
Meaning of the input Input can represent the magnitude of directly experiment sensory information or directly apply control information. The input changes slowly,and can be assumed constant value
Meaning of the input Input can represent the magnitude of directly experiment sensory information or directly apply control information. The input changes slowly,and can be assumed constant value

3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK Neurons do not compute alone.Neuron modify their state activations with external input and with the feedback from one another. This feedback takes the form of path-weighted signals from synaptically connected neurons
◼ Neurons do not compute alone. Neuron modify their state activations with external input and with the feedback from one another. 3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK ◼ This feedback takes the form of path-weighted signals from synaptically connected neurons

3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK Synaptic Connection Matrices n neurons in field Fx +p neurons in field Fy The ith neuron axon in Fx-a synapse mi jth neurons in Fy mii is constant,can be positive,negative or zero
◼ n neurons in field p neurons in field FX FY The ith neuron axon in a synapse jth neurons in mij mij is constant,can be positive,negative or zero. FX FY ◆ Synaptic Connection Matrices 3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK
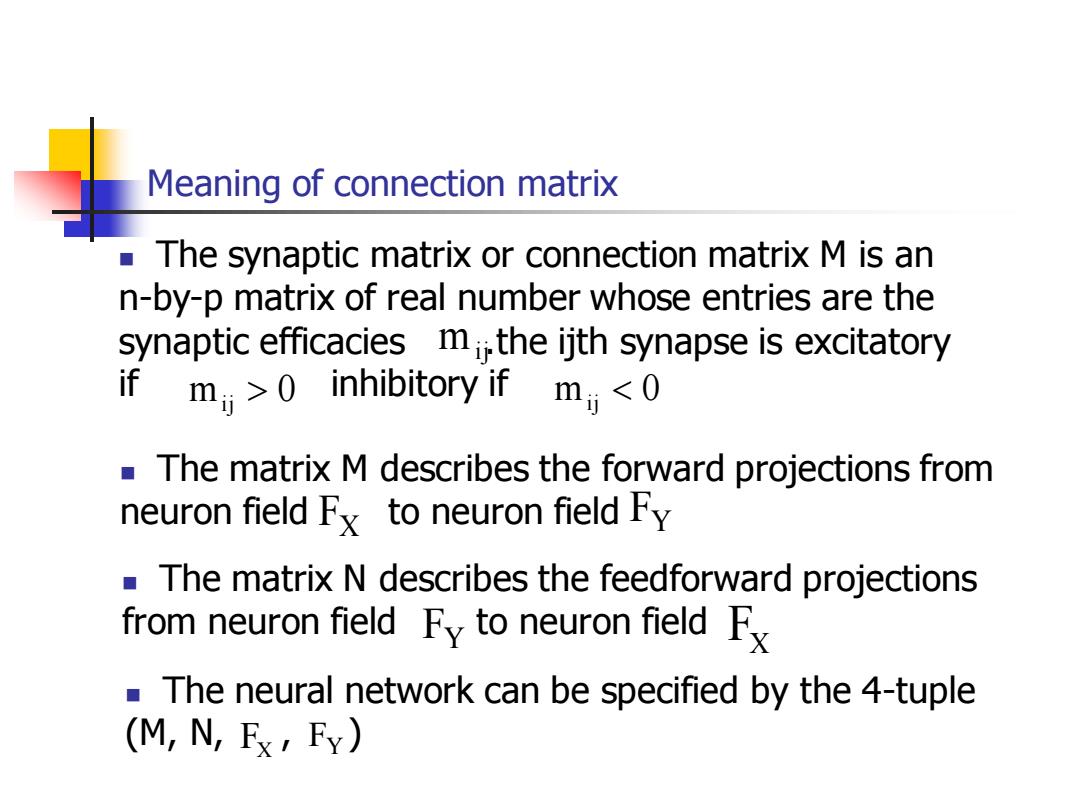
