Enzymes z Enzymes are proteins and certain class of RNA (ribozymes) which enhance the rate of a thermodynamically feasible reaction and are not permanently altered in the process
Enzymes z Enzymes are proteins and certain class of RNA (ribozymes) which enhance the rate of a thermodynamically feasible reaction and are not permanently altered in the process
Enzymes z Cofactors z Coenzymes z Holoenzyme z Apoenzyme
Enzymes z Cofactors z Coenzymes z Holoenzyme z Apoenzyme
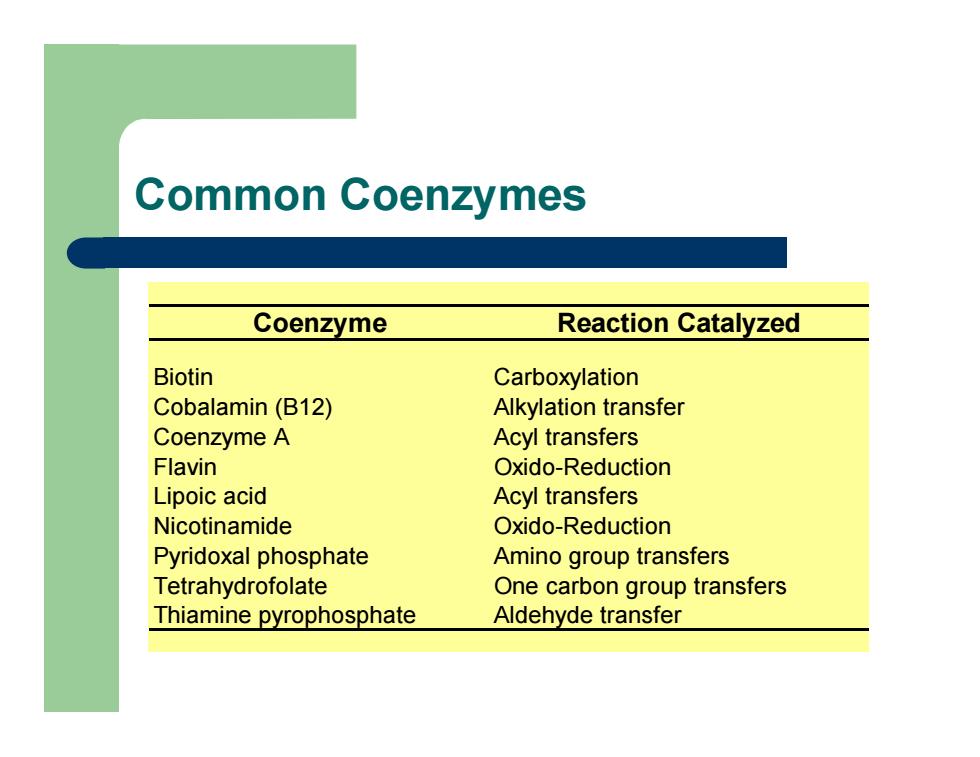
Common Coenzymes Coenzyme Reaction Catalyzed Biotin Carboxylation Cobalamin (B12) Alkylation transfer Coenzyme A Acyl transfers Flavin Oxido-Reduction Lipoic acid Acyl transfers Nicotinamide Oxido-Reduction Pyridoxal phosphate Amino group transfers Tetrahydrofolate One carbon group transfers Thiamine pyrophosphate Aldehyde transfer
Common Coenzymes Coenzyme Reaction Catalyzed Biotin Carboxylation Cobalamin (B12) Alkylation transfer Coenzyme A Acyl transfers Flavin Oxido-Reduction Lipoic acid Acyl transfers Nicotinamide Oxido-Reduction Pyridoxal phosphate Amino group transfers Tetrahydrofolate One carbon group transfers Thiamine pyrophosphate Aldehyde transfer

Why Enzymes? z Natures catalysts z Speed: 1016 over un-catalyzed rates! z Specificity: only the desired reaction occurs z Permit reactions under mild conditions
Why Enzymes? z Natures catalysts z Speed: 1016 over un-catalyzed rates! z Specificity: only the desired reaction occurs z Permit reactions under mild conditions
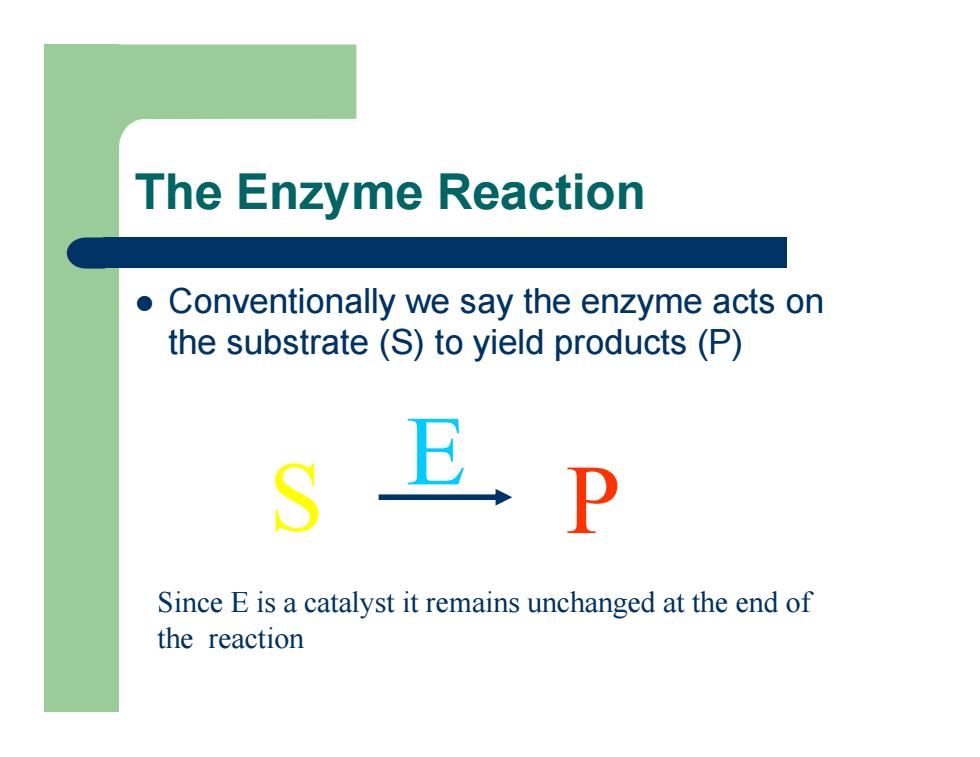
The Enzyme Reaction z Conventionally we say the enzyme acts on the substrate (S) to yield products (P) S P E Since E is a catalyst it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction
The Enzyme Reaction z Conventionally we say the enzyme acts on the substrate (S) to yield products (P) S P E Since E is a catalyst it remains unchanged at the end of the reaction