Modifications of Food Proteins
Modifications of Food Proteins

Food Processing and Storage z Cooking and Industrial processing – Overall beneficial effect z Decrease spoilage z Increases shelf stability – Unfavorable reactions at primary structure level z Losses in nutritional quality z Losses in functionality z Increased risk of toxicity z Desirable and undesirable flavor changes
Food Processing and Storage z Cooking and Industrial processing – Overall beneficial effect z Decrease spoilage z Increases shelf stability – Unfavorable reactions at primary structure level z Losses in nutritional quality z Losses in functionality z Increased risk of toxicity z Desirable and undesirable flavor changes

Processing & Storage z Factors that can adversely affect proteins include – Heat – Extremes in pH – Exposure to oxidative conditions z Caused by oxidizing lipids z Other oxidizing agents – Reaction with CHOs
Processing & Storage z Factors that can adversely affect proteins include – Heat – Extremes in pH – Exposure to oxidative conditions z Caused by oxidizing lipids z Other oxidizing agents – Reaction with CHOs

Moderate Heat Treatments z Globular proteins – Reduces solubility – No disruption or formation of covalent bonds – Primary structure unaffected z Beneficial – Inactivation of enzymes – Destruction of toxins or anti-nutritional factors – Improve digestibility
Moderate Heat Treatments z Globular proteins – Reduces solubility – No disruption or formation of covalent bonds – Primary structure unaffected z Beneficial – Inactivation of enzymes – Destruction of toxins or anti-nutritional factors – Improve digestibility
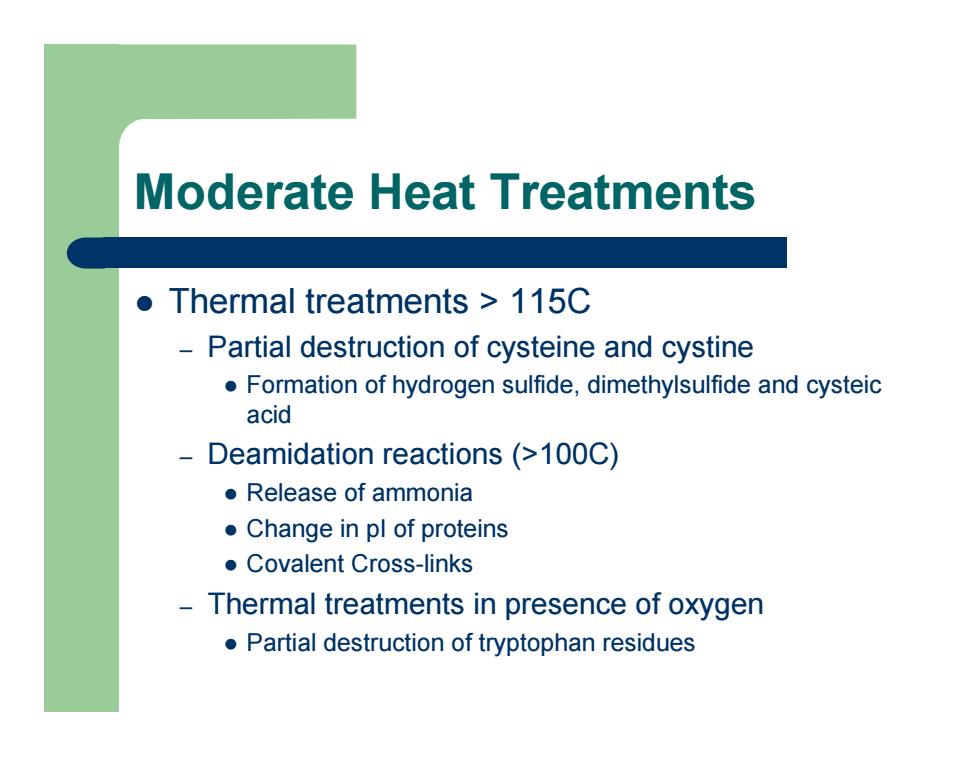
z Thermal treatments > 115C – Partial destruction of cysteine and cystine z Formation of hydrogen sulfide, dimethylsulfide and cysteic acid – Deamidation reactions (>100C) z Release of ammonia z Change in pI of proteins z Covalent Cross-links – Thermal treatments in presence of oxygen z Partial destruction of tryptophan residues Moderate Heat Treatments
z Thermal treatments > 115C – Partial destruction of cysteine and cystine z Formation of hydrogen sulfide, dimethylsulfide and cysteic acid – Deamidation reactions (>100C) z Release of ammonia z Change in pI of proteins z Covalent Cross-links – Thermal treatments in presence of oxygen z Partial destruction of tryptophan residues Moderate Heat Treatments