Meaning of connection matrix The synaptic matrix or connection matrix M is an n-by-p matrix of real number whose entries are the synaptic efficacies mi the ijth synapse is excitatory if mi>inhibitory if mi The matrix M describes the forward projections from neuron field Fx to neuron field Fy The matrix N describes the feedforward projections from neuron field Fy to neuron field Fx The neural network can be specified by the 4-tuple (M,N,Fx,FY)
Meaning of connection matrix ◼ The synaptic matrix or connection matrix M is an n-by-p matrix of real number whose entries are the synaptic efficacies .the ijth synapse is excitatory if inhibitory if m 0 ij m 0 ij mij ◼ The matrix M describes the forward projections from neuron field to neuron field FX FY ◼ The matrix N describes the feedforward projections from neuron field to neuron field FY FX ◼ The neural network can be specified by the 4-tuple (M, N, , ) FX FY
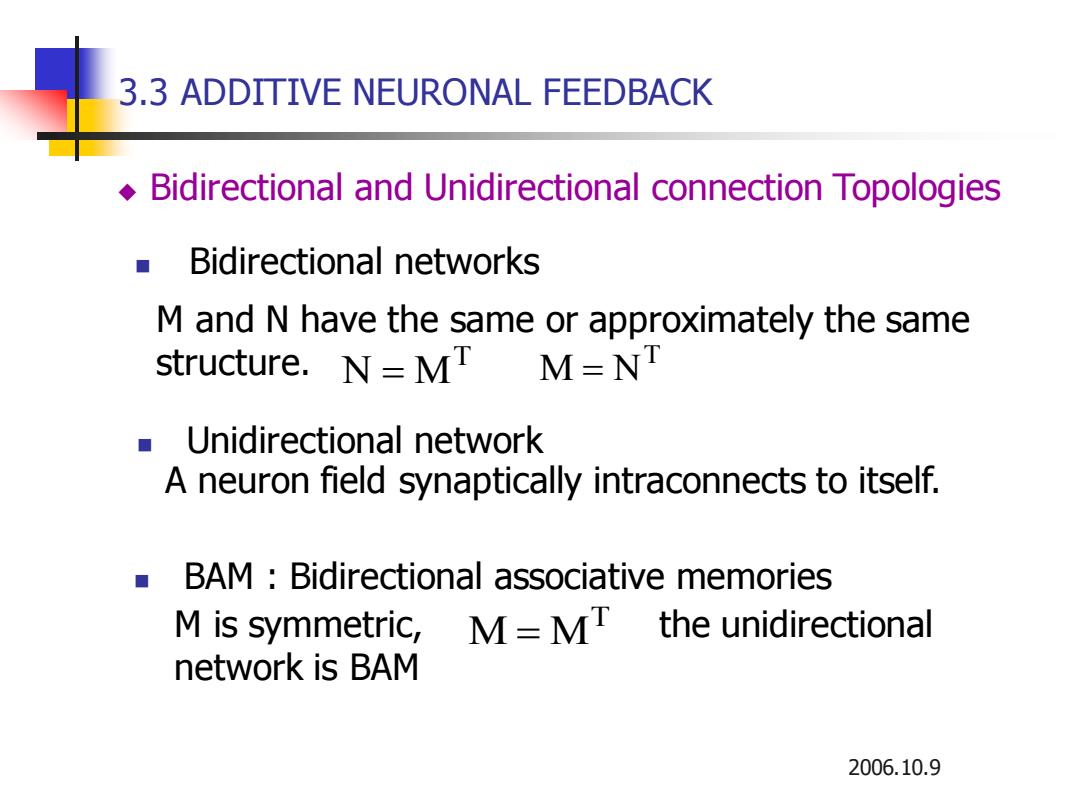
3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK Bidirectional and Unidirectional connection Topologies Bidirectional networks M and N have the same or approximately the same structure.N=MI M=NI Unidirectional network A neuron field synaptically intraconnects to itself. BAM Bidirectional associative memories M is symmetric,】 M=MI t the unidirectional network is BAM 2006.10.9
2006.10.9 ◼ Bidirectional networks M and N have the same or approximately the same structure. ◼ Unidirectional network T M = N M T N = A neuron field synaptically intraconnects to itself. ◼ BAM : Bidirectional associative memories M is symmetric, the unidirectional network is BAM M M T = ◆ Bidirectional and Unidirectional connection Topologies 3.3 ADDITIVE NEURONAL FEEDBACK