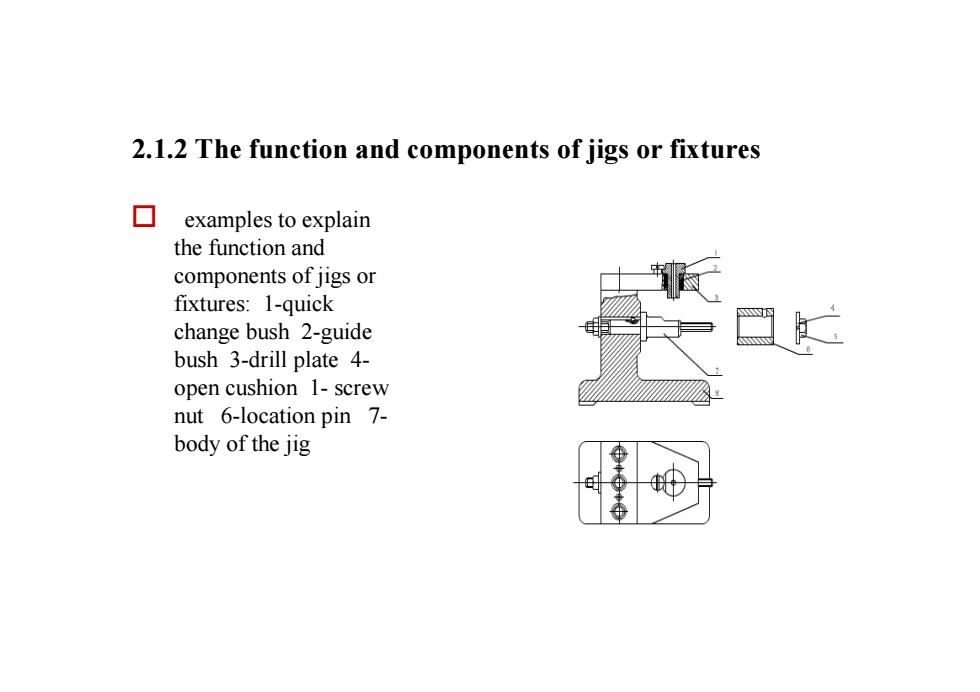
2.1.2 The function and components of jigs or fixturesexamples to explainthe function andcomponents of jigs orfixtures: 1-quickchange bush 2-guidebush 3-drill plate4-opencushion1-screwnut 6-location pin 7-body of the jig
2.1.2 The function and components of jigs or fixtures o examples to explain the function and components of jigs or fixtures: 1-quick change bush 2-guide bush 3-drill plate 4- open cushion 1- screw nut 6-location pin 7- body of the jig

Wecanknowfromtheexample:口2.1.2.1The function of jigs or fixtures :(1)Reduce thenonproductivetime, and raise the productionefficiency;(2) maintain the stability of machining accuracy :(3) enlarge the application scope of machine tools(4) release the working stress, and ensure secure production
We can know from the example: o 2.1.2.1The function of jigs or fixtures : (1)Reduce the nonproductive time, and raise the production efficiency; (2)maintain the stability of machining accuracy ; (3)enlarge the application scope of machine tools (4) release the working stress, and ensure secure production
