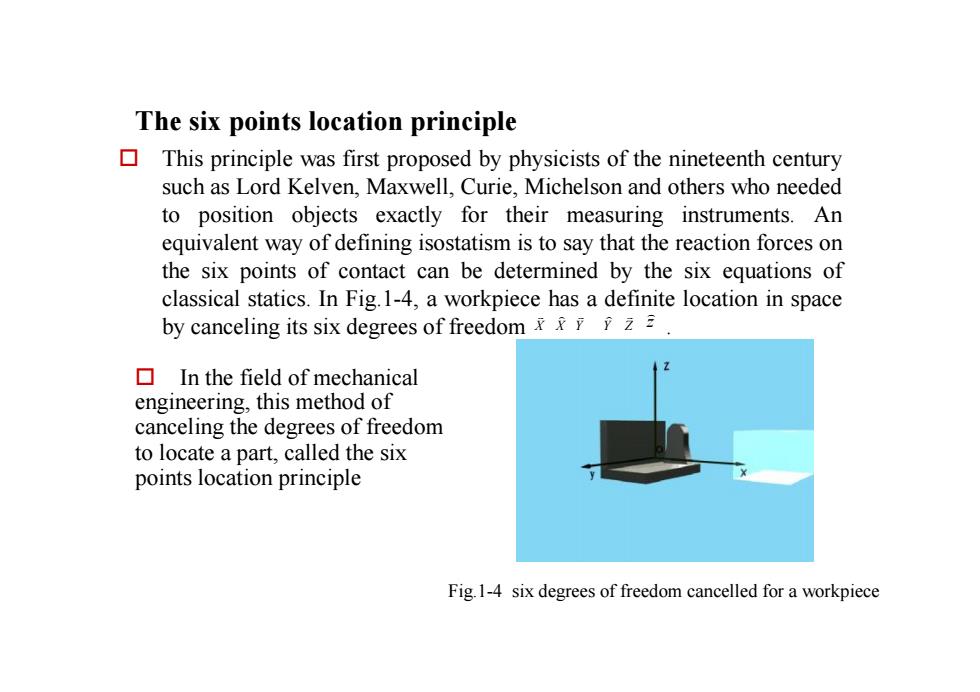
The six points location principle口This principle was first proposed by physicists of the nineteenth centurysuchasLordKelven,Maxwell,Curie,Michelson and otherswhoneededtoposition objects exactlyfor theirmeasuringinstruments.Anequivalent way of defining isostatism is to saythatthe reactionforcesonthe six points of contact can be determined by the six equations ofclassical statics.InFig.1-4,a workpiece has a definitelocation in spacebycancelingitssixdegreesoffreedomxxz2In the field of mechanicalengineering,thismethod ofcancelingthedegreesoffreedomto locate a part, called the sixpoints location principleFig.1-4sixdegreesoffreedomcancelledforaworkpiece
The six points location principle o In the field of mechanical engineering, this method of canceling the degrees of freedom to locate a part, called the six points location principle Fig.1-4 six degrees of freedom cancelled for a workpiece o This principle was first proposed by physicists of the nineteenth century such as Lord Kelven, Maxwell, Curie, Michelson and others who needed to position objects exactly for their measuring instruments. An equivalent way of defining isostatism is to say that the reaction forces on the six points of contact can be determined by the six equations of classical statics. In Fig.1-4, a workpiece has a definite location in space by canceling its six degrees of freedom X . ) Y ) Z v X v Y v z )

Concept:口Completelocation:all thesixdegreesof freedom havebeencancelled.口Incompletelocation:notallthe6degreesoffreedom havebeencancelled,but still satisfytherequirement..口Redundant location:two location elements have both cancelled thesamedegreeoffreedomforaworkpiece.口Insufficient location:thenumber oflocationpoints is lessthanthedegreesoffreedomwhichmustbecancelled,theworkpieceisinsufficientlylocated
