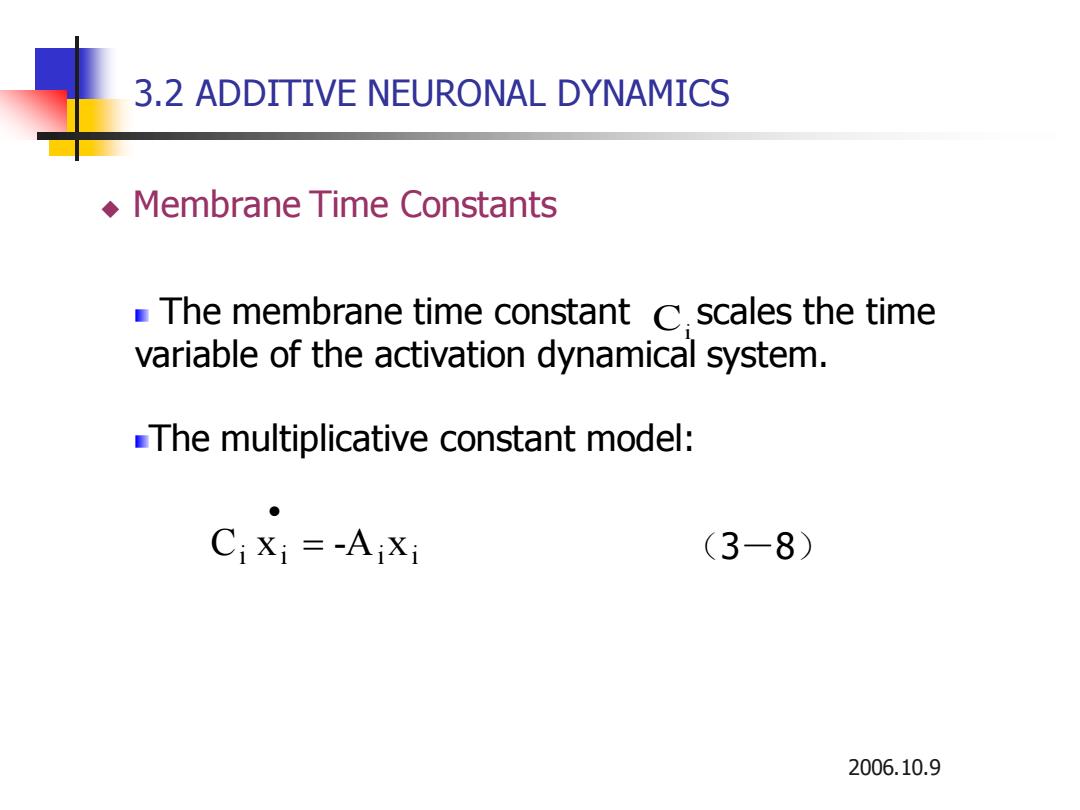
3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS Membrane Time Constants The membrane time constant C.scales the time variable of the activation dynamical system. The multiplicative constant model: Cixi=-AiXi (3一8) 2006.10.9
2006.10.9 The membrane time constant scales the time variable of the activation dynamical system. The multiplicative constant model: Ci i i i i C x = -A x • (3-8) 3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS ◆ Membrane Time Constants