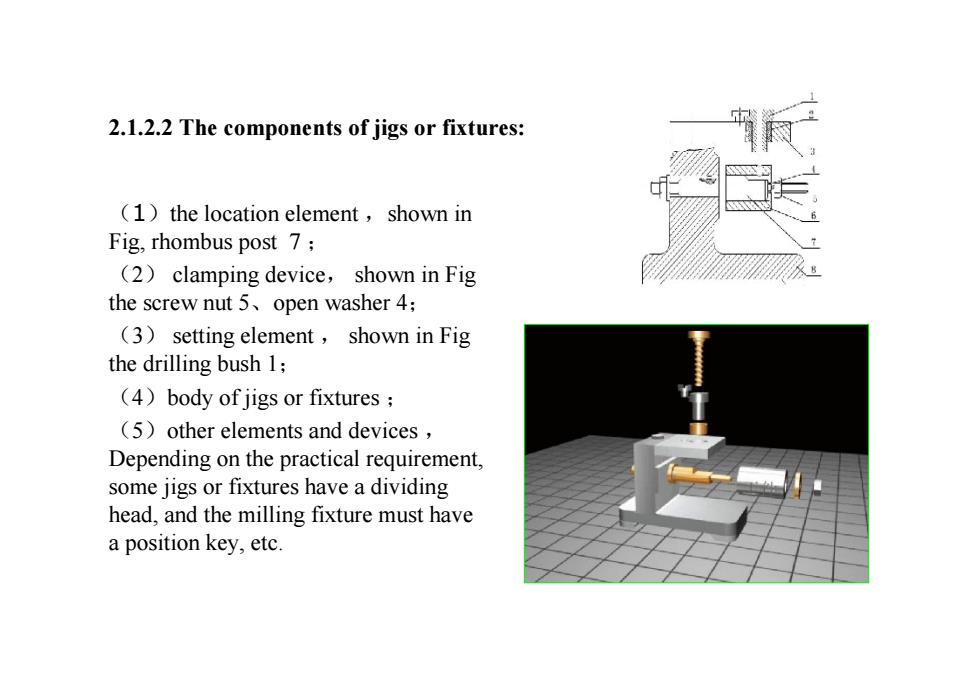
2.1.2.2 The components of jigs or fixtures:(1)thelocationelement,shown inFig, rhombus post 7 ;(2)clampingdevice,showninFigthescrewnut5、openwasher4:(3)settingelement, shown inFigthe drillingbush l;(4)body of jigs or fixtures;(5)otherelementsanddevicesDependingonthepractical requirement.some jigs or fixtures have a dividinghead,andthemillingfixturemusthaveapositionkey,etc
2.1.2.2 The components of jigs or fixtures: (1)the location element ,shown in Fig, rhombus post 7 ; (2) clamping device, shown in Fig the screw nut 5、open washer 4; (3) setting element , shown in Fig the drilling bush 1; (4)body of jigs or fixtures ; (5)other elements and devices , Depending on the practical requirement, some jigs or fixtures have a dividing head, and the milling fixture must have a position key, etc
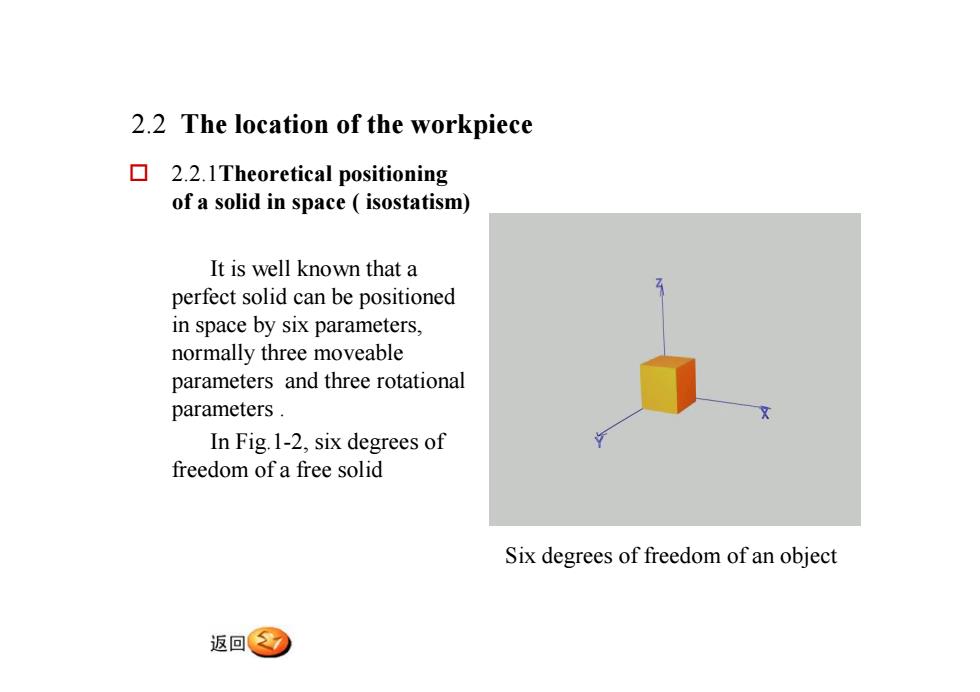
