
Protein Denaturation z Any modification in conformation not accompanied by rupture of peptide bonds z Ultimate step might correspond to a totally unfolded polypeptide structure z Reversible or irreversible
Protein Denaturation z Any modification in conformation not accompanied by rupture of peptide bonds z Ultimate step might correspond to a totally unfolded polypeptide structure z Reversible or irreversible
Effects of Denaturation z Decreased solubility z Altered water binding capacity z Loss of biological activity z Destruction of toxins z Improved digestibility z Increased intrinsic viscosity z Inability to crystallize
Effects of Denaturation z Decreased solubility z Altered water binding capacity z Loss of biological activity z Destruction of toxins z Improved digestibility z Increased intrinsic viscosity z Inability to crystallize
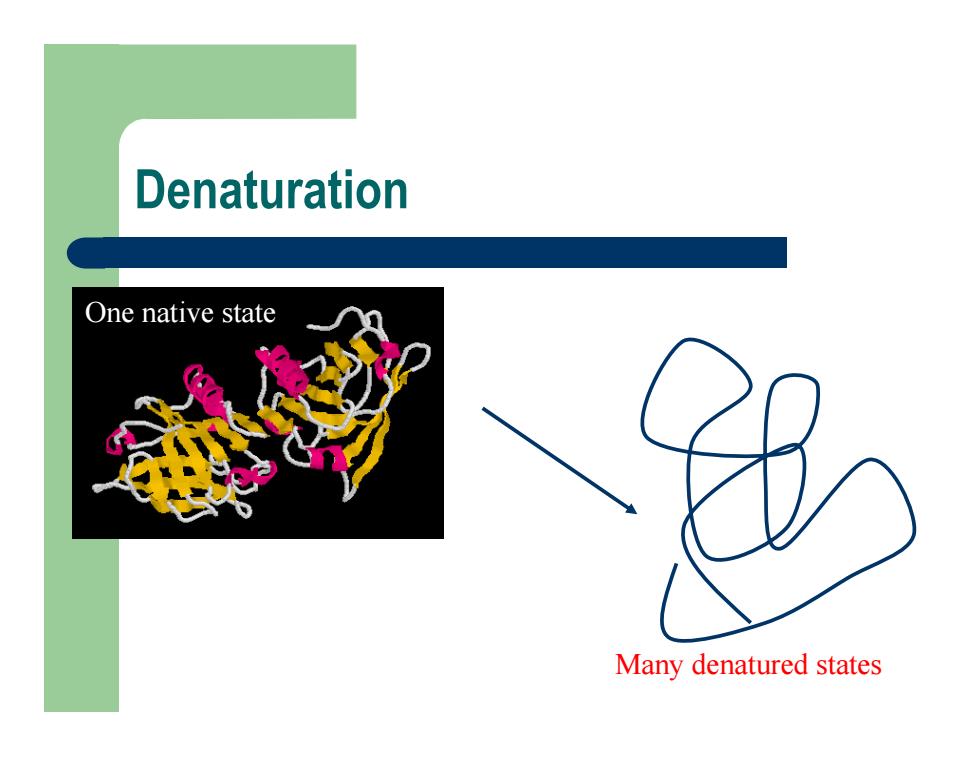
Denaturation One native state Many denatured states
Denaturation One native state Many denatured states
Physical Agents
Physical Agents
Thermal Denaturation z Rate of denaturation depends on the temperature z As T is increased – Affect interactions of tertiary structure – Increased flexibility → reversible – H-bonds begin to break → water interaction – Increased water binding – Increased viscosity of solution – Structures different from native protein
Thermal Denaturation z Rate of denaturation depends on the temperature z As T is increased – Affect interactions of tertiary structure – Increased flexibility → reversible – H-bonds begin to break → water interaction – Increased water binding – Increased viscosity of solution – Structures different from native protein