Solution and property ■solution x;(t)=x,(0)e property The smaller the capacitance the faster things change As the membrane capacitance increases toward positive infinity,membrane fluctuation slows to stop
Solution and property solution t C A i i i t x e − x ( ) = (0) i property The smaller the capacitance ,the faster things change As the membrane capacitance increases toward positive infinity,membrane fluctuation slows to stop
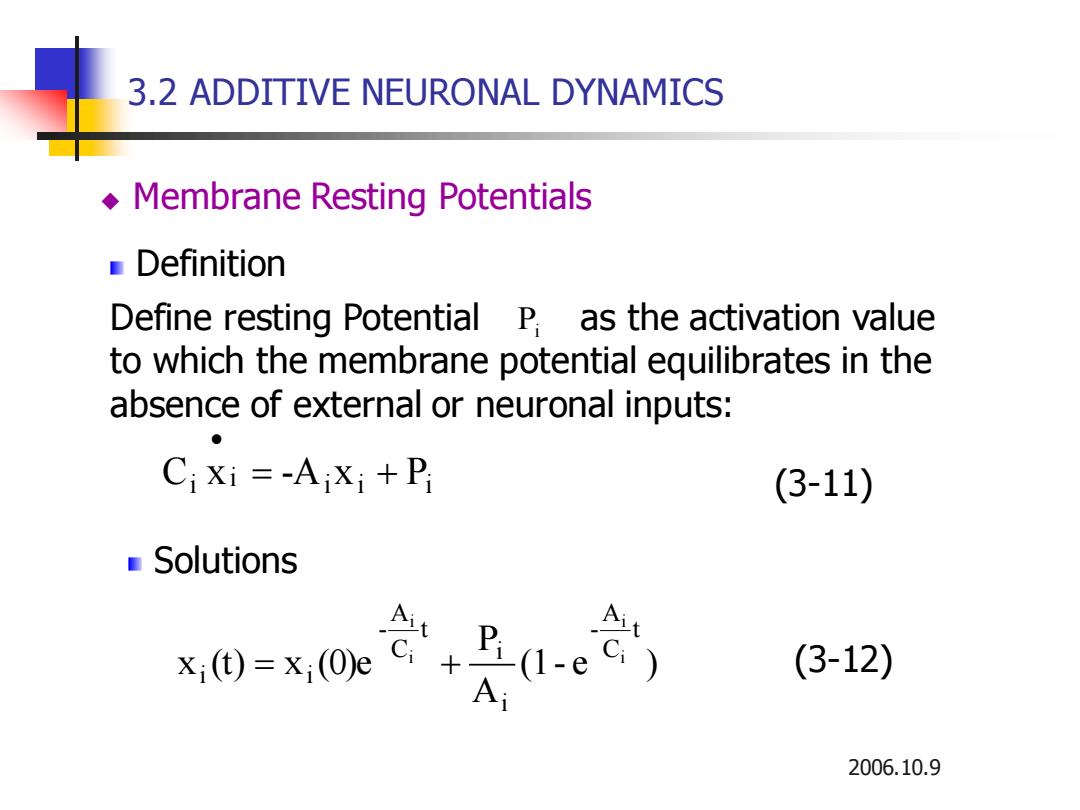
3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS Membrane Resting Potentials Definition Define resting Potential P as the activation value to which the membrane potential equilibrates in the absence of external or neuronal inputs: Cixi=-AiXi+P (3-11) Solutions Ait x1(t)=x;(0)e + (3-12) 2006.10.9
2006.10.9 3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS Define resting Potential as the activation value to which the membrane potential equilibrates in the absence of external or neuronal inputs: Pi i i i i Ci x = -A x + P • Solutions (1- e ) A P x (t) x (0)e t C A - i i t C A - i i i i i i = + Definition (3-11) (3-12) ◆ Membrane Resting Potentials

Note The time-scaling capacitance dose not affect the asymptotic or steady-state solution. The steady-state solution does not depend on the finite initial condition. In resting case,we can find the solution quickly
Note The time-scaling capacitance dose not affect the asymptotic or steady-state solution. The steady-state solution does not depend on the finite initial condition. In resting case,we can find the solution quickly

3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS Additive External Input ■Add input Apply a relatively constant numeral input to a neuron. ● Xi=Xi+li (3-13) solution x;()=x(0)et+I;(1-et) (3-14)
Add input Apply a relatively constant numeral input to a neuron. i i xi = -x + I • solution x (t) x (0)e I (1- e ) -t i -t i = i + (3-13) (3-14) ◆ Additive External Input 3.2 ADDITIVE NEURONAL DYNAMICS