2.2 The location of the workpiece口2.2.1Theoretical positioningofasolidinspace(isostatismIt is well known that aperfect solid can be positionedinspacebysixparameters,normallythreemoveableparameters and three rotationalparameters.In Fig. 1-2, six degrees offreedom ofa free solidSix degrees of freedom of an object返回
2.2 The location of the workpiece o 2.2.1Theoretical positioning of a solid in space ( isostatism) It is well known that a perfect solid can be positioned in space by six parameters, normally three moveable parameters and three rotational parameters . In Fig.1-2, six degrees of freedom of a free solid Six degrees of freedom of an object
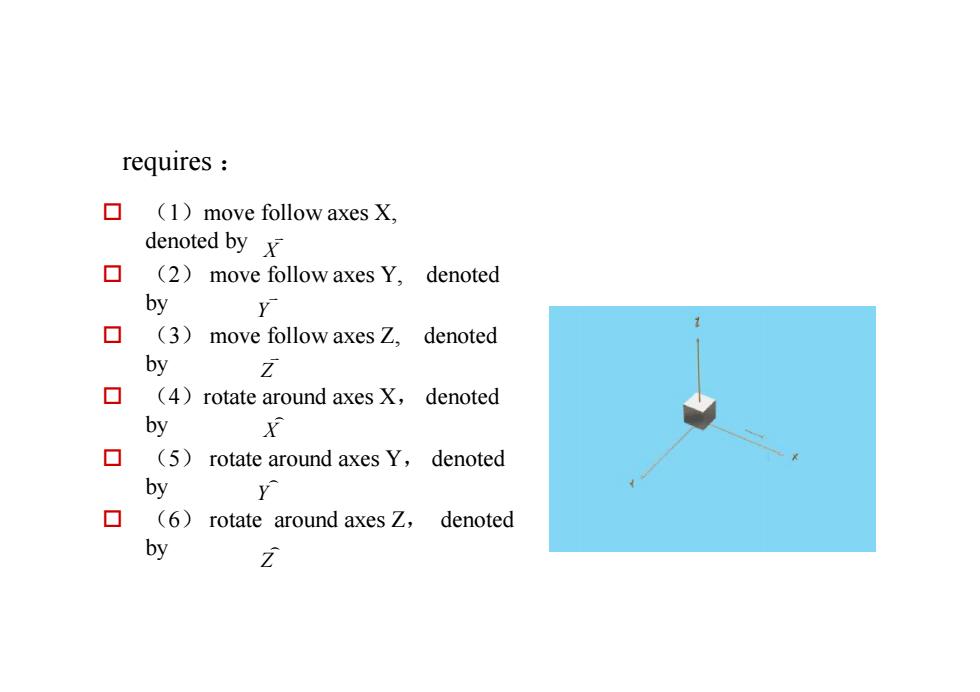
requires :口(1) movefollowaxes X,denoted by x口(2)movefollowaxesY,denotedbyY口(3)denotedmove followaxes Z.byZ口(4)rotatearound axes X, denotedbyx口(5)rotate around axes Y,denotedbyY口(6)rotate aroundaxesZ,denotedbyz
requires : o (1)move follow axes X, denoted by o (2) move follow axes Y, denoted by o (3) move follow axes Z, denoted by o (4)rotate around axes X, denoted by o (5) rotate around axes Y, denoted by o (6) rotate around axes Z, denoted by X v Y v Z v X ) Y ) Z )