Concept: o Complete location :all the six degrees of freedom have been cancelled. o Incomplete location :not all the 6 degrees of freedom have been cancelled,but still satisfy the requirement. o Redundant location : two location elements have both cancelled the same degree of freedom for a workpiece. o Insufficient location :the number of location points is less than the degrees of freedom which must be cancelled, the workpiece is insufficiently located
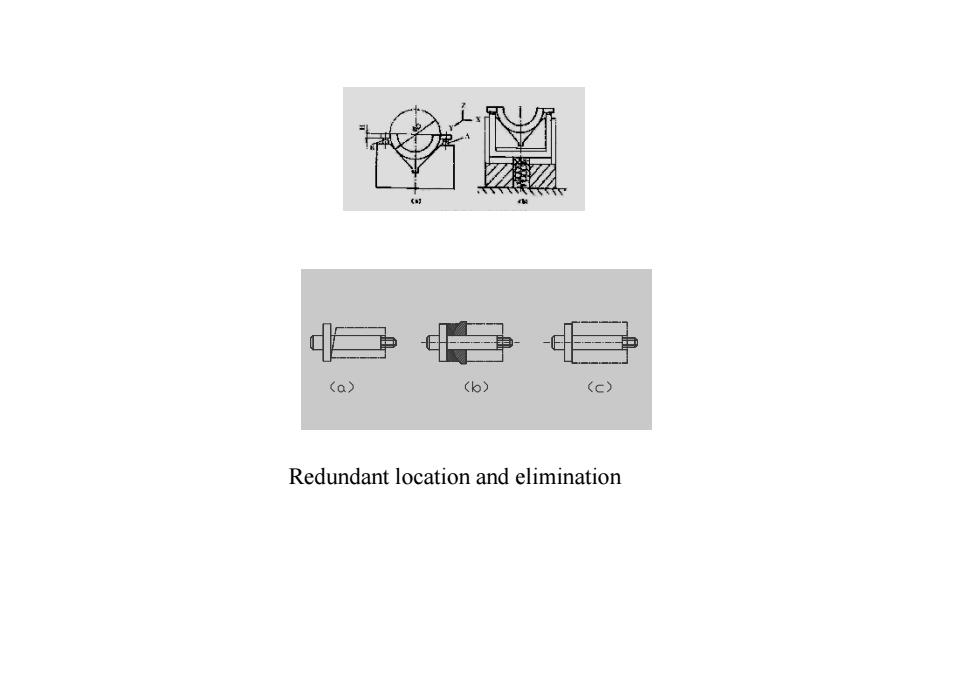
(b)(c)(a)Redundantlocationandelimination
Redundant location and elimination
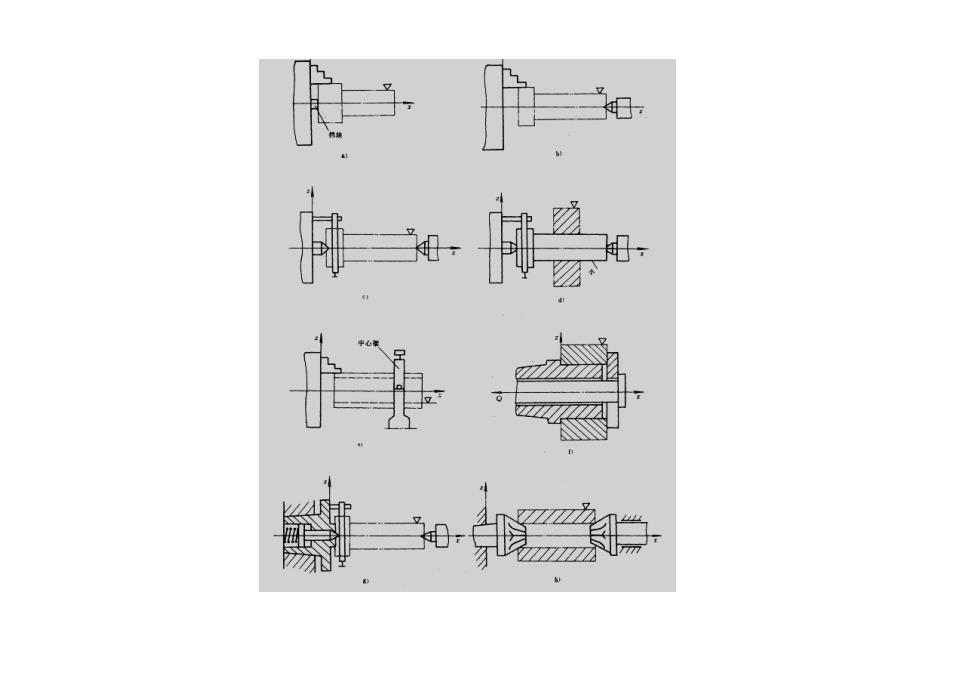

2.2.2Thelocationelements口Thedistribution of the location elements in jigs or fixtures must conform to thesix-pointprincipleonthe onehand.Ontheother hand, thedistribution envelopeof the location elements should be as large as possible so as to maketheweightof the workpiece and the cutting forcefall within the area formed by the supportpoints.2.2.2.1 The main technical specifications and usualmaterialusedforthelocationelements.口Concerning thetechnical specification:firstly,sufficientlocation accuracyand lowroughnessvalues must be ensured.Secondly,a definite wearresistance,hardnessandstiffnessmustbeensured.口Concerning the material used forthe location elements:generally,there aretwokindsofcommonlyusedmaterial:(1)mildsteel:suchas20or20Cr,HRC55~65;(2)highcarbonsteel:suchasT7、T8、T10
2.2.2The location elements o The distribution of the location elements in jigs or fixtures must conform to the six-point principle on the one hand. On the other hand, the distribution envelope of the location elements should be as large as possible so as to make the weight of the workpiece and the cutting force fall within the area formed by the support points. o 2.2.2.1 The main technical specifications and usual material used for the location elements. o Concerning the technical specification: firstly, sufficient location accuracy and low roughness values must be ensured. Secondly, a definite wear resistance, hardness and stiffness must be ensured. o Concerning the material used for the location elements: generally, there are two kinds of commonly used material: (1) mild steel :such as 20 or 20Cr, HRC55~65; (2)high carbon steel :such as T7、T8、T10