than do the reactants
The fundamental equations of thermodynamics z The first law of thermodynamics Δ U = Δ Q + Δ w the total energy of a system is constant. z Enthalpy, H, is a function that describes energy changes at constant pressure. Δ Hp = cp (ΔT) p z For a biological system it defines the internal energy of a system – HEAT ΔH = +ve => heat is absorbed => ENDOTHERMIC ΔH = -ve => heat is evolved (given out) => EXOTHERMIC
The fundamental equations of thermodynamics z The first law of thermodynamics Δ U = Δ Q + Δ w the total energy of a system is constant. z Enthalpy, H, is a function that describes energy changes at constant pressure. Δ Hp = cp (ΔT) p z For a biological system it defines the internal energy of a system – HEAT ΔH = +ve => heat is absorbed => ENDOTHERMIC ΔH = -ve => heat is evolved (given out) => EXOTHERMIC
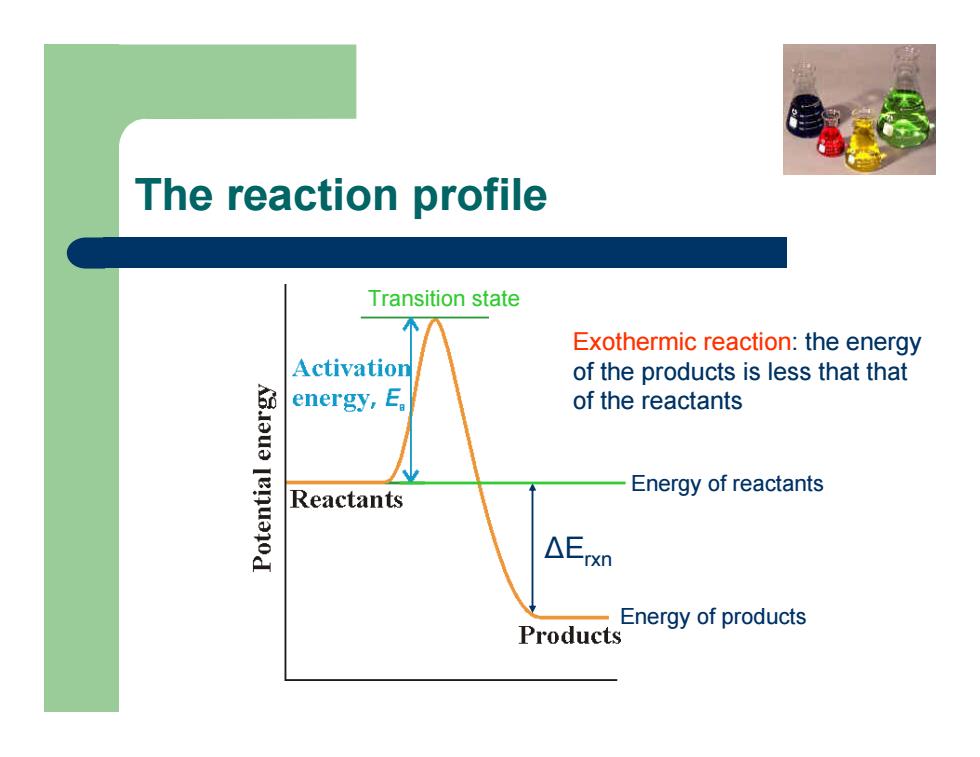
The reaction profile Δ Erxn Transition state Energy of reactants Energy of products Exothermic reaction: the energy of the products is less that that of the reactants
The reaction profile Δ Erxn Transition state Energy of reactants Energy of products Exothermic reaction: the energy of the products is less that that of the reactants
